Abstract
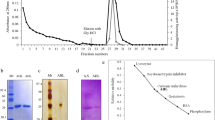
We present the purification and characterization of the two most abundant isoforms of lectins isolated from Tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) seeds, which have been shown to differentially affect the survival of different cancer cells. They were separated by concanavalin A-affinity chromatography. After purification, to release the N-glycans, they were digested with the endoglycosidases PNGase and Glycanase A. Fractions resulted from the hydrolysis products were analyzed to determine their carbohydrate composition. Mass spectrometry data indicated that both isoforms contained high mannose glycans being mannose 6 the most abundant form. Furthermore, based on sequence Ans-X-Ser/Thr, where X is any amino acid except proline, a glycosylation site was determined on asparagine 36. When their metal requirement to preserve their biological activity was determined, the lectins showed differences. While lectin A (LA) agglutination activity was best in the presence of magnesium, lectin B (LB) was best with calcium. Additionally, only LA exhibited affinity to human type-A erythrocytes. Although both lectins showed small differences in their properties, an identical structure-model for both lectins was generated by the homology modelling process. Also, the analysis of ligand binding sites and in silico glycosylation were achieved. Molecular docking with colon adenocarcinoma associated-N-glycans revealed some highly possible interactions and, on the other hand, that N-glycan interaction zones of Tepary bean lectins is not restricted to the carbohydrate binding domain but to an extended part of their surface, which could lead new strategies to explain their biological activity.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinho, S.S., Reis, C.A.: Glycosylation in cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 15, 540–555 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3982
An, H.J., Peavy, T.R., Hedrick, J.L., Lebrilla, C.B.: Determination of N glycosylation sites and site heterogeneity in glycoproteins. Anal. Chem. 75(20), 5628–5637 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac034414x
Goldstein, I.J., Hughes, R.C., Monsigny, M., Osawa, T. y Sharon, N.: What should be called a lectin? Nature. 285, 66 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/285066b0
Mody, R., Joshi, S., Chaney, W.: Use of lectins as diagnostic and therapeutic tools for cancer. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods. 33, 1–10 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/1056-8719(94)00052-6
Ferriz-Martínez, R.A., Torres-Arteaga, I.C., Blanco-Labra, A., García-Gasca, T.: The role of plant lectins in cancer treatment. In: Mejia-Vazquez, M.C., Navarro, S. (eds.) New Approaches in the Treatment of Cancer, pp. 71–89. Nova Science Publishers Inc, New York (2010)
Gupta, G., Surolia, A., Sampathkumar, S.G.: Lectin microarrays for glycomic analysis. OMICS 14, 419–436 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2009.0150
Hong, C.E., Park, A.K., Lyu, S.Y.: Synergistic anticancer effects of lectin and doxorubicin in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 394, 225–235 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2099-y
García-Gasca, T., Hernández-Rivera, E., López-Martínez, J., Casta, A.L., Yllescas-Gasca, L., Rodríguez, A.J., Blanco-Labra, A.: Effects of Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) Protease Inhibitor and Semi pure Lectin Fractions on Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer. 64(8), 1269–1278 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/01635581.2012.722246
Ferriz-Martínez, R., García-García, K., Torres-Arteaga, I., Rodríguez-Mendez, A.J., Guerrero-Carrillo, M.J., Moreno-Celis, U., Ángeles-Zaragoza, M.V., Blanco-Labra, A., Gallegos-Corona, M.A., Robles-Álvarez, J.P., Mendiola-Olaya, E., Andrade-Montemayor, H.M., García, O.P., García-Gasca, T.: Tolerability assessment of a lectin fraction from Tepary bean seeds (Phaseolus acutifolius) orally administered to rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2, 63–69 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.10.015
Moreno-Celis, U., López-Martínez, J., Blanco-Labra, A., Cervantes-Jiménez, R., Estrada-Martínez, L.E., García-Pascalin, E., Guerrero-Carrillo, M.D.J., Rodríguez-Méndez, A.J., Mejía, C., Ferriz-Martínez, R.A., García-Gasca, T.: Phaseolus acutifolius Lectin Fractions Exhibit Apoptotic Effects on Colon Cancer: Preclinical Studies Using Dimethilhydrazine or Azoxi-Methane as Cancer Induction Agents. Molecules. 22, 1670 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101670
Alatorre-Cruz, J.M., Pita-López, W., López-Reyes, R.G., Ferriz-Martínez, R.A., Cervantes-Jiménez, R., Guerrero-Carrillo, M.J., Aranda-Vargas, P.J., López-Herrera, G., Rodríguez-Méndez, A.J., Zamora-Arroyo, A., Gutiérrez-Sánchez, H., Reis de Souza, T., Blanco-Labra, A., García-Gasca, T.: Effects of intragastrically-administered Tepary bean lectins on digestive and immune organs: preclinical evaluation. Toxicol. Rep. 5, 56–64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.12.008
Mirkov, T.E., Wahlstrom, J.M., Hagiwara, K., Finardi-Filho, F., Kjemtrup, S., Chrispeels, M.J.: Evolutionary relationships among proteins in the phytohemagglutinin-arcelin-alpha-amylase inhibitor family of the common bean and its relatives. Plant Mol. Biol. 26, 1103–1113 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040692
