Abstract
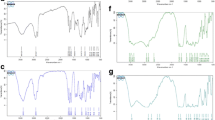
Methotrexate (MTX), the first-line drug for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), can cause considerable toxicity, which limits effective dosage regimens. Moreover, it has rapid clearance, which leads to poor patient compliance. To mitigate such challenges, this study aimed to validate the use of MTX-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (NPs) in treating Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA) arthritis in rats. Healthy Wistar rats (n = 30) were divided into five groups. The first group served as healthy control, while the second group served as arthritic control. Group 3 was administered methotrexate, while groups 4 and 5 were MTX-loaded NP-treated groups. NPs were prepared by solvent evaporation method and characterized by zeta size, potential, polydispersity index (PDI), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. NPs were 190 nm in size, and PDI was 0.25, confirming the uniform distribution of NPs. A significant increase in paw thickness was noted up to the 21st day of the study, which was reversed by a high dose of MTX-loaded NPs. MTX NPs significantly reduced the level of pro-inflammatory markers, including TNF-α and IL-6, along with improving control of oxidative stress biomarkers. The findings of biochemical, haematological, radiological, and histopathological investigations further confirmed amelioration of necrosis and cellular infiltration. It can be concluded that MTX-loaded chitosan NPs are promising candidates for treating FCA-induced arthritis in a rat model.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Akhtar B, Muhammad F, Aslam B, Saleemi MK (2020a) Toxicity studies of oral and transdermal formulations of gentamicin loaded PLGA nanoparticles in animal model. Pak Vet J 40(1):67–72
Akhtar B, Muhammad F, Aslam B, Saleemi MK, Sharif A (2020b) Biodegradable nanoparticle based transdermal patches for gentamicin delivery: formulation, characterization and pharmacokinetics in rabbits. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 57:101680
Akhtar B, Muhammad F, Aslam B, Saleemi MK, Sharif A (2020c) Pharmacokinetic profile of chitosan modified poly lactic co-glycolic acid biodegradable nanoparticles following oral delivery of gentamicin in rabbits. Int J Biol Macromol 164:1493–1500
Anwar M, Muhammad F, Akhtar B, Rehman S, Saleemi MK (2020) Nephroprotective effects of curcumin loaded chitosan nanoparticles in cypermethrin induced renal toxicity in rabbits. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:1–9
Anwar M, Muhammad F, Akhtar B (2021) Biodegradable nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 64:102638
Avci AB, Feist E, Burmester GR (2018) Targeting IL-6 or IL-6 receptor in rheumatoid arthritis: what’s the difference? BioDrugs 32:531–546
Bhalekar MR, Upadhaya PG, Madgulkar AR (2016) Fabrication and efficacy evaluation of chloroquine nanoparticles in CFA-induced arthritic rats using TNF-α ELISA. Eur J Pharm Sci 84:1–8
Brown PM, Pratt AG, Isaacs JD (2016) Mechanism of action of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis, and the search for biomarkers. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:731–742
Ciro Y, Rojas J, Alhajj MJ, Carabali GA, Salamanca CH (2020) Production and characterization of chitosan–polyanion nanoparticles by polyelectrolyte complexation assisted by high-intensity sonication for the modified release of methotrexate. Pharmaceuticals 13:11
Cutolo M, Sulli A, Pizzorni C, Seriolo B, Straub R (2001) Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 60:729–735
Dogra S, Mahajan R (2013) Systemic methotrexate therapy for psoriasis: past, present and future. Clin Exp Dermatol 38:573–588
Ekambaram S, Perumal SS, Subramanian V (2010) Evaluation of antiarthritic activity of Strychnos potatorum Linn seeds in Freund’s adjuvant induced arthritic rat model. BMC Complement Altern Med 10:1–9
Favalli EG, Biggioggero M, Crotti C, Becciolini A, Raimondo MG, Meroni PL (2019) Sex and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 56:333–345
Gadve S, Hulle P, Shelke M, Mohite M (2015) Development of UV–visible spectrophotometric method for the analysis of methotrexate in tablet formulations. Int J Pharm Chem Biol Sci 5:4
Gao J, Wang C, Wei W (2021) The effects of drug transporters on the efficacy of methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sci 268:118907
Garg NK, Singh B, Tyagi RK, Sharma G, Katare OP (2016) Effective transdermal delivery of methotrexate through nanostructured lipid carriers in an experimentally induced arthritis model. Colloids Surf B 147:17–24
