Abstract.
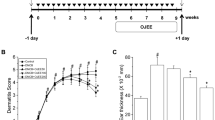
Extracts of Tanacetum parthenium (L.) Sch. Bip., a plant known under the common name “Feverfew”, contains the sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide, a potent skin sensitizer. To eliminate the risk of skin sensitization from Feverfew, we developed a parthenolide-depleted extract of Feverfew (PD-Feverfew) and determined its effectiveness as an anti-inflammatory agent. We confirmed that PD-Feverfew was sufficiently depleted of parthenolide since PD-Feverfew did not inhibit TNF-α induced-NF-κB activity unlike parthenolide containing whole Feverfew. PD-Feverfew directly inhibited the activity of pro-inflammatory enzymes 5-lipoxygenase, phosphodiesterase-3 and phosphodiesterase-4. PD-Feverfew inhibited the release of pro-inflammatory mediators nitric oxide, PGE2 and TNF-α from macrophages and TNF-α, IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-4 from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Additionally, PD-Feverfew inhibited TPA-induced release of PGE2 from human skin equivalents. In vivo, PD-Feverfew inhibited oxazolone-induced dermatitis, and was more potent than whole Feverfew in reducing TPA-induced dermatitis. Finally the efficacy of PD-Feverfew was confirmed clinically by a reduction in erythema in a methyl nicotinate-induced vasodilation model. In conclusion, our results indicate that PD-Feverfew extracts have potent anti-inflammatory activity suggesting that this botanical would be efficacious in relieving inflammation without inducing immune sensitization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sur, R., Martin, K., Liebel, F. et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Parthenolide-Depleted Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium). Inflammopharmacol 17, 42–49 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-008-8040-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-008-8040-9