Torres-Arteaga, I., Castro-Guillén, J.L., Mendiola-Olaya, E., García-Gasca, T., Ángeles-Zaragoza, M.C., García-Santoyo, V., Torres-Castillo, J.A., Aguirre, C., Phinney, B., Blanco-Labra, A.: Characterization of Two Non-Fetuin-Binding Lectins from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) Seeds with Differential Cytotoxicity on Colon Cancer Cells. J. Glicobiol. 5, 1 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-958X.1000117
Moreno-Celis, U., López-Martínez, F.J., Cervantes-Jiménez, R., Ferríz-Martínez, R.A., Blanco-Labra, A., García-Gasca, T.: Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) Lectins Induce Apoptosis and Cell Arrest in G0/G1 by P53(Ser46) Phosphorylation in Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 25(5), 1021 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051021
Turner, R.H., Liener, I.E.: The use of glutaraldehyde-treated erythrocytes for assaying the agglutinating activity of lectins. Anal Biochem. 68, 651–653 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(75)90663-6
Laemmli, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Bradford, M.A.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Wong, J.H., Wong, C.C., Ng, T.B.: Purification and characterization of a galactose-specific lectin with mitogenic activity from pinto beans. Biochem. Biophys. Acta (BBA). 1760(5), 808–813 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.02.015
Guex, N., Peitsch, M.C., Schwede, T.: Automated comparative protein structure modeling with SWISS-MODEL and Swiss-PdbViewer: A historical perspective. Electrophoresis 30, S162–S173 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.200900140
Bertoni, M., Kiefer, F., Biasini, M., Bordoli, L., Schwede, T.: Modeling protein quaternary structure of homo- and hetero-oligomers beyond binary interactions by homology. Sci. Rep. 7, 10480 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09654-8
Bienert, S., Waterhouse, A., de Beer, T.A.P., Tauriello, G., Studer, G., Bordoli, L., Schwede, T.: The SWISS-MODEL Repository - new features and functionality. Nucleic. Acids Res. 45, D313–D319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1132
Waterhouse, A., Bertoni, M., Bienert, S., Studer, G., Tauriello, G., Gumienny, R., Heer, F.T., de Beer, T.A.P., Rempfer, C., Bordoli, L., Lepore, R., Schwede, T.: SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 46(W1), W296–W303 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
Studer, G., Rempfer, C., Waterhouse, A.M., Gumienny, G., Haas, J., Schwede, T.: QMEANDisCo - distance constraints applied on model quality estimation. Bioinformatics 36(6), 1765–1771 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz828
Martínez-Alarcón, D., Varrot, A., Fitches, E., Gatehouse, J.A., Cao, M., Pyati, P., Blanco-Labra, A., García-Gasca, T.: Recombinant Lectin from Tepary Bean (Phaseolus acutifolius) with Specific Recognition for Cancer-Associated Glycans: Production, Structural Characterization, and Target Identification. Biomolecules 10, 654 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040654
Yang, J., Roy, A., Zhang, Y.: Protein-ligand binding site recognition using complementary binding-specific substructure comparison and sequence profile alignment. Bioinformatics 29, 2588–2595 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt447
Yang, J., Ambrish Roy, A., Zhang, Y.: BioLiP: a semi-manually curated database for biologically relevant ligand-protein interactions. Nucleic. Acids Res. 41, D1096–D1103 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks966
Bohne-Lang, A., von der Lieth, C.-W.: GlyProt: in silico glycosylation of proteins. Nucleic. Acids Res. 33, W214-219 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki385
Emsley, P., Brunger, A.T., Lütteke, T.: Tools to Assist Determination and Validation of Carbohydrate 3D Structure Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 1273, 229–240 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2343-4_17
Böhm, M., Bohne-Lang, A., Frank, M., Loss, A., Rojas-Macias, M. A., Lütteke, T.: Glycosciences.DB: an annotated data collection linking glycomics and proteomics data (2018 update). Nucleic. Acids Res. 47(D1), D1195-D1201 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky994
Loß, A., Bunsmann, P., Bohne, A., Loss, A., Schwarzer, E., Lang, E., von der Lieth, C.W.: SWEET-DB: an attempt to create annotated data collections for carbohydrates. Nucleic. Acids Res. 30, 405–408 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.405
Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Aebi, M., Packer, N.H., Seeberger, P.H., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G., Darvill, A., Kinoshita, T., Prestegard, J.J., Schnaar, R.L., Freeze, H.H., Marth, J.D., Bertozzi, C.R., Etzler, M.E., Frank, M., Vliegenthart, J.F.G., Lütteke, T., Perez, S., Bolton, E., Rudd, P., Paulson, J., Kanehisa, M., Toukach, P., Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F., Dell, A., Narimatsu, H., York, W., Taniguchi, N., Kornfeld, S.: Symbol Nomenclature for Graphical Representations of Glycans. Glycobiology 25(12), 1323–1324 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwv091
Cheng, K., Zhou, Y., Neelamegham, S.: DrawGlycan-SNFG: a robust tool to render glycans and glycopeptides with fragmentation information. Glycobiology 27(3), 200–205 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cww115
