Abstract
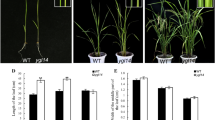
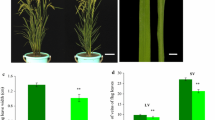
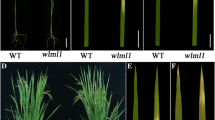
Leaf color is a highly important agronomic trait, and mutants with altered leaf coloration can serve as excellent models for studies on chloroplast development and chlorophyll biosynthesis, enabling the cloning of genes involved in these processes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). In this study, we isolated a stable genetic rice mutant, oryza sativa albino leaf 50 (osal50), from a breeding population of the japonica cultivar GP50. This mutant exhibited a distinctive albino phenotype, with white-striped leaves in seedlings and white panicles at the heading stage. Compared with wild-type GP50, the osal50 mutant showed lower chlorophyll and carotenoid accumulation, together with abnormal chloroplast ultrastructure. Genetic analysis demonstrated that a recessive nuclear gene was responsible for the albino phenotype of osal50, and a map-based cloning strategy delimited OsAL50 to a 160-kb physical interval on chromosome 1, flanked by two single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers, CAPS-08 and CAPS-37, that included 26 putative open reading frames. Sequence and expression analyses revealed LOC_Os01g20110 as the candidate OsAL50 gene, which was confirmed by knockout using CRISPR/Cas9. Subcellular localization and protein sequence analyses suggested that OsAL50 likely encodes an endoribonuclease E-like protein localized to the chloroplasts. Further investigation indicated that OsAL50 plays a vital role in the regulation of photosynthetic pigment metabolism, photosynthesis, and chloroplast biogenesis. In summary, we identified a novel albino mutant that will serve as useful genetic material for studies of chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development in rice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Bara S, Carpousis AJ (2015) RNA degradosomes in bacteria and chloroplast: classification, distribution and evolution of RNase E homologs. Mol Microbiol 97:1021–1035
Bae CH, Abe T, Matsuyama T, Fukunishi N, Nagata N, Nakano T, Kaneko Y, Miyoshi K, Matsushima H, Yoshida S (2001) Regulation of chloroplast gene expression is affected in ali, a novel tobacco albino mutant. Ann Bot 88:545–553
Chen T, Zhang YD, Zhao L, Zhu Z, Lin J, Zhang SB, Wang CL (2009) Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of a green-revertible albino gene gra(t) in rice. J Genet Genomics 36:117–123
Chen YP, Zhai Z, Yang WJ, Sun J, Shu XL, Wu DX (2015) Genetic analysis and fine mapping of St-wp gene in mutant rice with stripe white leaf and white panicle. Acta Agric Nucl Sin 29:1246–1252 (Chinese with English abstract)
Chen P, Hu HT, Zhang Y, Wang ZW, Dong GJ, Cui YT, Qian Q, Ren DY, Guo LB (2018) Genetic analysis and fine-mapping of a new rice mutant, white and lesion mimic leaf1. Plant Growth Regul 85:425–435
Deng XJ, Zhang HQ, Wang Y, HeF LJ, XiaoX S, Li W, Wang GH, Wang GL (2014) Mapped clone and functional analysis of lear-color gene Ygl7 in a rice hybrid (Oryza sativa L. spp. indica). PLoS ONE 9:e99564
Du ZX, Hao HY, He JP, Wang JP, Huang Z, Xu J, Fu HH, Fu JR, He HH (2020) GraS is critical for chloroplast development and affects yield in rice. J Integr Agr 19:2603–2615
Dunford R, Walden RM (1991) Plastid genome structure and plastid-related transcript levels in albino barley plants derived from another culture. Curr Genet 20:339–347
Gong XD, Su QQ, Lin DZ, Jiang Q, Xu JL, Zhang JH, Teng S, Dong YJ (2014) The rice OsV4 encoding a novel pentatricopeptide repeat protein is required for chloroplast development during the early leaf stage under cold stress. J Integr Plant Biol 56:400–410
