Abstract
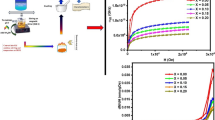
Zirconium oxide (zirconia) exists in three crystalline forms of monoclinic, tetragonal and cubic structures at atmospheric pressures. The cubic form of zirconia is well known for its mechanical, electrochemical and optical applications. Fe-doped cubic zirconia (high temperature phase) compositions are synthesized by microwave combustion method. Here, we present a Mössbauer investigation of Zr1 − x Fe x O2 composition within a range of Fe (0.03 < x < 0.09). 57Fe Mössbauer spectra were recorded at room temperature and at low temperature (77 K) for all samples. 3% Fe-doped ZrO2 shows doublet and the corresponding 6% and 9% Fe-doped ZrO2 samples show superimposed sextet and doublets. The isomer shift and quadrupole moment indicate, Iron to be in III oxidation state and to occupy different octahedral sites, associated with some amount of disorder. X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Fe-doped ZrO2 samples appear as very well crystalline. The Miller indices refer to the cubic fluorite-type ZrO2 structure. The magnetic behavior shows increase in moment and decrease in coercivity, with increase in Fe concentration. The M vs. H plots of the as-prepared Zr1-x Fe x O2 essentially show typical hysteresis loops, indicating room temperature ferromagnetism. Thus, the introduced microwave combustion route is an effective process to achieve multifunctional Fe-doped Zirconia with coexistent magnetic properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hong, N.H., Poirot, N., Sakal, J.: Evidence for magnetism due to oxygen vacancies in Fe-doped HfO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 042503 (2006)
Karmakar, D., Mandal, S.K., Kadam, R.M., Paulose, P.L., Rajarajan, A.K., Nath, T.K., Das, A.K., Dasgupta, I., Das, G.P.: Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped ZnO nanocrystals: experiment and theory. Phys. Rev., B 75, 144404 (2007)
Hong, N.H., Sakai, J., Poirot, N., Ruyter, A.: Laser ablated Ni-doped HfO2 thin films: room temperature ferromagnets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 242505 (2005)
Ramachandran Rao, M.S., Kundaliya, D.C., Ogale, S.B., Fu, L.F., Welz, S.J., Browning, N.D., Zaitsev, V., Varughese, B., Cardoso, C.A., Curtin, A., Dhar, S., Shinde, S.R., Venkatesan, T., Lofland, S.E., Schwarz, S.A.: Search for ferromagnetism in undoped and cobalt-doped HfO2 − δ . Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 142505 (2006)
Matsumoto, Y., Murakami, M., Shono, T., Hasegawa, T., Fukumura, T., Kawasaki, M., Ahmet, P., Chikyow, T., Koshihara, S., Koinuma, H.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism in transparent transition metal-doped titanium dioxide. Science 291, 854 (2001)
Venkatesan, M., Fitzgerald, C.B., Coey, J.M.D.: Thin films: unexpected magnetism in a dielectric oxide. Nature (London) 430, 630 (2004)
Coey, J.M.D., Venkatesan, M., Stamenov, P., Fitzgerald, C.B., Dorneles, L.S.: Magnetism in hafnium dioxide. Phys. Rev., B 72, 024450 (2005)
Hong, N.H., Sakai, J., Poirot, N., Brize, V.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism observed in undoped semiconducting and insulating oxide thin films. Phys. Rev., B 73, 132404 (2006)
Radavanovic, P.V., Gamelin, D.R.: High-temperature ferromagnetism in Ni2 + -Doped ZnO aggregates prepared from colloidal diluted magnetic semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 157202 (2003)
Khare, N., Kappers, M.J., Wei, M., Blamire, M.G., MacManus-Driscoll, J.L.: Defect-induced ferromagnetism in Co-doped ZnO. Adv. Mater. 18, 1449 (2006)
Hong, N.H., Sakai, J., Houng, N.T., Poirot, N., Ruyter, A.: Role of defects in tuning ferromagnetism in diluted magnetic oxide thin films. Phys. Rev., B 72, 045336 (2005)
Archer, T., Das, C., Pemmaraju, C.D., Sanvito, S.: Magnetic properties of ZrO2-diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, e118 (2007)
Manoharan, S.S., Swati, Prasanna, S.J., Rao, M.L., Sahu, R.K.: Microwave-assisted synthesis of fine particle oxides employing wet redox mixtures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 2469 (2002)
Manoharan, S.S., Patil, K.C.: Combustion synthesis of metal chromite powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75(4), 1012 (1992)
Bhame, S.D., Joly, V.L.J., Joy, P.A.: Effect of disorder on the magnetic properties of LaMn0.5Fe0.5O3. Phys. Rev., B 72, 054426 (2005)
Potzger, K., Zhou, S., Reuther, H., Mucklich, A., Eichhorn, F., Schell, N., Skorupa, W., Helm, M., Fassmender, J., Herrmannsdorfer, T., Papageorgiou, T.P.: Fe implanted ferromagnetic ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 052508 (2006)
Fitzgerald, C.B., Venkatesan, M., Douvalis, A.P., Huber, S., Coey, J.M.D.: SnO2 doped with Mn, Fe or Co: room temperature dilute magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 7390 (2004)
Sundaresan, A., Bhargavi, R., Rangarajan, N., Siddesh, U., Rao, C.N.R.: Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of nanoparticles of the otherwise nonmagnetic oxides. Phys. Rev., B 74, 161306(R) (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, T.R., Manoharan, S.S., Kurian, S. et al. Mössbauer spectroscopic study of iron-doped zirconia synthesized by microwave route. Hyperfine Interact 188, 43–49 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-008-9885-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-008-9885-4