Abstract
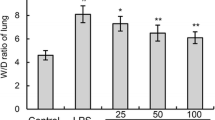
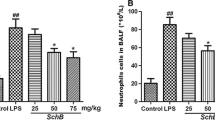
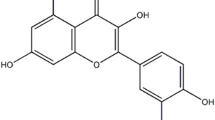
Chelerythrine (CHE), a quaternary benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid, exhibits a wide spectrum of pharmacological effects. Although CHE has been used to treat various diseases, the protective effects of CHE on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxic shock have not been explored. The aims of the study were to investigate the protective effects of CHE on LPS-induced endotoxic shock in mice and clarify the mechanism of the effects. We found that pretreatment with CHE (1, 5, and 10 mg/kg, po) at 1 and 12 h before injected intraperitoneally with 1 mg/kg LPS markedly decreased the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and myeloperoxidase (MPO) and attenuated the lung histopathological changes. Meanwhile, the effects were dependent on the inhibition of the expression of p65 nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). The protective effects of CHE on LPS-induced endotoxic shock can be attributed to attenuating inflammatory cytokines and inhibition of the expression of NF-κB.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki, K., T. Tajima, Y. Yabushita, A. Nakamura, U. Nezu, M. Takahashi, M. Kimura, and Y. Terauchi. 2008. A novel initial codon mutation of the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter gene in a Japanese patient with Gitelman’s syndrome. Endocrine Journal 55: 557.
Freudenberg, M., and C. Galanos. 1990. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides: structure, metabolism and mechanisms of action. International Reviews of Immunology 6: 207–221.
Bone, R.C., C.J. Grodzin, and R.A. Balk. 1997. Sepsis: a new hypothesis for pathogenesis of the disease process. CHEST Journal 112: 235–243.
He, M., H.Y. Lau, S.W. Ng, and M. Bhatia. 2007. Chemokines in acute inflammation: regulation, function and therapeutic strategies. International Journal of Integrative Biology 1: 18.
Lappin, E., and A.J. Ferguson. 2009. Gram-positive toxic shock syndromes. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 9: 281–290.
Jansen, M.J., T. Hendriks, M.T. Vogels, J.W. van der Meer, and R.J.A. Goris. 1996. Inflammatory cytokines in an experimental model for the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 24: 1196–1202.
Neurath, M.F., I. Fuss, M. Pasparakis, L. Alexopoulou, S. Haralambous, K.H. Meyer zum Büschenfelde, W. Strober, and G. Kollias. 1997. Predominant pathogenic role of tumor necrosis factor in experimental colitis in mice. European Journal of Immunology 27: 1743–1750.
Blenman, K.R.M., F.R. Bahjat, L.L. Moldawer, and L. Morel. 2004. Aberrant signaling in the TNFα/TNF receptor 1 pathway of the NZM2410 lupus-prone mouse. Clinical Immunology 110: 124–133.
Ma, X. 2001. TNF-α and IL-12: a balancing act in macrophage functioning. Microbes and Infection 3: 121–129.
Yoshimoto, T., K. Nakanishi, S. Hirose, K. Hiroishi, H. Okamura, Y. Takemoto, A. Kanamaru, T. Hada, T. Tamura, and E. Kakishita. 1992. High serum IL-6 level reflects susceptible status of the host to endotoxin and IL-1/tumor necrosis factor. The Journal of Immunology 148: 3596–3603.
Damas, P., D. Ledoux, M. Nys, Y. Vrindts, D. De Groote, P. Franchimont, and M. Lamy. 1992. Cytokine serum level during severe sepsis in human IL-6 as a marker of severity. Annals of Surgery 215: 356.
Bhatia, M., and S. Moochhala. 2004. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Journal of Pathology 202: 145–156.
LaRosa, S.P., and S.M. Opal. 2008. Sepsis strategies in development. Clinics in Chest Medicine 29: 735–747.
Klosterhalfen, B., K. Hörstmann-Jungemann, P. Vogel, S. Flohé, F. Offner, C.J. Kirkpatrick, and P.C. Heinrich. 1992. Time course of various inflammatory mediators during recurrent endotoxemia. Biochemical Pharmacology 43: 2103–2109.
Martich, G.D., A.J. Boujoukos, and A.F. Suffredini. 1993. Response of man to endotoxin. Immunobiology 187: 403–416.
Szarka, R.J., N. Wang, L. Gordon, P.N. Nation, and R.H. Smith. 1997. A murine model of pulmonary damage induced by lipopolysaccharide via intranasal instillation. Journal of Immunological Methods 202: 49–57.
