Abstract
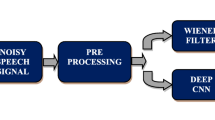
Speech enhancement is a process of improving the quality and intelligibility of the degraded speech signal. Various techniques have been demonstrated in the literature employing regression that subtract noise or predict clean signals. This research proposes a novel technique in speech signal analysis with enhancement using wavelet based denoising. Here the input is noisy speech signal and noise is removed using combined wavelet Fourier transform and train stacked encoder with non-negative matrix factorization integrated with convolutional ResNet architecture. Then used pairs of noisy as well as clean speech for training convolutional ResNet architecture at both input and output. The neural network was entirely retrained utilising combinations of wavelet-based denoising and clean speech, using outputs of wavelet denoising as its inputs. Segmental Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality are the parameters considered in the experimental study.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data generated or analysed during this study are included in the published article.
References
Abdulbaqi, J., Gu, Y., & Marsic, I. (2019). RHR-Net: A residual hourglass recurrent neural network for speech enhancement. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.07294
Abdullah, S. M. S. A., Ameen, S. Y. A., Sadeeq, M. A., & Zeebaree, S. (2021). Multimodal emotion recognition using deep learning. Journal of Applied Science and Technology Trends, 2(02), 52–58.
Abdullah, S., Zamani, M., & Demosthenous, A. (2022). A compact CNN-based speech enhancement with adaptive filter design using gabor function and region-aware convolution. IEEE Access, 10, 130657.
Bie, X., Leglaive, S., Alameda-Pineda, X., & Girin, L. (2022). Unsupervised speech enhancement using dynamical variationalautoencoders. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 30, 2993–3007.
Braithwaite, D. T., & Kleijn, W. B. (2019). Speech enhancement with variance constrained autoencoders. In Interspeech (pp. 1831–1835).
Chaiani, M., Selouani, S. A., Boudraa, M., & Yakoub, M. S. (2022). Voice disorder classification using speech enhancement and deep learning models. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 42(2), 463–480.
Gutiérrez-Muñoz, M., & Coto-Jiménez, M. (2022). An experimental study on speech enhancement based on a combination of wavelets and deep learning. Computation, 10(6), 102.
Han, C., Luo, Y., & Mesgarani, N. (2020). Real-time binaural speech separation with preserved spatial cues. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6404–6408). IEEE.
Huang, Z., Watanabe, S., Yang, S. W., García, P., & Khudanpur, S. (2022). Investigating self-supervised learning for speech enhancement and separation. In ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6837–6841). IEEE.
Hwang, J. W., Park, R. H., & Park, H. M. (2021). Efficient audio-visual speech enhancement using deep U-Net with early fusion of audio and video information and RNN attention blocks. IEEE Access, 9, 137584–137598.
Jabari, S., Rezaee, M., Fathollahi, F., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Multispectral change detection using multivariate Kullback-Leibler distance. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 147, 163–177.
Karthik, A., & MazherIqbal, J. L. (2021). Efficient speech enhancement using recurrent convolution encoder and decoder. Wireless Personal Communications, 119(3), 1959–1973.
Kim, H., Kang, K., & Shin, J. W. (2022). Factorized MVDR deep beamforming for multi-channel speech enhancement. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 29, 1898–1902.
Kim, H., & Shin, J. W. (2021). Target exaggeration for deep learning-based speech enhancement. Digital Signal Processing, 116, 103109.
Kominek, J., & Black, A. W. (2004). The CMU Arctic speech databases. In Proceedings of the fifth ISCA workshop on speech synthesis, Vienna, Austria, 20–22 September 2004.
Le, X., Lei, T., Chen, K., & Lu, J. (2022). Inference skipping for more efficient real-time speech enhancement with parallel RNNs. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 30, 2411–2421.
Li, A., Zheng, C., Zhang, L., & Li, X. (2022). Glance and gaze: A collaborative learning framework for single-channel speech enhancement. Applied Acoustics, 187, 108499.
