Abstract
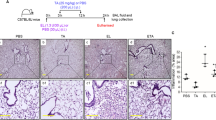
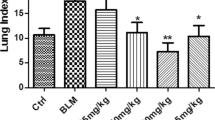
Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) is a chronic and irreversible scarring disease in the lung with limited treatment options. Therefore, it is critical to identify new therapeutic options. This study was undertaken to identify the effects of tannic acid (TA), a naturally occurring dietary polyphenol, in a mouse model of PF. Bleomycin (BLM) was intratracheally administered to induce PF. Administration of TA significantly reduced BLM-induced histological alterations, inflammatory cell infiltration and the levels of various inflammatory mediators (nitric oxide, leukotriene B4 and cytokines). Additionally, treatment with TA also impaired BLM-mediated increases in pro-fibrotic (transforming growth factor-β1) and fibrotic markers (alpha-smooth muscle actin, vimentin, collagen 1 alpha and fibronectin) expression. Further investigation indicated that BLM-induced phosphorylation of Erk1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2) in lungs was suppressed by TA treatment. Findings of this study suggest that TA has the potential to mitigate PF through inhibiting the inflammatory response and fibrotic process in lungs and that TA might be useful for the treatment of PF in clinical practice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini C, Gurrieri C (2006) Chemokine/cytokine cocktail in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc 3:357–363
Barszcz M, Taciak M, Tuśnio A, Skomiał J (2018) Effects of dietary level of tannic acid and protein on internal organ weights and biochemical blood parameters of rats. PLoS One 13:e0190769
Brock TG, Lee YJ, Maydanski E, Marburger TL, Luo M, Paine R 3rd, Golden MP (2005) Nuclear localization of leukotriene A4 hydrolase in type II alveolar epithelial cells in normal and fibrotic lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 289:L224–L232
Camelo A, Dunmore R, Sleeman MA, Clarke DL (2014) The epithelium in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: breaking the barrier. Front Pharmacol 4:173
Chu X, Wang H, Jiang YM, Zhang YY, Bao YF, Zhang X, Zhang JP, Guo H, Yang F, Luan YC, Dong YS (2016) Ameliorative effects of tannic acid on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. J Pharmacol Sci 130:15–23
Dallagi A, Girouard J, Hamelin-Morrissette J, Dadzie R, Laurent L, Vaillancourt C, Lafond J, Carrier C, Reyes-Moreno C (2015) The activating effect of IFN-γ on monocytes/macrophages is regulated by the LIF-trophoblast-IL-10 axis via Stat1 inhibition and Stat3 activation. Cell Mol Immunol 12:326–341
Desai O, Winkler J, Minasyan M, Herzog EL (2018) The role of immune and inflammatory cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front Med (Lausanne) 5:43
Fernandez IE, Eickelberg O (2012) The impact of TGF-β on lung fibrosis: from targeting to biomarkers. Proc Am Thorac Soc 9:111–116
Flechsig P, Hartenstein B, Teurich S, Dadrich M, Hauser K, Abdollahi A, Gröne HJ, Angel P, Huber PE (2010) Loss of matrix metalloproteinase-13 attenuates murine radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:582–590
Genovese T, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R, Failla M, Mazzon E, Sortino MA, Frasca G, Gili E, Crimi N, Caputi AP, Vancheri C (2005) Inhibition or knock out of inducible nitric oxide synthase result in resistance to bleomycin-induced lung injury. Respir Res 6:58
Gibbons MA, MacKinnon AC, Ramachandran P, Dhaliwal K, Duffin R, Phythian-Adams AT, Van Rooijen N, Haslett C, Howie SE, Simpson AJ, Hirani N, Gauldie J, Iredale JP, Sethi T, Forbes SJ (2011) Ly6Chi monocytes direct alternatively activated profibrotic macrophage regulation of lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 184:569–581
Gurujeyalakshmi G, Wang Y, Giri SN (2000) Suppression of bleomycin-induced nitric oxide production in mice by taurine and niacin. Nitric Oxide 4:399–411
Hasan SA, Eksteen B, Reid D, Paine HV, Alansary A, Johannson K, Gwozd C, Goring KA, Vo T, Proud D, Kelly MM (2013) Role of IL-17A and neutrophils in fibrosis in experimental hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 131:1663–1673
Hsu YC, Wang LF, Chien YW (2007) Nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of diffuse pulmonary fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med 42:599–607
Huang SK, Peters-Golden M (2008) Eicosanoid lipid mediators in fibrotic lung diseases: ready for prime time? Chest 133:1442–1450
