Abstract
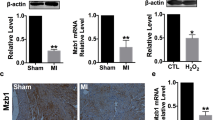
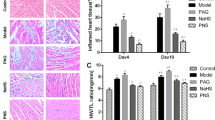
Viral myocarditis has been found to be one of the leading causes of sudden death in young adults. However, no effective drugs have been developed to intervene the progression of myocarditis. Accordingly, the present study is carried out to explore the protective role played by melatonin in the setting of viral myocarditis with a focus on Mst1-Hippo pathway, mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress. Cardiac function was determined via echocardiographic examination. Mitochondrial function and ER stress were detected via ELISA, western blots, and immunofluorescence. Our data demonstrated that virus injection induced cardiac dysfunction as evidenced by reduced contractile function in myocardium. Besides, LDH release assay and western blotting analysis demonstrated that cardiomyocyte death was activated by virus injection. Interestingly, melatonin treatment improved cardiac function and repressed virus-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis. At the molecular levels, mitochondrial dysfunction was induced by virus infection, as indicated by mitochondrial membrane potential reduction, mPTP opening rate elevation and caspase-9-related apoptosis activation. Besides, ER stress parameters were also elevated in virus-treated cardiomyocytes. Interestingly, melatonin treatment maintained mitochondrial dysfunction and repressed ER stress. To the end, we found that Mst1 was upregulated by virus infection; this effect was attenuated through supplementation with melatonin. However, Mst1 overexpression reduced the beneficial impact exerted by melatonin on cardiomyocyte viability, mitochondrial function and ER homeostasis. Our study illustrated that melatonin treatment attenuated viral myocarditis via sustaining cardiomyocyte viability, repressing mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibiting ER stress in a manner dependent on Mst1 inhibition.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ba X, Boldogh I (2018) 8-Oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1: beyond repair of the oxidatively modified base lesions. Redox Biol 14:669–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.008
Brazao V, Colato RP, Santello FH, Vale GTD, Gonzaga NA, Tirapelli CR, Prado JCD Jr (2018) Effects of melatonin on thymic and oxidative stress dysfunctions during Trypanosoma cruzi infection. J Pineal Res 65:e12510. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12510
Cameron AR et al (2018) Metformin selectively targets redox control of complex I energy transduction. Redox Biol 14:187–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.08.018
Chandra M et al (2018) Cardiac-specific inactivation of LPP3 in mice leads to myocardial dysfunction and heart failure. Redox Biol 14:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.015
Coverstone ED et al (2018) A novel genetic marker of decreased inflammation and improved survival after acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol 113:38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0697-7
Darden J, Payne LB, Zhao H, Chappell JC (2019) Excess vascular endothelial growth factor—a disrupts pericyte recruitment during blood vessel formation. Angiogenesis 22:167–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9648-z
Frustaci A, Chimenti C (2012) Immunosuppressive therapy in virus-negative inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Herz 37:854–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00059-012-3694-x
Fukumoto M et al (2018) Tip-cell behavior is regulated by transcription factor FoxO1 under hypoxic conditions in developing mouse retinas. Angiogenesis 21:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9588-z
Gonzalez NR, Liou R, Kurth F, Jiang H, Saver J (2018) Antiangiogenesis and medical therapy failure in intracranial atherosclerosis. Angiogenesis 21:23–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9578-1
Han L, Wang C, Guo S, Liu S, Yang L (2016) Therapeutic effect of recombinant lentiviral vector containing succinate dehydrogenase iron-sulfur protein on the treatment of experimental autoimmunity myocarditis. Med Hypotheses 93:97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2016.05.028
Han JY, Jeong HI, Park CW, Yoon J, Ko J, Nam SJ, Lim BK (2018) Cholic acid attenuates ER stress-induced cell death in Coxsackievirus-B3 infection. J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:109–114. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1708.08009
Jin Q et al (2018) DUSP1 alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing the Mff-required mitochondrial fission and Bnip3-related mitophagy via the JNK pathways. Redox Biol 14:576–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.004
Jung M, Dodsworth M, Thum T (2018) Inflammatory cells and their non-coding RNAs as targets for treating myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol 114:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0712-z
Kanwar MK, Yu J, Zhou J (2018) Phytomelatonin: recent advances and future prospects. J Pineal Res 65:e12526. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12526
Kazakov A et al (2018) Raf kinase inhibitor protein mediates myocardial fibrosis under conditions of enhanced myocardial oxidative stress. Basic Res Cardiol 113:42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0700-3