Guo T, Huang X, Huang YX, Liu YZ, Zhang JG, Chen ZQ, Wang H (2012) Characterizations of a mutant gene hw-1(t) for green-revertible albino, high tillering and dwarf in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron Sin 38:23–35 (Chinese with English abstract)
Han B, Xue YB, Li JY, Deng XW, Zhang QF (2007) Rice functional genomics research in China. Philos T R Soc B 362:1009–1021
Hanaoka M, Kanamaru K, Fujiwara M, Takahashi H, Tanaka K (2005) Glutamyl-tRNA mediates a switch in RNA polymerase use during chloroplast biogenesis. EMBO Rep 6:545–550
Hsieh MH, Googman HM (2005) The Arabidopsis IspH homolog is involved in the plastid nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 138:641–653
Inada H, Kusumi K, Nishimura M, Iba K (1996) Specific expression of the chloroplast gene foe RNA polymerase (rpoB) at an early stage of leaf development in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 37:229–232
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (2005) The mapbased sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Jian L, Wang ZK, Zeng DD, Qian R, Shi CH, Jin XL (2017) Characterization and fine mapping of a green-revertible albino (albg) mutant in rice. Acta Agric Nucl Sin 31:2289–2297 (Chinese with English abstract)
Kapoor S, Maheshwari SC, Tyagi AK (1994) Developmental and light-dependent cues interact to establish steady-state levels of transcripts for photosynthesis-related genes (pabA, psbD, psaA and rbcL) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Curr Genet 25:362–366
Karlin-Neumann GA, Sun L, Tobin EM (1988) Expression of light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-protein genes is phytochrome regulated in etiolated Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings. Plant Physiol 88:1323–1331
Katiyar A, Smita S, Lenka SK, Rajwanshi R, Chinnusamy V, Bansal KC (2012) Genome-wide classification and expression analysis of MYB transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genomics 13:544
Kobayashi NI, Yamaji N, Yamamoto H, Okubo K, Ueno H, Costa A, Tanoi K, Matsumura H, Fujii-Kashino M, Horiuchi T, Nayef MA, Shabala S, An G, Ma JF, Horie T (2017) OsHKT1;5 mediates Na+ exclusion in the vasculature to protect leaf blades and reproductive tissues from salt toxicity in rice. Plant J 91:657–670
Kuaumi K, Yara A, Mitsui N, Tozawa Y, Iba K (2004) Characterization of a rice nuclear-encoded plastid RNA polymerase gene OsRpoTp. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1194–1201
Kusumi K, Iba K (2014) Establishment of the chloroplast genetic system in rice during early leaf development and at low temperatures. Front Plant Sci 5:386
Kusumi K, Sakata C, Nakamuta T, Kawasaki S, Yoshimura A, Iba K (2011) A plastid protein NUS1 is essential for buildup of the genetic system for early chloroplast development under cold stress conditions. Plant J 68:1039–1050
Kyozuka J, Mcelroy D, Hayakawa T, Xie Y, Wu R, Shimamoto K (1993) Light-regulated and cell-specific expression of tomato rbcS-gusA and rice rbcS-gusA fusion genes in transgenic rice. Plant Physiol 102:991–1000
Lan T, Wang B, Ling QP, Xu CH, Tong ZJ, Liang KJ, Duan YL, Wu WR (2010) Fing mapping of cisc(t), a gene for cold-induced seedling chlorosis, and identification of its candidate in rice. Chin Sci Bull 55:2183–2187 (Chinese with English abstract)
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) Mapmaker: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Li HC, Ji GB, Wang Y, Qian Q, Xu JC, Sodmergen LG, Zhao XF, Chen MS, Zhai WX, Li DY, Zhu LH (2018a) WHITE PANICLE 3, a novel nucleus-encoded mitochondrial protein, is essential for proper development and maintenance of chloroplasts and mitochondria in rice. Front Plant Sci 9:762