Gerards AH, de Lathouder S, de Groot E, Dijkmans B, Aarden L (2003) Inhibition of cytokine production by methotrexate. Studies in healthy volunteers and patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 42:1189–1196
Hayer S, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Denis MC, Armaka M, Hoffmann M, Bäcklund J, Nandakumar KS, Niederreiter B, Geka C, Fischer A (2021) ‘SMASH’recommendations for standardised microscopic arthritis scoring of histological sections from inflammatory arthritis animal models. Ann Rheum Dis 80:714–726
Hazlewood GS, Barnabe C, Tomlinson G, Marshall D, Devoe DJ, Bombardier C (2016) Methotrexate monotherapy and methotrexate combination therapy with traditional and biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis. Cochr Database Syst Rev 2016:8
Kumar V, Leekha A, Tyagi A, Kaul A, Mishra AK, Verma AK (2017) Preparation and evaluation of biopolymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery system in effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm Res 34:654–667
Kumar V, Leekha A, Kaul A, Mishra AK, Verma AK (2020) Role of folate-conjugated glycol-chitosan nanoparticles in modulating the activated macrophages to ameliorate inflammatory arthritis: in vitro and in vivo activities. Drug Deliv Transl Res 10:1057–1075
Lathouder SD, Gerards A, de Groot E, Valkhof M, Dijkmans B, Aarden L (2004) Bioassay for detection of methotrexate in serum. Scand J Rheumatol 33:167–173
Levy RA, de Jesus GR, de Jesus NR, Klumb EM (2016) Critical review of the current recommendations for the treatment of systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases during pregnancy and lactation. Autoimmun Rev 15:955–963
Liu Y, Wang S, Zhang R, Lan W, Qin W (2017) Development of poly(lactic acid)/chitosan fibers loaded with essential oil for antimicrobial applications. Nanomaterials 7:194
Manan M, Saleem U, Akash MSH, Qasim M, Hayat M, Raza Z, Ahmad B (2020) Antiarthritic potential of comprehensively standardized extract of Alternanthera bettzickiana. In vitro and in vivo studies. ACS Omega 5:19478–19496
Medina C, Santos-Martinez M, Radomski A, Corrigan O, Radomski M (2007) Nanoparticles: pharmacological and toxicological significance. Br J Pharmacol 150:552–558
Nath B, Barbhuiya T (2014) Studies on the density and surface area of nanoparticles from Camellia sinensis, a natural source. J Chem Pharm Res 6:608–610
Ogata A, Kato Y, Higa S, Yoshizaki K (2019) IL-6 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive review. Mod Rheumatol 29:258–267
Pirmardvand Chegini S, Varshosaz J, Taymouri S (2018) Recent approaches for targeted drug delivery in rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis and treatment. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 46:502–514
Rajitha P, Biswas R, Sabitha M, Jayakumar R (2017) Methotrexate in the treatment of psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis: mechanistic insights, current issues and novel delivery approaches. Curr Pharm Des 23:3550–3566
Schwalfenberg, G. K. 2012. Solar radiation and vitamin D: mitigating environmental factors in autoimmune disease. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, 2012.
Sung Y-K, Cho S-K, Kim D, Won S, Choi C-B, Bang S-Y, Hong S-J, Kim HA, Koh E-M, Lee H-S (2017) Characteristics and outcomes of rheumatoid arthritis patients who started biosimilar infliximab. Rheumatol Int 37:1007–1014
Wu Z, Xu K, Min J, Chen M, Shen L, Xu J, Jiang Q, Han G, Pan L, Li H (2020) Folate-conjugated hydrophobicity modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles for targeted delivery of methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater 18:2280800020962629
Yaghoubi A, Ghojazadeh M, Abolhasani S, Alikhah H, Khaki-Khatibi F (2015) Correlation of serum levels of vitronectin, malondialdehyde and Hs-CRP with disease severity in coronary artery disease. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res 7:113
Funding
The study has not received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by MUS, BA, AS, FM, MIA, KA, and YJ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MUS and BA, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
All the in vivo experiments were conducted after approval from the institutional ethics committee.
Consent to participate
N/A.
Consent to publish
N/A.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saleem, M.U., Muhammad, F., Sharif, A. et al. Methotrexate-loaded biodegradable nanoparticles exert anti-arthritic effect by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines in Freund’s complete adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Inflammopharmacol 30, 1079–1091 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-00977-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-00977-1