Kiel AM, Goodwill AG, Baker HE, Dick GM, Tune JD (2018) Local metabolic hypothesis is not sufficient to explain coronary autoregulatory behavior. Basic Res Cardiol 113:33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0691-0
Kyto V, Saraste A, Saukko P, Henn V, Pulkki K, Vuorinen T, Voipio-Pulkki LM (2004) Apoptotic cardiomyocyte death in fatal myocarditis. Am J Cardiol 94:746–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.05.056
Li X et al (2018a) Melatonin alleviates low PS I-limited carbon assimilation under elevated CO2 and enhances the cold tolerance of offspring in chlorophyll b-deficient mutant wheat. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12453
Li R, Xin T, Li D, Wang C, Zhu H, Zhou H (2018b) Therapeutic effect of Sirtuin 3 on ameliorating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: the role of the ERK-CREB pathway and Bnip3-mediated mitophagy. Redox Biol 18:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.011
Lin L, Zhang M, Yan R, Shan H, Diao J, Wei J (2017) Inhibition of Drp1 attenuates mitochondrial damage and myocardial injury in Coxsackievirus B3 induced myocarditis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 484:550–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.116
Lochner A, Marais E, Huisamen B (2018) Melatonin and cardioprotection against ischaemia/reperfusion injury: what’s new? A review. J Pineal Res 65:e12490. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12490
Mehra P et al (2018) Cardiac mesenchymal cells from diabetic mice are ineffective for cell therapy-mediated myocardial repair. Basic Res Cardiol 113:46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0703-0
Moore JBT et al (2018) Epigenetically modified cardiac mesenchymal stromal cells limit myocardial fibrosis and promote functional recovery in a model of chronic ischemic cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol 114:3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0710-1
Nam DH, Han JH, Lee TJ, Shishido T, Lim JH, Kim GY, Woo CH (2015) CHOP deficiency prevents methylglyoxal-induced myocyte apoptosis and cardiac dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol 85:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.05.016
Nawaz IM et al (2018) N-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-Phe-Leu-Phe-Leu-Phe (BOC2) inhibits the angiogenic activity of heparin-binding growth factors. Angiogenesis 21:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9581-6
Pearson G, Chai B, Vozheiko T, Liu X, Kandarpa M, Piper RC, Soleimanpour SA (2018) Clec16a, Nrdp1, and USP8 form a ubiquitin-dependent tripartite complex that regulates beta-cell mitophagy. Diabetes 67:265–277. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0321
Preau S et al (2016) Endotoxemia engages the rhoa kinase pathway to impair cardiac function by altering cytoskeleton, mitochondrial fission, and autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal 24:529–542. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6421
Riehle C, Bauersachs J (2018) Of mice and men: models and mechanisms of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol 114:2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0711-0
Sajib S, Zahra FT, Lionakis MS, German NA, Mikelis CM (2018) Mechanisms of angiogenesis in microbe-regulated inflammatory and neoplastic conditions. Angiogenesis 21:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9583-4
Shang X et al (2019) Sepsis-related myocardial injury is associated with Mst1 upregulation, mitochondrial dysfunction and the Drp1/F-actin signaling pathway. J Mol Histol 1:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-018-09809-5
Shi C et al (2018) Yap promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and mobilization via governing cofilin/F-actin/lamellipodium axis by regulation of JNK/Bnip3/SERCA/CaMKII pathways. Redox Biol 14:59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.08.013
Sun S et al (2018) Advanced oxidation protein products induce S-phase arrest of hepatocytes via the ROS-dependent, beta-catenin-CDK2-mediated pathway. Redox Biol 14:338–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.011
Ter Horst EN et al (2018) Elevated monocyte-specific type I interferon signalling correlates positively with cardiac healing in myocardial infarct patients but interferon alpha application deteriorates myocardial healing in rats. Basic Res Cardiol 114:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0709-7
Wang X, Song Q (2018) Mst1 regulates post-infarction cardiac injury through the JNK-Drp1-mitochondrial fission pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett 23:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-018-0085-1
Yang T, Cao C, Yang J, Liu T, Lei XG, Zhang Z, Xu S (2018) miR-200a-5p regulates myocardial necroptosis induced by Se deficiency via targeting RNF11. Redox Biol 15:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.025
Yu W, Xu M, Zhang T, Zhang Q, Zou C (2018) Mst1 promotes cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the ERK-CREB pathway and repressing FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy. J Physiol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-018-0627-3
