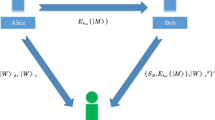
Abstract
Recently, Xia et al. proposed a semi-quantum blind signature protocol based on five-particle GHZ state. Their protocol can reduce the computation burden of the communicants. However, their protocol is not secure against forgery attack. We prove that the message sender and the signature receiver may conspire to forge the signer’s signature, because they master all the private keys of the signer. Then, both the signer and the signature receiver can deny a valid signature. Then, based on the three-particle GHZ state, an improved semi-quantum blind signature protocol is proposed. In the improved protocol, the signer shares the signing key with the trusted arbitrator. Even the message sender and the signature receiver conspire, it is infeasible for them to forge the signer’s signature. The improved scheme is secure against the disavowal attack. It has the better efficiency and practicability than the old version as well.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New direction in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22(6), 644–654 (1976)
Jian, H., Zhang, J., Bai, W.: A new signature scheme based on a multitude of mathematical problems. Electron. Sci. Technol. 24(4), 15–16+42 (2011)
Shor, P.W.: Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 41(2), 303–332 (1999)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum computation and quantum information. Cambridge University Press, UK, Cambridge (2000)
Wen, X., Niu, X., Ji, L., et al.: A weak blind signature scheme based on quantum cryptography. Opt. Commun. 282(4), 666–669 (2009)
Chaum D.: Blind signatures for untraceable payments. In: Chaum, D., Rivest, R.L., Sherman, A.T. (eds), Advances in Cryptology, pp. 199–203. Springer, Boston (1983)
Su, Q., Huang, Z., Wen, Q.Y., et al.: Quantum blind signature based on two-state vector formalism. Opt. Commun. 283(21), 4408–4410 (2010)
Yang, C.W., Hwang, T., Luo, Y.P.: Enhancement on “quantum blind signature based on two-state vector formalism.” Quantum Inf. Process. 12(1), 109–117 (2013)
Wang, M.M., Chen, X.B., Yang, Y.X.: A blind quantum signature protocol using the GHZ states. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 9, 32–37 (2013)
Siavash, K., Ali, Z.: A sessional blind signature based on quantum cryptography. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(1), 121–130 (2014)
Tian, Y., Chen, H., Ji, S.F., et al.: A broadcasting multiple blind signature scheme based on quantum teleportation. Opt. Quant. Electron. 46(6), 769–777 (2014)
Zhang, W., Qiu, D., Zou, X., Mateus, P.: Analyses and improvement of a broadcasting multiple blind signature scheme based on quantum GHZ entanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(6), 150 (2017)
Li, W., Shi, J., Shi, R., et al.: Blind quantum signature with controlled four-particle cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(8), 2579–2587 (2017)
Luo, Y.P., Tsai, S.L., Hwang, T., et al.: On “A new quantum blind signature with unlinkability.” Quantum Inf. Process. 16(4), 87 (2017)
Guo, X., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A trusted third-party e-payment protocol based on quantum blind signature without entanglement. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(9), 2657–2664 (2018)
Yang, Y.Y., Xie, S.C., Zhang, J.Z., et al.: An improved quantum proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine seven-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56(7), 2293–2302 (2017)
Zhang, J.L., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C., et al.: Improvement of a quantum proxy blind signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(6), 1612–1621 (2018)
Liu, G., Ma, W., Cao, H., et al.: A novel quantum group proxy blind signature scheme based on five-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(6), 1999–2008 (2019)
Liang, X., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., et al.: Quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on four-qubit cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(1), 31–39 (2019)
Chen, J.J., You, F.C., Li, Z.Z.: Quantum multi-proxy blind signature based on cluster state. Quantum Inf. Process. 21(3), 104 (2022)
Boyer, M., Kenigsberg, D., Mor, T.: Quantum key distribution with classical bob. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 098901 (2007)
Zhao, X.Q., Chen, H.Y., Wang, Y.Q., et al.: Semi-quantum bi-signature scheme based on W states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 58(10), 3239–3251 (2019)
Yang, C.W., Lin, J., Tsa, C.W., et al.: Cryptanalysis of a semi-quantum bi-signature scheme based on W states. Entropy 24(10), 1408 (2022)
Chen, L.Y., Liao, Q., Tan, R.C., et al.: Offline arbitrated semi-quantum signature scheme with four-particle cluster state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59(12), 3685–3695 (2020)
Xia, C.Y., Li, H., Hu, J.: Semi-quantum digital signature protocol based on Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen steering. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 55(32), 325302 (2022)
Schrödinger, E., Born, M.: Discussion of probability relations between separated systems. Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 31, 555 (1935)
Wiseman, H.M., Jones, S.J., Doherty, A.C.: Steering, entanglement, nonlocality, and the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 140402 (2007)
Xu, Y., Cheng, K., Liu, T., et al.: A lightweight semi-quantum e-payment protocol based on blockchain. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60(11–12), 4196–4209 (2021)
Xia, C., Li, H., Hu, J.: A semi-quantum blind signature protocol based on five-particle GHZ state. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136(6), 01605 (2021)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 560, 7–11 (2014)
Zou, X., Qiu, D., Li, L., et al.: Semiquantum-key distribution using less than four quantum states. Phys. Rev. A 79(5), 052312 (2009)
Boyer, M., Gelles, R., Kenigsberg, D., et al.: Semiquantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 79(3), 032341 (2009)
Boyer, M., Katz, M., Liss, R., et al.: Experimentally feasible protocol for semiquantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 96(6), 062335 (2017)
Boykin, P.O., Roychowdhury, V.: Optimal encryption of quantum bits. Phys. Rev. A 67(4), 645–648 (2003)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.62272090) and the Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province (Grant No.22A413010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. The scheme was designed by Jie cao and Chaoyang Li, the security of the scheme was analyzed by Xiangjun Xin and Fagen Li. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jie Cao and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflicts of Interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Xin, X., Li, C. et al. Security Analysis and Improvement of a Blind Semi-quantum Signature. Int J Theor Phys 62, 87 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05350-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05350-8