Li X, He Y, Yang J, Jia YH, Zeng HL (2018b) Gene mapping and transcriptome profiling of a practical photo-thermo-sensitive rice male sterile line with seedling-specific green-revertible albino leaf. Plant Sci 266:37–45
Li JL, Han GL, Sun CF, Sui N (2019) Research advances of MYB transcription factors in plant stress resistance and breeding. Plant Signal Behav 14:e1613131
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Method Enzymol 148:350–382
Liu RH, Meng JL (2003) MapDraw: a Microsoft Excel macro for drawing genetic linkage maps based on given genetic linkage data. Hereditas 25:317–321
Long D, Martin M, Sundberg E, Swinburne J, Puangsomlee P, Coupland G (1993) The maize transposable element system Ac/Ds as a mutagen in Arabidopsis: identification of an albino mutation induced by Ds insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:10370–10374
Lv YS, Shao GN, Qiu JH, Jiao GA, Sheng ZH, Xie LH, Wu YW, Tang SQ, Wei XJ, Hu PS (2017) White leaf and Panicle 2, encoding a PEP-associated protein, is required for chloroplast biogenesis under heat stress in rice. J Exp Bot 68:5147–5160
Lv J, Shang LG, Chen Y, Han Y, Yang XY, Xie SZ, Bai WQ, Hu MY, Wu H, Lei KR, Yang YN, Ge SZ, Trinh HP, Zhang Y, Guo LB, Wang ZW (2020) OsSLC1 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein essential for early chloroplast development and seedling survival. Rice 13:25
Matsuoka M (1990) Classification and characterization of cDNA that encodes the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b binding protein of photosystem II from rice. Plant Cell Physiol 31:519–526
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Mudd EA, Sullivan S, Gisby MF, Mironov A, Kwon CS, Chung W, Day A (2008) A 125 kDa RNase E/G-like protein in present in plastids and is essential for chloroplast development and autotrophic growth in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 59:2597–2610
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Peng Y, Zhang Y, Lv J, Zhang JH, Li P, Shi XL, Wang YF, Zhang HL, He ZH, Teng S (2012) Characterization and fine mapping of a novel rice albino mutant low temperature albino 1. J Genet Genomics 39:385–396
Rao YC, Yang YL, Xu J, Li XJ, Leng YJ, Dai LP, Huang LC, Shao GS, Ren DY, Hu J, Guo LB, Pan JW, Zeng DL (2015) EARLY SENESCENCE 1 encodes a SCAR-LIKE PROTEIN2 that affects water loss in rice. Plant Physiol 169:1225–1239
Schein A, Sheffy-Levin S, Glaser F, Schuster G (2008) The RNase E/G-type endoribonuclease of higher plants is located in the chloroplast and cleaves RNA similarly to the E. coli enzyme. RNA 14:1057–1068
Schmied J, Hedtke B, Grimm B (2011) Overexpression of HEMA1 encoding glutamyl-tRNA reductase. J Plant Physiol 168:1372–1379
Shang LN, Chen XL, Mi SN, Wei G, Wang L, Zhang YY, Lei T, Lin YX, Huang LJ, Zhu MD, Wang N (2019) Phenotypic identification and gene mapping of temperature-sensitive green-revertible albino mutant tsa2 in rice (Oryza sariva L.). Acta Agron Sin 45:662–675 (Chinese with English abstract)
Song J, Wei XJ, Shao GN, Sheng ZH, Chen DB, Liu CL, Jiao GA, Xie LH, Tang SQ, Hu PS (2014) The rice nuclear gene WLP1 encoding a chloroplast ribosome L13 protein is needed for chloroplast development in rice grown under low temperature conditions. Plant Mol Biol 84:301–314
Su N, Hu ML, Wu DX, Wu FQ, Fei GL, Lan Y, Chen XL, Shu XL, Zhang X, Wan JM (2012) Disruption of a rice pentatricopeptide repeat protein causes a seedling-specific albino phenotype and its utilization to enhance seed purity in hybrid rice production. Plant Physiol 159:227–238
Su Y, Hu SK, Zhang B, Ye WJ, Niu YF, Guo LB, Qian Q (2017) Characterization and fine mapping of a new early leaf senescence mutant es3(t) in rice. Plant Growth Regul 81:419–431
Sugimoto H, Kusumi K, Noguchi K, Yano M, Yoshimura A, Iba K (2007) The rice nuclear gene, VIRESCENT 2, is essential for chloroplast development and encodes a novel type of guanylate kinase targeted to plastids and mitochondria. Plant J 52:512–527