Hussain T, Tan B, Yin Y, Blachier F, Tossou MC, Rahu N (2016) Oxidative stress and inflammation: what polyphenols can do for us? Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:7432797
Kato M, Sasaki S, Nakamura T, Kurokawa K, Yamada T, Ochi Y, Ihara H, Takahashi F, Takahasi K (2019) Gastrointestinal adverse effects of nintedanib and the associated risk factors in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep 9:12062
Kekevian A, Gershwin ME, Chang C (2014) Diagnosis and classification of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Autoimmun Rev 13:508–512
Kinder BW, Brown KK, Schwarz MI, Ix JH, Kervitsky A, King TE Jr (2008) Baseline BAL neutrophilia predicts early mortality in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 133:226–232
Koval A, Pieme CA, Queiroz EF, Ragusa S, Ahmed K, Blagodatski A, Wolfender JL, Petrova TV, Katanaev VL (2018) Tannins from Syzygium guineense suppress Wnt signaling and proliferation of Wnt-dependent tumors through a direct effect on secreted Wnts. Cancer Lett 435:110–120
Kowal-Bielecka O, Distler O, Kowal K, Siergiejko Z, Chwiecko J, Sulik A, Gay RE, Lukaszyk AB, Gay S, Sierakowski S (2003) Elevated levels of leukotriene B4 and leukotriene E4 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with scleroderma lung disease. Arthritis Rheum 48:1639–1646
Izumo T, Kondo M, Nagai A (2009) Effects of a leukotriene B4 receptor antagonist on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J 34:1444–1451
Li B, Wang JH (2011) Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in wound healing: force generation and measurement. J Tissue Viability 20:108–120
Liu HW, Dong XF, Tong JM, Zhang Q (2011) A comparative study of growth performance and antioxidant status of rabbits when fed with or without chestnut tannins under high ambient temperature. Anim Feed Sci Tech 164:89–95
Liu HW, Zhou D, Tong JM, Vaddella V (2012) Influence of chestnut tannins on welfare, carcass characteristics, meat quality, and lipid oxidation in rabbits under high ambient temperature. Meat Sci 90:164–169
Margaritopoulos G, Vasarmidi E, Antoniou K (2016) Pirfenidone in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Core Evid 2016:11–22
Moore BB, Hogaboam CM (2008) Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L152–L160
Murray LA, Chen Q, Kramer MS, Hesson DP, Argentieri RL, Peng X, Gulati M, Homer RJ, Russell T, Van Rooijen N, Elias JA, Hogaboam CM, Herzog EL (2011) TGF-beta driven lung fibrosis is macrophage dependent and blocked by serum amyloid P. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:154–162
Myllärniemi M, Kaarteenaho R (2015) Pharmacological treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: preclinical and clinical studies of pirfenidone, nintedanib, and N-acetylcysteine. Eur Clin Respir J 2:26385
Nakamura Y, Tsuji S, Tonogai Y (2003) Method for analysis of tannic acid and its metabolites in biological samples: application to tannic acid metabolism in the rat. J Agric Food Chem 51:331–339
Nkyimbeng T, Ruppert C, Shiomi T, Dahal B, Lang G, Seeger W, Okada Y, D’Armiento J, Günther A (2013) Pivotal role of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in extracellular matrix turnover in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One 8:e73279
Oikonomou N, Harokopos V, Zalevsky J, Valavanis C, Kotanidou A, Szymkowski DE, Kollias G, Aidinis V (2006) Soluble TNF mediates the transition from pulmonary inflammation to fibrosis. PLoS One 1:e108
Organ L, Bacci B, Koumoundouros E, Barcham G, Milne M, Kimpton W, Samuel C, Snibson K (2015) Structural and functional correlations in a large animal model of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm Med 15:81
Pattarayan D, Sivanantham A, Krishnaswami V, Loganathan L, Palanichamy R, Natesan S, Muthusamy K, Rajasekaran S (2018a) Tannic acid attenuates TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by effectively intervening TGF-β signaling in lung epithelial cells. J Cell Physiol 233:2513–2525
Pattarayan D, Sivanantham A, Bethunaickan R, Palanichamy R, Rajasekaran S (2018b) Tannic acid modulates fibroblast proliferation and differentiation in response to pro-fibrotic stimuli. J Cell Biochem 119:6732–6742
Pithayanukul P, Ruenraroengsak P, Bavovada R, Pakmanee N, Suttisri R (2007) In vitro investigation of the protective effects of tannic acid against the activities of Naja kaouthia venom. Pharm Biol 45:94–97
Radhakrishnan D, Yamashita C, Gillio-Meina C, Fraser DD (2014) Translational research in pediatrics III: bronchoalveolar lavage. Pediatrics 134:135–154
