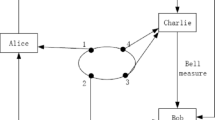
Abstract
In this paper, we propose a choreographed distributed electronic voting scheme, which is based on quantum group blind signature. Our distributed electronic voting scheme could really protect the message owner’s privacy and anonymity which the classical electronic voting systems can not provide. The electors can exercise their voting rights effectively, and no one other than the tallyman Bob knows the contents of his vote. Moreover, we use quantum key distribution protocol and quantum one-time pad to guarantee its unconditional security. Furthermore, when there was a dispute, the group supervisor David can detect the source of the signature based on the signature’s serial number \(SN\).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gritzalis, D.: Secure electronic voting. In: 7th Computer Security Incidents Response Teams Workshop Syros, Greece (2002)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A quantum multi-proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine four-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(2), 809–816 (2016)
Shao, A.X., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: A quantum multi-proxy multi-blind-signature scheme based on genuine six-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55, 5216–5224 (2016)
Fan, C., Lei, C.: Efficient blind signature scheme based on quadratic residues. Electron. Lett. 32(9), 811–813 (1996)
Yang, Y.Y., Zhang, J.Z., Xie, S.C.: An improved quantum proxy blind signature scheme based on genuine seven-qubit entangled state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56 (7), 2293–2302 (2017)
Harn, L.: Cryptanalysis of the blind signature based on the discrete logarithm. Electron. Lett. 31(14), 1136–1137 (1995)
Lysyanskaya, A., Ramzan, Z.: Group blind digital signature: a scalable solution to electronic cash. In: Proceedings of the 2nd Financial Cryptography Conference (1998)
Mohammed, E., Emarah, A.E., El-Shennawy, K.: A Blind Signature Scheme Based on Elgamal Signature. In: EURO-COMM 2000. Information Systems for Enhanced Public Safety and Security, pp 51–53. IEEE/AFCEA (2000)
Chien, H., Jan, J., Tseng, Y.: Eighth international conference on parallel and distributed systems (ICPADS01) 44 (2001)
Xu, G.B., Zhang, K.J.: A novel quantum group signature scheme without using entangled states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(7), 2577–2587 (2015)
Hillery, M.: Quantum voting and privacy ptotection: first steps. Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. https://doi.org/10.1117/2.1200610.0419 (2006)
Vaccaro, J.A., Spring, J., Chefles, A.: Quantum protocols for anonymous voting and surveying. Phys. Rev. A 75(1), 012333 (2007)
Wen, X.J., Cai, X.J.: Secure quantum voting protocol. Shangdong Univ. (Natural Science) 46(9), 9–13 (2011)
Yi, Z., He, G.Q., Zeng, G.H.: Quantum voting protocol using two-mode squeezed states. Acta Phys. Sin. 58(5), 3166–3172 (2009)
Horoshko, D., Kilin, S.: Quantum anonymous voting with anonymity check. Phys. Lett. A 375(8), 1172–1175 (2011)
Tian, J.H., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P.: A voting protocol based on the controlled quantum operation teleportation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(5), 2303–2310 (2016)
Cao, H.J., Ding, L.Y., Yu, Y.F., et al.: An electronic voting system achieved by using quantum proxy sinature. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(9), 4081–4088 (2016)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Computers, pp 175–179. IEEE (1984)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441–444 (2000)
Mayers, D.: Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. Assoc.: Comput. Math. 48(1), 351–406 (2001)
Inamon, H., Lutkenhaus, N., Mayers, D.: Unconditional security of practical quantum key distribution. Eur. Phys. J. D 41(3), 599–627 (2007)
Qi, J.X.: Quantum detection of a four-qubit entangled states. J. Xian University Posts Telecommun. 18(5), 63–65 (2013)
Guo, W., Zhang, J.Z., Li, Y.P., et al.: Multi-proxy strong blind quantum signature scheme. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(8), 3524–3536 (2016)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., et al.: Two-step quantum direct communication using the Einstein-podolsky-Rosen pair block. Phys. Rev. A 68, 042317 (2003)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L.: Secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad. Phys. Rev. A 69, 052319 (2004)
Cai, Q.Y., Li, B.W.: Deterministic secure communication without using entanglement. Chin. Lett. 21, 601–603 (2004)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., et al.: Cryptanalysis of multiparty controlled quantum secure direct communication using Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state. Opt. Commun. 283(1), 192–195 (2010)
Lin, S., Wen, Q.Y., Gao, F., et al.: Quantum secure direct communication with x-type entangled states. Phys. Rev. A 78(6), 064304 (2008)
Cao, H.J., Ding, L.Y., Jiang, X.L., et al.: A new proxy electronic voting scheme achieved by six-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(3), 674–681 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61402275, 61402015, 61273311), the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2015JM6263, 2016JM6069), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(Grant No. GK201402004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JL., Zhang, JZ. & Xie, SC. A Choreographed Distributed Electronic Voting Scheme. Int J Theor Phys 57, 2676–2686 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3789-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3789-0