Abstract
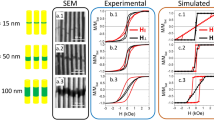
Ferromagnetic nanoparticles can be used for data storage, spintronics, and other applications. Especially vortex states are often suggested to be used to store information. Due to the shape anisotropy dominating in nanoparticles, magnetization reversal processes can be expected to depend not only on the dimensions, but also on the orientation with respect to the external magnetic field. While several papers evaluate magnetization dynamics, including vortex precessions, in round nanodots, square nanodots are less often investigated. Here we report on different magnetization reversal processes found in micromagnetic simulations of square Fe nanodots with lateral dimensions between 100 nm and 500 nm and thicknesses between 10 nm and 50 nm. Choosing magnetic field orientations parallel to one of the square edges and under 45∘, seven different reversal mechanisms were found, most of them including a single-vortex state, while in some cases two, three or more vortex-antivortex pairs were found. The ground state, i.e. the magnetic state at vanishing external magnetic field, was often a single-vortex state, making the nanodot with the respective dimensions suitable for data storage applications. The stability of this state, i.e. the field range over which it existed, depended strongly on the lateral dimensions and the dot thickness and was largest for small lateral dimensions and large thicknesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehrmann, A., Komraus, S., Blachowicz, T., Domino, K., Nees, M.-K., Jakobs, P.-J., Leiste, H., Mathes, M., Schaarschmidt, M.: Pseudo exchange bias due to rotational anisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 412, 7–10 (2016)
Ehrmann, A., Blachowicz, T., Komraus, S., Nees, M.-K., Jakobs, P.-J., Leiste, H., Mathes, M., Schaarschmidt, M.: Magnetic properties of square Py nanowires: irradiation dose and geometry dependence. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 173903 (2015)
Pagnanelli, F., Altimari, P., Bellagamba, M., Granata, G., Moscardini, E., Schiavi, P.G., Toro, L.: Pulsed electrodeposition of cobalt nanoparticles on copper: influence of the operating parameters on size distribution and morphology. Electrochim. Acta 155, 228–235 (2015)
Romero, M., Pardo, H., Faccio, R., Suescun, L., Vazquez, S., Laborda, I., Fernandez-Werner, L., Acosta, A., Castiglioni, J., Mombru, A.W.: A Study on the polymer precursor formation and microstructure evolution of square-shaped (La0.5Ba0.5)(Mn0.5Fe0.5)O3 ceramic nanoparticles. J. Ceramic Sci. Tech. 6, 221–230 (2015)
Blachowicz, T., Ehrmann, A.: Square nano-magnets as bit-patterned media with doubled possible data density. Mater. Today Proc. 4, S226–S231 (2017)
Ehrmann, A., Blachowicz, T.: Interaction between magnetic nanoparticles in clusters. AIMS Mater. Sci. 4, 383–390 (2017)
Mouhib, M., Benayad, N., Azhari, M.: Mixed spin (1/2,1) transverse Ising nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 419, 325–337 (2016)
Kaneyoshi, T.: Shape dependences of magnetic properties in 2D Ising nano-particles. Phase Trans. 86, 404–418 (2013)
Hellwig, O., Heyderman, L.J., Petracic, O., Zabel, H.: Competing Interactions in Patterned and Self-Assembled Magnetic Nanostructures. Springer Tracts Modern Phys. 246, 189–234 (2013)
Lemos, C.G.O., Figueiredo, W., Santos, M.: Exchange bias for core/shell magnetic nanoparticles. Physica A Stat. Mech. Appl. 433, 148–160 (2015)
Fabian, A., Czerner, M., Heiliger, C., Elm, M.T., Hofmann, D.M., Klar, P.J.: Domain formation in rectangular magnetic nanoparticle assemblies. Phys. Rev. B 98, 054401 (2018)
Mohler, G., Harter, A.W.: Micromagnetic investigation of resonance frequencies in ferromagnetic particles. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 10E313 (2005)
Kozlov, A.G., Pustovalov, E.V., Kolesnikov, A.G., Chebotkevich, L.A., Samardak, A.S.: Induced magnetic anisotropies dependent micromagnetic structure of epitaxial Co nanostrip arrays. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 459, 118–124 (2018)
Tillmanns, A., Blachowicz, T.: Adjusting exchange bias and coercivity of magnetic layered systems with varying anisotropies. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 083923 (2011)
Kan, J.J., Lubarda, M.V., Chan, K.T., Uhlir, V., Scholl, A., Lomakin, V., Fullerton, E.E.: Periodic chiral magnetic domains in single-crystal nickel nanowires. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2, 064406 (2018)
Donahue, M.J., Porter, D.G.: OOMMF User’s Guide, Version 1.0 Interagency Report NISTIR 6376. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (1999)
Gilbert, T.L.: A phenomenological theory of damping in ferromagnetic materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 40, 3443 (2004)
Kneller, E.F., Hawig, R.: The exchange-spring magnet: a new material principle for permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 27, 3588 (1991)
Lemcke, O.: Thetaevolve module for OOMMF. available: http://www.nanoscience.de/groupr/stm-spstm/projects/temperature/download.shtml (2002)
Ehrmann, A., Blachowicz, T.: Vortex and double-vortex nucleation during magnetization reversal in Fe nanodots of different dimensions, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., submitted
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Volkswagen Foundation grant “Adaptive Computing with Electrospun Nanofiber Networks” no. 93679, by the SUT Rector Grant 14/990/RGJ18/0099 as well as the internal SUT project BK-229/RIF/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Magnetic Materials and Nanomaterials (MMN 2018), Boumerdes, Algeria, 1-4 July 2018
Edited by Abderrahim Guittoum
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrmann, A., Blachowicz, T. Systematic study of magnetization reversal in square Fe nanodots of varying dimensions in different orientations. Hyperfine Interact 239, 48 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-018-1523-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-018-1523-1