Abstract
Background
Inflammation is a prominent clinical manifestation in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, often associated with insulin resistance, metabolic dysregulation, and other complications.
Aim of the study
The present study has been designed to check the serum levels of PAR-1 and correlate with various clinical manifestations and inflammatory cytokines levels in type 2 diabetic subjects.
Material and Methods
The study population was divided into two groups, healthy volunteers (n = 15): normal glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (4.26 ± 0.55) and type 2 diabetic subjects (n = 30): HbA1c levels (7.80 ± 2.41). The serum levels of PAR-1 (ELISA method) were studied in both groups and correlated with demographic parameters age, weight, body mass index (BMI), and conventional inflammation biomarkers like C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), interleukin 8 (IL-8), and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).
Results
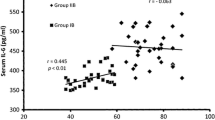
The demographic variables including the body weight (77.38 ± 10.00 vs. controls 55.26 ± 6.99), BMI (29.39 ± 3.61 vs. controls 25.25 ± 4.01), glycemic index HbA1c (7.80 ± 2.41 vs. controls 4.26 ± 0.55) were found to be statistically increased in T2DM subjects than the healthy control group. The levels of various inflammatory biomarkers and PAR-1 were significantly elevated in T2DM groups in comparison to healthy volunteers. The univariate and multivariate regression analysis revealed that elevated PAR-1 levels positively correlated with increased body weight, BMI, HbA1c, and inflammatory cytokines.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that the elevated serum PAR-1 levels serve as an independent predictor of inflammation in T2DM subjects and might have prognostic value for determining T2DM progression.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to confidential reasons but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Antoniak S, Cardenas JC, Buczek LJ et al (2017) Protease-activated receptor 1 contributes to angiotensin II-induced cardiovascular remodeling and inflammation. Cardiology 136(4):258–268. https://doi.org/10.1159/000452269
Asokananthan N, Graham PT, Fink J et al (2002) Activation of protease-activated receptor (PAR)-1, PAR-2, and PAR-4 stimulates IL-6, IL-8, and prostaglandin E2 release from human respiratory epithelial cells. J Immunol 168(7):3577–3585. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.168.7.3577
Austin KM, Covic L, Kuliopulos A (2013) Matrix metalloproteases and PAR1 activation. Blood, J Hematol Am Soc 121(3):431–439
Calle MC, Fernandez ML (2012) Inflammation and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab 38(3):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2011.11.006
Chen H, Smith M, Herz J et al (2021) The role of protease-activated receptor 1 signaling in CD8 T cell effector functions. Iscience 24(11):103387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103387
Cunningham MA, Rondeau E, Chen X et al (2000) Protease-activated receptor 1 mediates thrombin-dependent, cell-mediated renal inflammation in crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med 191(3):455–462. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.191.3.455
De Beer FC, Hind CR, Fox KM et al (1982) Measurement of serum C-reactive protein concentration in myocardial ischaemia and infarction. Heart 47(3):239–243. https://doi.org/10.1136/hrt.47.3.239
de Jager J, Dekker JM, Kooy A et al (2006) Endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation explain much of the excess cardiovascular mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26(5):1086–1093. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000215951.36219.a4
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L et al (2015) Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.19
Dobrica E, Gaman MA, Cozma MA, Gaman AM, Diaconu CC (2019) Macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus: did hypertension change the setting? J Hypertens 37:e140–e141. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.hjh.0000571816.00025.b3
El Sheikh WM, Alahmar IE, Salem GM, El-Sheikh MA (2019) Tumor necrosis factor alpha in peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatry Neurosurg 55(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41983-019-0080-0
El-Edel RH, Fathy WM, Abou-Elela DH, Emara MM, El-Khair NT (2020) Role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Menoufia Med J 33(3):920. https://doi.org/10.4103/mmj.mmj_430_18
Fan Y, Zhang W, Mulholland M (2005) Thrombin and PAR-1-AP increase proinflammatory cytokine expression in C6 cells1. J Surg Res 129(2):196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2005.07.041
Fang X, Liao R, Yu Y, Li J, Guo Z, Zhu T (2019) Thrombin induces secretion of multiple cytokines and expression of protease-activated receptors in mouse mast cell line. Mediat Inflamm. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4952131
Fowler MJ (2008) Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes 26(2):77–82. https://doi.org/10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77
Galicia-Garcia U, Benito-Vicente A, Jebari S et al (2020) Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci 21(17):6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275