Takeuchi R, Kimura S, Saotome A, Sakaguchi K (2007) Biochemical properties of a plastidial DNA Polymerase of rice. Plant Mol Biol 64:601–611
Tomiyama M, Inoue SI, Tsuzuki T, Soda M, Morimoto S, Okigaki Y, Ohishi T, Mochizuki N, Takahashi K, Kinoshita T (2014) Mg-chelatase I subunit 1 and Mg-protoporphyrin IX methyltransferase affect the stomatal aperture in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res 127:553–563
Walter M, Piepenburg K, Schottler MA, Petersen K, Kahlau S, Tiller N, Drechsel O, Weingartner M, Kudla J, Bock R (2010) Konckout of the plastid RNase E leads to defective RNA processing and chloroplast ribosome deficiency. Plant J 64:851–863
Wang PR, Gao JX, Wan CM, Zhang FT, Xu ZJ, Huang XQ, Sun XQ, Deng XJ (2010) Divinyl chlorophyll(ide) a can be converted to monovinyl chlorophyll(ide) a by a divinyl reductase in rice. Plant Physiol 153:994–1003
Wang YL, Wang CM, Zheng M, Lyu J, Xu Y, Li XH, Niu M, Long WH, Wang D, Wang HY, Terzaghi W, Wang YH, Wang JM (2016) WHITE PANICLE1, a Val-tRNA synthetase regulating chloroplast ribosome biogenesis in rice, is essential for early chloroplast development. Plant Physiol 170:2110–2123
Wang ZW, Lv J, Xie SZ, Zhang Y, Qiu ZN, Chen P, Cui YT, Niu YF, Hu SK, Jiang HZ, Ge SZ, Trinh HP, Lei KR, Bai WQ, Zhang Y, Guo LB, Ren DY (2018) OsSLA4 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein essential for early chloroplast development and seedling growth in rice. Plant Growth Regul 84:249–260
Wang YL, Wang YH, Ren YL, Duan EC, Zhu XP, Hao YY, Zhu JP, Chen RB, Lei J, Teng X, Zhang YY, Wang D, Zhang X, Guo XP, Jiang L, Liu SJ, Tian YL, Liu X, Chen LM, Wang HY, Wang JM (2021) White panicle2 encoding thioredoxin z, regulates plastid RNA editing by interacting with multiple organellar RNA editing factors in rice. New Phytol 229:2693–2706
Wei XY, Zeng YH, Zhang R, Huang JH, Yang WX, Zou WG, Xu XM (2019) Fine mapping and identification of the rice blast-resistance locus Pi-kf2(t) as a new member of the Pi2/Pi9 multigene family. Mol Breed 39:108
Wei XY, Zeng YH, Yang WX, Xiao CC, Hou XP, Huang JH, Zou WG, Xu XM (2023) Development of high-quality fragrant indica CMS line by editing Badh2 gene using CRISPR-Cas9 technology in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Agron Sin 49:2144–2159 (Chinese with English abstract)
Wu LW, Ren DY, Hu SK, Li GM, Dong GJ, Jiang L, Hu XM, Ye WJ, Cui YT, Zhu L, Hu J, Zhang GH, Gao ZY, Zeng DL, Qian Q, Guo LB (2016) Mutation of OsNaPRT1 in the NAD salvage pathway leads to withered leaf tips in rice. Plant Physiol 171:1085–1098
Xu JM, Yang J, Wu ZC, Liu HL, Huang FL, Wu YR, Carrie C, Narsai R, Murcha M, Whelan J, Wu P (2013) Identification of a Dual-Targeted protein belonging to the mitochondrial carrier family that is required for early leaf development in rice. Plant Physiol 161:2036–2048
Yang YL, Xu J, Huang LC, Leng YJ, Dai LP, Rao YC, Chen L, Wang YQ, Tu ZJ, Hu J, Ren DY, Zhang GH, Zhu L, Guo LB, Qian Q, Zeng DL (2016) PGL, encoding chlorophyllide a oxygenase 1, impacts leaf senescence and indirectly affects grain yield and quality in rice. J Exp Bot 67:1279–1310
Yang F, Debatosh D, Song T, Zhang JH (2021) Light harvesting-like protein 3 interacts with phytoene synthase and is necessary for carotenoid and chlorophyll biosynthesis in rice. Rice 14:32
Yoo SC, Cho SH, Sugimoto H, Li JJ, Kusumi K, Koh HJ, Iba K, Paek NC (2009) Rice Virescent3 and Stripe1 encoding the large and small subunits of ribonucleotide reductase are required for chloroplast biogenesis during early leaf development. Plant Physiol 150:388–401