Reinert T, Baldotto CSDR, Nunes FAP, Scheliga AADS (2013) Bleomycin-induced lung injury. J Cancer Res 2013:480608
Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, Cottin V, Flaherty KR, Hansell DM, Inoue Y, Kim DS, Kolb M, Nicholson AG, Noble PW, Selman M, Taniguchi H, Brun M, Le Maulf F, Girard M, Stowasser S, Schlenker-Herceg R, Disse B, Collard HR, INPULSIS Trial Investigators (2014) Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 370:2071–2082
Richeldi L, Collard HR, Jones MG (2017) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 389:1941–1952
Salminen JP, Karonen M (2011) Chemical ecology of tannins and other phenolics: we need a change in approach. Funct Ecol 25:325–338
Scalbert A, Manach C, Morand C, Rémésy C, Jiménez L (2005) Dietary polyphenols and the prevention of diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 45:287–306
Shieh JM, Tseng HY, Jung F, Yang SH, Lin JC (2019) Elevation of IL-6 and IL-33 levels in serum associated with lung fibrosis and skeletal muscle wasting in a bleomycin-induced lung injury mouse model. Mediators Inflamm 2019:7947596
Sivanantham A, Pattarayan D, Bethunaickan R, Kar A, Mahapatra SK, Thimmulappa RK, Palanichamy R, Rajasekaran S (2019a) Tannic acid protects against experimental acute lung injury through downregulation of TLR4 and MAPK. J Cell Physiol 234:6463–6476
Sivanantham A, Pattarayan D, Rajasekar N, Kannan A, Loganathan L, Bethunaickan R, Mahapatra SK, Palanichamy R, Muthusamy K, Rajasekaran S (2019b) Tannic acid prevents macrophage-induced pro-fibrotic response in lung epithelial cells via suppressing TLR4-mediated macrophage polarization. Inflamm Res 68:1011–1024
Soodaeva S, Kubysheva N, Klimanov I, Nikitina L, Batyrshin I (2019) Features of oxidative and nitrosative metabolism in lung diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1689861
Summer R, Krishna R, Schriner D, Cuevas-Mora K, Sales D, Para R, Roman J, Nieweld C, Gochuico BR, Romero F (2019) Matrix metalloproteinase activity in the lung is increased in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis 14:162
Vu TN, Chen X, Foda HD, Smaldone GC, Hasaneen NA (2019) Interferon-γ enhances the antifibrotic effects of pirfenidone by attenuating IPF lung fibroblast activation and differentiation. Respir Res 20:206
Wilborn J, Bailie M, Coffey M, Burdick M, Strieter R, Peters-Golden M (1996) Constitutive activation of 5-lipoxygenase in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 97:1827–1836
Williamson JD, Sadofsky LR, Hart SP (2015) The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced lung injury in animals and its applicability to human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung Res 41:57–73
Wilson MS, Wynn TA (2009) Pulmonary fibrosis: pathogenesis, etiology and regulation. Mucosal Immunol 2:103–121
Wynn TA (2011) Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp Med 208:1339–1350
Yang J, Wheeler SE, Velikoff M, Kleaveland KR, LaFemina MJ, Frank JA, Chapman HA, Christensen PJ, Kim KK (2013) Activated alveolar epithelial cells initiate fibrosis through secretion of mesenchymal proteins. Am J Pathol 183:1559–1570
Acknowledgements
S. R. thankfully acknowledges the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for awarding Ramalingaswami re-entry fellowship (BT/RLF/Re-entry/36/2013). This study was also supported in part by the Department of Science and Technology (DST; Award No: YSS/2014/000125) (to S. R.), Government of India. The first author (N. R.) gratefully acknowledges the support of Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), New Delhi, India for the award of ICMR‐Senior Research Fellowship (SRF; Award No: 45/42/2019‐PHA/BMS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR has conceptualized, designed the experiments, acquired financial support, supervised the study, and wrote the manuscript; SGP has supervised the study and revised the manuscript; NR performed most of the experiments; AS involved in the acquisition of data; NR, AS and SR analysed data and interpreted the results; AK and SKM participated in cytokine analysis; RA and RKT contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajasekar, N., Sivanantham, A., Kar, A. et al. Tannic acid alleviates experimental pulmonary fibrosis in mice by inhibiting inflammatory response and fibrotic process. Inflammopharmacol 28, 1301–1314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00707-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00707-5