Ganz ML, Wintfeld N, Li Q et al (2014) The association of body mass index with the risk of type 2 diabetes: a case–control study nested in an electronic health records system in the United States. Diabetol Metab Syndr 6(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-6-50
Ghouse J, Isaksen JL, Skov MW et al (2020) Effect of diabetes duration on the relationship between glycaemic control and risk of death in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 22(2):231–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13891
Gray N, Picone G, Sloan F, Yashkin A (2015) The relationship between BMI and onset of diabetes mellitus and its complications. South Med J 108(1):29. https://doi.org/10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000214
Guh DP, Zhang W, Bansback N et al (2009) The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 9(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-9-88
Gupta R, Pamecha H (2020) To study relationship of serum hsCRP with type 2 diabetes mellitus, its vascular complications and non-diabetics-case control study. J Assoc Phys India 68(8):25–29
Heuberger DM, Schuepbach RA (2019) Protease-activated receptors (PARs): mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic modulators in PAR-driven inflammatory diseases. Thrombosis J 17:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12959-019-0194-8
Hurley A, Smith M, Karpova T et al (2013) Enhanced effector function of CD8+ T cells from healthy controls and HIV-infected patients occurs through thrombin activation of protease-activated receptor 1. J Infect Dis 207(4):638–650. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jis730
Junge CE, Sugawara T, Mannaioni G et al (2003) The contribution of protease-activated receptor 1 to neuronal damage caused by transient focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(22):13019–13024. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2235594100
Kahn ML, Nakanishi-Matsui M, Shapiro MJ, Ishihara H, Coughlin SR (1999) Protease-activated receptors 1 and 4 mediate activation of human platelets by thrombin. J Clin Investig 103(6):879–887. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI6042
Kanmani S, Kwon M, Shin MK, Kim MK (2019) Association of C-reactive protein with risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus, and role of obesity and hypertension: a large population-based Korean cohort study. Sci Rep 9(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40987-8
Lee PR, Johnson TP, Gnanapavan S et al (2017) Protease-activated receptor-1 activation by granzyme B causes neurotoxicity that is augmented by interleukin-1β. J Neuroinflammation 14(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-017-0901-y
Lintermans LL, Stegeman CA, Heeringa P, Abdulahad WH (2014) T cells in vascular inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol 5:504. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00504
Liu X, Yu J, Song S, Yue X, Li Q (2017) Protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1): a promising molecular target for cancer. Oncotarget 8(63):107334
Liu Y, Tang ZZ, Zhang YM et al (2020) Thrombin/PAR-1 activation induces endothelial damages via NLRP1 inflammasome in gestational diabetes. Biochem Pharmacol 175:113849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113849
Mari B, Imbert V, Belhacene N et al (1994) Thrombin and thrombin receptor agonist peptide induce early events of T cell activation and synergize with TCR cross-linking for CD69 expression and interleukin 2 production. J Biol Chem 269(11):8517–8523. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37225-3
Navale AM, Paranjape AN (2013) Role of inflammation in development of diabetic complications and commonly used inflammatory markers with respect to diabetic complications. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5(Suppl 2):1–5
Nazari A, Sardoo AM, Fard ET et al (2017) Is IL-6 increased in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients independent of nephropathic complication. Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 5(2):1102
Pan A, Wang Y, Yuan JM, Koh WP (2017) High-sensitive C-reactive protein and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: a case–control study nested within the Singapore Chinese Health Study. BMC Endocr Disord 17(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-017-0159-5
Pawlinski R, Tencati M, Hampton CR et al (2007) Protease-activated receptor-1 contributes to cardiac remodeling and hypertrophy. Circulation 116(20):2298–2306. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.692764
Pradeepa R, Mohan V (2021) Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in India. Indian J Ophthalmol 69(11):2932. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO_1627_21
Randeria SN, Thomson GJ, Nell TA, Roberts T, Pretorius E (2019) Inflammatory cytokines in type 2 diabetes mellitus as facilitators of hypercoagulation and abnormal clot formation. Cardiovasc Diabetol 18(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-019-0870-9