Li, X. X., Li, D., Ren, W. X., & Zhang, J. S. (2022). Loosening identification of multi-bolt connections based on wavelet transform and ResNet-50 convolutional neural network. Sensors, 22(18), 6825.
Lin, J., van Wijngaarden, A. J. D. L., Wang, K. C., & Smith, M. C. (2021b). Speech enhancement using multi-stage self-attentive temporal convolutional networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 29, 3440–3450.
Lin, Y. C., Yu, C., Hsu, Y. T., Fu, S. W., Tsao, Y., & Kuo, T. W. (2021a). SEOFP-NET: Compression and acceleration of deep neural networks for speech enhancement using sign-exponent-only floating-points. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 30, 1016–1031.
Llombart, J., Ribas, D., Miguel, A., Vicente, L., Ortega, A., & Lleida, E. (2021). Progressive loss functions for speech enhancement with deep neural networks. EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing, 2021(1), 1–16.
Michelsanti, D., Tan, Z. H., Zhang, S. X., Xu, Y., Yu, M., Yu, D., & Jensen, J. (2021). An overview of deep-learning-based audio-visual speech enhancement and separation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 29, 1368–1396.
Passos, L. A., Khubaib, A., Raza, M., & Adeel, A. (2022). Multimodal speech enhancement using burst propagation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.03275.
Polyak, A., Wolf, L., Adi, Y., Kabeli, O., & Taigman, Y. (2021). High fidelity speech regeneration with application to speech enhancement. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 7143–7147). IEEE.
Rao, W., Fu, Y., Hu, Y., Xu, X., Jv, Y., Han, J., Jiang, Xie, L., Wang, Y., Watanabe, S., et al. (2021). Interspeech 2021 conferencing speech challenge: Towards far-field multi-channel speech enhancement for video conferencing. arXiv:2104.00960.
Reddy, C. K., Dubey, H., Koishida, K., Nair, A., Gopal, V., Cutler, R., Braun, S., Gamper, H., Aichner, R., & Srinivasan, S. (2021). Interspeech 2021 deep noise suppression challenge. In Interspeech.
Ribas, D., Miguel, A., Ortega, A., & Lleida, E. (2022). Wiener filter and deep neural networks: A well-balanced pair for speech enhancement. Applied Sciences, 12(18), 9000.
Sun, K., & Zhang, X. (2021). UltraSE: Single-channel speech enhancement using ultrasound. In Proceedings of the 27th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking (pp. 160–173).
Toloosham, B., & Koishida, K. (2022). A training framework for stereo-aware speech enhancement using deep neural networks. In ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 6962–6966). IEEE.
Tolooshams, B., Giri, R., Song, A. H., Isik, U., & Krishnaswamy, A. (2020). Channel-attention dense u-net for multichannel speech enhancement. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP) (pp. 836–840). IEEE.
Wang, R., Chencho, An, S., Li, J., Li, L., Hao, H., & Liu, W. (2021). Deep residual network framework for structural health monitoring. Structural Health Monitoring, 20, 1443–1461.
Yuliani, A. R., Amri, M. F., Suryawati, E., Ramdan, A., & Pardede, H. F. (2021). Speech enhancement using deep learning methods: A review. Jurnal Elektronikadan Telekomunikasi, 21(1), 19–26.
Zhang, Q., Qian, X., Ni, Z., Nicolson, A., Ambikairajah, E., & Li, H. (2022). A time-frequency attention module for neural speech enhancement. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 31, 462.
Zheng, C., Liu, W., Li, A., Ke, Y., & Li, X. (2022). Low-latency monaural speech enhancement with deep filter-bank equalizer. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 151(5), 3291–3304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasarao, V. Speech signal analysis and enhancement using combined wavelet Fourier transform with stacked deep learning architecture. Int J Speech Technol 26, 735–742 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-023-10044-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-023-10044-x