Zhang HT, Li JJ, Yoo JH, Yoo SC, Cho SH, Koh HJ, Seo HS, Paek NC (2006) Rice Chlorina-1 and Chlorina-9 encode ChlD and ChlI subunits of Mg-chelatase, a key enzyme for chlorophyll synthesis and chloroplast development. Plant Mol Biol 62:325–337
Zhang ZG, Cui XA, Wang YW, Wu JX, Gu XF, Lu TG (2017) The RNA editing factor WSP1 is essential for chloroplast development in rice. Mol Plant 10:86–98
Zhang T, Feng P, Li YF, Yu P, Yu GL, Sang XC, Ling YH, Zeng XQ, Li YD, Huang JY, Zhang TQ, Zhao FM, Wang N, Zhang CW, Yang ZL, Wu RH, He GH (2018) VIRESCENT-ALBINO LEAF 1 regulates leaf color development and cell division in rice. J Exp Bot 69:4791–4804
Zhang LS, Mi SN, Wang L, Wei G, Zheng YJ, Zhou K, Shang LN, Zhu MD, Wang N (2019) Physiological and biochemical analysis and gene mapping of a novel short radicle and albino mutant sra1 in rice. Acta Agron Sin 45:556–567 (Chinese with English abstract)
Zheng H, Wang ZR, Tian YL, Liu LL, Lv F, Kong WY, Bai WT, Wang PR, Wang CL, Yu XW, Liu X, Jiang L, Zhao ZG, Wang JM (2019) Rice albino 1, encoding a glycyl-tRNA synthetase, is involved in chloroplast development and establishment of the plastidic ribosome system in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 139:495–503
Zhou KN, Xia JF, Ma TC, Wang YL, Li ZF (2018) Mapping and mutation analysis of stripe leaf and white panicle gene SLWP in rice. Chin J Rice Sci 32:325–334 (Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-01), the Fujian Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2021J01535, 2021J01536), and the Sanming Municipal Science and Technology Project (2022-N-7).
Funding
Funding was supported by Agriculture Research System of China,CARS-01 ,Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province,2021J01536, 2021J01535, Sanming Municipal Science and Technology Project,2022-N-7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ and XW contributed equally to this work. YZ carried out molecular-marker development, genetic analysis, molecular mapping, candidate gene analysis, physical-map and phylogenetic-tree construction, and wrote the manuscript. XW carried out molecular-marker development, genetic analysis, molecular mapping and expression analysis. CX and RZ participated in genetic analysis, molecular mapping, and physical-map construction. JH carried out mapping-population construction and participated in genetic analysis and molecular mapping. XX designed the research and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Dawei Xue.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10725_2023_1116_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file4 (PDF 554 KB)—Primers used for expression analysis of genes associated with chloroplast development, chlorophyll biosynthesis, and photosynthesis
10725_2023_1116_MOESM5_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file5 (PDF 554 KB)—Functional annotation of 26 candidate genes for OsAL50 based on the RGAP http://rice.plantbiology.msu.edu/
10725_2023_1116_MOESM6_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file6 (PDF 457 KB)—Mutation analysis within the promoter region of LOC_Os01g20110 in 20 rice varieties, where “--”indicates base deletion
10725_2023_1116_MOESM8_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file8 (PDF 404 KB)—Subcellular localization of OsAL50 in rice protoplasts. a Observation of free green fluorescent protein (GFP) signals in rice protoplasts. b Observation of OsAL50-GFP fluorescent signals in rice protoplasts. Bars: 10 μm
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Wei, X., Xiao, C. et al. Fine mapping and identification of a novel albino gene OsAL50 that is required for chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Growth Regul (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-01116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-023-01116-8