Zha X, Yue Y, Dong N, Xiong S (2015) Endoplasmic reticulum stress aggravates viral myocarditis by raising inflammation through the IRE1-associated NF-kappaB pathway. Can J Cardiol 31:1032–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2015.03.003
Zhang C et al (2017a) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate acute myocarditis by modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and extracellular signal regulated 1/2-mediated apoptosis. Mol Med Rep 15:3515–3520. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6454
Zhang H, Yue Y, Sun T, Wu X, Xiong S (2017b) Transmissible endoplasmic reticulum stress from myocardiocytes to macrophages is pivotal for the pathogenesis of CVB3-induced viral myocarditis. Sci Rep 7:42162. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42162
Zhang B, Hou R, Zou Z, Luo T, Zhang Y, Wang L, Wang B (2018) Mechanically induced autophagy is associated with ATP metabolism and cellular viability in osteocytes in vitro. Redox Biol 14:492–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.10.021
Zhang H, Jin B, Faber JE (2019) Mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease cause rarefaction of pial collaterals and increased severity of ischemic stroke. Angiogenesis 22:263–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9655-0
Zhao XM et al (2018a) Melatonin improves the fertilization capacity and developmental ability of bovine oocytes by regulating cytoplasmic maturation events. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12445
Zhao H et al (2018b) Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and obesity through polarizing M2 macrophages and beiging in white adipose tissue. Diabetes 67:235–247. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0356
Zhou C, Routh VH (2018) Thioredoxin-1 overexpression in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus preserves the counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia during type 1 diabetes in male rats. Diabetes 67:120–130. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0930
Zhou H et al (2017a) Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2-mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12413
Zhou H et al (2017b) Ripk3 induces mitochondrial apoptosis via inhibition of FUNDC1 mitophagy in cardiac IR injury. Redox Biol 13:498–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.07.007
Zhou F, Jiang X, Teng L, Yang J, Ding J, He C (2018a) Necroptosis may be a novel mechanism for cardiomyocyte death in acute myocarditis. Mol Cell Biochem 442:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3188-5
Zhou H, Li N, Yuan Y, Jin YG, Guo H, Deng W, Tang QZ (2018b) Activating transcription factor 3 in cardiovascular diseases: a potential therapeutic target. Basic Res Cardiol 113:37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0698-6
Zhou H, Shi C, Hu S, Zhu H, Ren J, Chen Y (2018c) BI1 is associated with microvascular protection in cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury via repressing Syk-Nox2-Drp1-mitochondrial fission pathways. Angiogenesis 21:599–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9611-z
Zhou H et al (2018d) NR4A1 aggravates the cardiac microvascular ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy and promoting Mff-required mitochondrial fission by CK2alpha. Basic Res Cardiol 113:23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-018-0682-1
Zhou H, Wang S, Hu S, Chen Y, Ren J (2018e) ER-mitochondria microdomains in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: a fresh perspective. Front Physiol 9:755. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00755
Zhou H, Wang S, Zhu P, Hu S, Chen Y, Ren J (2018f) Empagliflozin rescues diabetic myocardial microvascular injury via AMPK-mediated inhibition of mitochondrial fission. Redox Biol 15:335–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.12.019
Zhou H, Zhu P, Wang J, Zhu H, Ren J, Chen Y (2018g) Pathogenesis of cardiac ischemia reperfusion injury is associated with CK2alpha-disturbed mitochondrial homeostasis via suppression of FUNDC1-related mitophagy. Cell Death Differ 25:1080–1093. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0086-7
Zhu H et al (2018) Melatonin protected cardiac microvascular endothelial cells against oxidative stress injury via suppression of IP3R-[Ca(2+)]c/VDAC-[Ca(2+)]m axis by activation of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 23:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-017-0827-4
Funding
This study is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (No: 2018A030313067), Key Specialist Department Training Project of Foshan City, Guangdong Province of China (No: Fspy 3-2015034), Science and Technology Innovation Project from Foshan, Guangdong (FS0AA-KJ218-1301-0006 and FS0AA-KJ218-1301-0010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HCOY, YT, and JKZ conceived the research; YT and YLZ performed the experiments; all authors participated in discussing and revising the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, H., Zhong, J., Lu, J. et al. Inhibitory effect of melatonin on Mst1 ameliorates myocarditis through attenuating ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Mol Hist 50, 405–415 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09836-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09836-w