Reddy S, Amutha A, Rajalakshmi R et al (2017) Association of increased levels of MCP-1 and cathepsin-D in young onset type 2 diabetes patients (T2DM-Y) with severity of diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Complicat 31(5):804–809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.02.017
Roudbary SA, Saadat F, Forghanparast K, Sohrabnejad R (2011) Serum C-reactive protein level as a biomarker for differentiation of ischemic from hemorrhagic stroke. Acta Med Iran 49:149–152
Saeed MA, Ng GZ, Däbritz J et al (2017) Protease-activated receptor 1 plays a proinflammatory role in colitis by promoting Th17-related immunity. Inflamm Bowel Dis 23(4):593–602. https://doi.org/10.1097/MIB.0000000000001045
Sassy-Prigent C, Heudes D, Mandet C et al (2000) Early glomerular macrophage recruitment in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes 49(3):466–475. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.49.3.466
Satoh J, Yagihashi S, Toyota T (2003) The possible role of tumor necrosis factor-α in diabetic polyneuropathy. Exp Diabesity Res 4(2):65–71. https://doi.org/10.1155/EDR.2003.65
Schoergenhofer C, Schwameis M, Gelbenegger G et al (2018) Inhibition of protease-activated receptor (PAR1) reduces activation of the endothelium, coagulation, fibrinolysis and inflammation during human endotoxemia. Thromb Haemost 118(07):1176–1184. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0038-1655767
Shadick NA, Cook NR, Karlson EW et al (2006) C-reactive protein in the prediction of rheumatoid arthritis in women. Arch Intern Med 166(22):2490–2494. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.166.22.2490
Shavit-Stein E, Gofrit SG, Gayster A et al (2020) Treatment of diabetic neuropathy with a novel PAR1-targeting molecule. Biomolecules 10(11):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111552
Smail MM, Howarth CF, Singh J, Ismail AM (2019) Inflammation and diabetic cardiomyopathy. In: Aronow WS, Murashita T (eds) Inflammatory heart diseases. IntechOpen, London
Spranger J, Kroke A, Mohlig M et al (2003) Inflammatory cytokines and the risk to develop type 2 diabetes: results of the prospective population-based European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam study. Diabetes 52(3):812–817. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.3.812
Swaroop JJ, Rajarajeswari D, Naidu JN (2012) Association of TNF-α with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian J Med Res 135(1):127. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-5916.93435
Thorand B, Löwel H, Schneider A et al (2003) C-reactive protein as a predictor for incident diabetes mellitus among middle-aged men: results from the MONICA Augsburg cohort study, 1984–1998. Arch Intern Med 163(1):93–99. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.163.1.93
Tognetto M, D’Andrea MR, Trevisani M et al (2003) Proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) activation contracts the isolated human renal artery in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 139(1):21–27
Tsalamandris S, Antonopoulos AS, Oikonomou E et al (2019) The role of inflammation in diabetes: current concepts and future perspectives. Eur Cardiol Rev 14(1):50
Waasdorp M, Florquin S, Duitman J, Spek CA (2019) Pharmacological PAR-1 inhibition reduces blood glucose levels but does not improve kidney function in experimental type 2 diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J 33(10):10966–10972. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900516R
Willis Fox O, Preston RJ (2020) Molecular basis of protease-activated receptor 1 signaling diversity. J Thromb Haemost 18(1):6–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.14643
World Health Organization (2022) https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Accessed 20 May 2022
Zieske AW, Tracy RP, McMahan CA et al (2005) Elevated serum C-reactive protein levels and advanced atherosclerosis in youth. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25(6):1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000164625.93129.64
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the management of Chitkara University, Punjab for the motivation to complete this manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS, IG, SP, PM performed the study. AS analysed data, wrote the manuscript and conducted literature survey. GS conceptualized the study, performed statistical analysis and reviewed the final manuscript draft. SG reviewed the final manuscript draft and helped in statistical analysis. TGS, RSJ, RSS helped in preparation of the final manuscript draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The experimental study was approved by the institutional human ethical committee (IHEC) of Chitkara College of Pharmacy, Chitkara University, Rajpura, Punjab, India (EC/NEW/INST/2021/531/59). The research was performed in accordance with ICH E6- Good Clinical Practice guidelines, as well as the Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and relevant amendments.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, S., Sood, A., Gautam, I. et al. Serum protease-activated receptor (PAR-1) levels as a potential biomarker for diagnosis of inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients. Inflammopharmacol 30, 1843–1851 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01049-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01049-0