Tracey, K.J., B. Beutler, S.F. Lowry, J. Merryweather, S. Wolpe, I.W. Milsark, R.J. Hariri, T.J. Fahey, A. Zentella, and J.D. Albert. 1986. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science 234: 470–474.
Kruidenier, La., and H. Verspaget. 2002. Oxidative stress as a pathogenic factor in inflammatory bowel disease—radicals or ridiculous? Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 16: 1997–2015.
Takeuchi, K., T. Yasuhiro, Y. Asada, and Y. Sugawa. 1998. Role of nitric oxide in pathogenesis of aspirin-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Digestion 59: 298–307.
Klebanoff, S.J. 2005. Myeloperoxidase: friend and foe. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 77: 598–625.
Kim, I.-S., Y.-J. Park, S.-J. Yoon, and H.-B. Lee. 2010. Ephedrannin A and B from roots of Ephedra sinica inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory mediators by suppressing nuclear factor-κB activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. International Immunopharmacology 10: 1616–1625.
Wise, G.E., and S. Yao. 2003. Expression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in the rat dental follicle. Archives of Oral Biology 48: 47–54.
Heinzel, F.P., R.M. Rerko, P. Ling, J. Hakimi, and D.S. Schoenhaut. 1994. Interleukin 12 is produced in vivo during endotoxemia and stimulates synthesis of gamma interferon. Infection and Immunity 62: 4244–4249.
Suzuki, K., K. Tateda, T. Matsumoto, F. Gondaira, S. Tsujimoto, and K. Yamaguchi. 2000. Effects of interaction between Escherichia coli verotoxin and lipopolysaccharide on cytokine induction and lethality in mice. Journal of Medical Microbiology 49: 905–910.
Yadav, S.K., B. Adhikary, S. Chand, B. Maity, S.K. Bandyopadhyay, and S. Chattopadhyay. 2012. Molecular mechanism of indomethacin-induced gastropathy. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 52: 1175–1187.
Remick, D.G., G.R. Bolgos, J. Siddiqui, J. Shin, and J.A. Nemzek. 2002. Six at six: interleukin-6 measured 6 h after the initiation of sepsis predicts mortality over 3 days. Shock 17: 463–467.
Ito, H., M. Takazoe, Y. Fukuda, T. Hibi, K. Kusugami, A. Andoh, T. Matsumoto, T. Yamamura, J. Azuma, and N. Nishimoto. 2004. A pilot randomized trial of a human anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody in active Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology 126: 989–996.
Luo, J., J. Cao, X. Jiang, and H. Cui. 2010. Effect of low molecular weight heparin rectal suppository on experimental ulcerative colitis in mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 64: 441–445.
Reinisch, W., C. Gasché, W. Tillinger, J. Wyatt, C. Lichtenberger, M. Willheim, C. Dejaco, T. Waldhör, S. Bakos, and H. Vogelsang. 1999. Clinical relevance of serum interleukin-6 in Crohn’s disease: single point measurements, therapy monitoring, and prediction of clinical relapse. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 94: 2156–2164.
Buraczynska, M., L. Jozwiak, P. Ksiazek, E. Borowicz, and P. Mierzicki. 2007. Interleukin-6 gene polymorphism and faster progression to end-stage renal failure in chronic glomerulonephritis. Translational Research 150: 101–105.
Benamar, K., E.B. Geller, and M.W. Adler. 2002. Effect of a μ-opioid receptor-selective antagonist on interleukin-6 fever. Life Sciences 70(18): 2139–2145.
Beffa, D.C., A.J. Fischman, S.P. Fagan, V.F. Hamrahi, K.W. Paul, M. Kaneki, Y.-M. Yu, R.G. Tompkins, and E.A. Carter. 2011. Simvastatin treatment improves survival in a murine model of burn sepsis: role of interleukin 6. Burns 37: 222–226.
Cheng, L.N., X.L. Huang, W. Shi, J.Y. Xiang, and H.T. Gan. 2009. Tetrandrine ameliorates dextran-sulfate-sodium-induced colitis in mice through inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activation. International Journal of Colorectal Disease 24: 5–12.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported in part by the Shanxi National Science Foundation of international cooperation projects (No. 2013KW26-02) to W.F. Li. The authors are very grateful to professor Y.M. Zhang for their technical assistance from Xi’an Jiaotong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, X., Mu, Q., Li, W. et al. Protective Effects of Chelerythrine Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Endotoxic Shock in Mice. Inflammation 37, 1968–1975 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9929-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9929-7