DeLano, W.L.: The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System (Version 2.3.4.) DeLano Scientific LLC. San Carlos, CA, USA (2022). https://pymol.org/2/
Alocci, D., Mariethoz, J., Gastaldello, A., Gasteiger, E., Karlsson, N.G., Kolarich, D., Packer, N.H., Lisacek, F.: GlyConnect: glycoproteomics goes visual, interactive and analytical, Software tools and data resources. J. Prot. Research. 18(2), 664–677 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00766
Pérez, S., Sarkar, A., Rivet, A., Breton, C., Imberty, A.: Chapter 18. Glyco3D: A portal for structural glycosciences. In: Lütteke, T., Frank, M. (eds.). Glycoinformatics, Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 1273. pp. 241–258. Springer Science+Business Media, New York (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2343-4_18
Kirschner, K.N., Yongye, A.B., Tschampel, S.M., Daniels, C.R., Foley, B.L., Woods, R.J.J.: GLYCAM06: A generalizable biomolecular force field. Carbohydrates. Comput. Chem. 29, 622–655 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20820
Venkatraman, V., Yang, Y.D., Sael, L., Kihara, D.: Protein-protein docking using region-based 3D Zernike descriptors. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 407 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-407
Adasme, M.F., Linnemann, K.L., Bolz, S.N., Kaiser, F., Salentin, S., Haupt, V.J., Schroeder, M.: PLIP 2021: expanding the scope of the protein–ligand interaction profiler to DNA and RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(W1), W530–W534 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab294
Srinivasan, N., Rufino, S.D., Pepys, M.B., Wood, S., Blundell, T.L.: A superfamily of proteins with the lectin fold. Chemtracts. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 6, 149–164 (1996)
Altschul, S.F., Madden, T.L., Schaffer, A.A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., Lipman, D.J.: Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3389–3402 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., Bealer, K., Madden, T.L.: BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10, 421 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Remmert, M., Biegert, A., Hauser, A., Söding, J.: HHblits: lightning-fast iterative protein sequence searching by HMM-HMM alignment. Nat. Methods. 9, 173–175 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1818
Sharon, N., Lis, H.: How proteins bind carbohydrates: lessons from legume lectins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 6586–6591 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/jf020190s
Wittmann, V., Pieters, R.J.: Bridging lectin binding sites by multivalent carbohydrates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 4492 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60089k
Fu, L., Zhou, C., Yao, S., Yu, J.Y., Liu, B., Bao, J.K.: Plant lectins: Targeting programmed cell death pathways as antitumor agents. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 43, 1442–1449 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2011.07.004
Bellis, S.L., Reis, C.A., Varki, A., Kannagi, R., Stanley, P.: Chapter 47 Glycosylation Changes in Cancer. In: Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Mohnen, D., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., Schnaar, R.L., Seeberger, P.H. (eds.): Essentials of Glycobiology [Internet]. 4th edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York (2022). https://doi.org/10.1101/glycobiology.4e.47
Häuselmann, I., Borsig, L.: Altered tumor-cell glycosylation promotes metastasis. Front. Oncol. 4, 28 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00028
Noda, K., Miyoshi, E., Uozumi, N., Yanagidani, S., Ikeda, Y., Gao, C., Suzuki, K., Yoshihara, H., Yoshikawa, K., Kawano, K., Hayashi, N., Hori, M., Taniguchi, N.: Gene expression of alpha1-6 fucosyltransferase in human hepatoma tissues: A possible implication for increased fucosylation of alpha-fetoprotein. Hepatology 28, 944–952 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.510280408
Funding
Funding was provided by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología [project number CB-2014–01241181].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, purification, and characterization of Tepary bean lectins, data collection and analysis were performed by Iovanna Torres-Arteaga, José Luis Castro-Guillén, Elizabeth Mendiola-Olaya, Teresa García-Gasca, Cesar Aguirre-Mancilla, Alondra L. Ortega-de-Santiago, and Alejandro Blanco-Labra. Carbohydrate identification and analysis were performed by Iovanna Torres-Arteaga, Mariana Barboza, and Carlito B. Lebrilla. Homology modelling, in silico glycosylation, and docking analysis was achieved by José Luis Castro-Guillén. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Iovanna Torres-Arteaga, José Luis Castro-Guillén, Elizabeth Mendiola-Olaya, and Alejandro Blanco-Labra, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
Authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Torres-Arteaga, I., Blanco-Labra, A., Mendiola-Olaya, E. et al. Comparative study, homology modelling and molecular docking with cancer associated glycans of two non-fetuin-binding Tepary bean lectins. Glycoconj J 40, 69–84 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10091-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-022-10091-7