Abstract
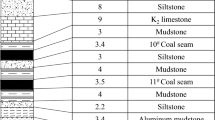
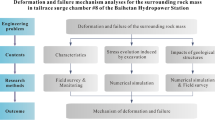
In this paper, the deformation characteristics of underground powerhouse of Wudongde Hydropower Station is obtained by the field observation. Two theoretical models, triangular block and the four-sided simply supported plate and beam models, are put forward to analyze the deformation characteristics of the side wall. As well, the numerical method UDEC software is used to verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis. The above three methods are used to analyze the severe deformation of the upstream side walls, which is near 7# and 8# units after the roof blasting of L3 adit. The deformation of the downstream arch bases near 9# and 10# units is more severe than the upstream side walls near 7# and 8# units. After the construction process was changed, no serious deformation occurred in the follow-up parts of the upstream. Based on that, the following results are shown. First, the steep dip angle of the layer cuts the surrounding rock into the triangular cantilever blocks, which reduces the integrity of the surrounding rock. The serious deformation of the upstream side wall near 7# and 8# units are caused by the weakening of the stability of the triangular cantilever block caused by the explosion of the L3 adit. Second, the maximum deformation of the surrounding rock of the main powerhouse decreases with the increase of the steep dip angle of the layer. Third, the weak material at the arch seat at the downstream of 9#–10# unit leads to the deformation of surrounding rock greater than that of 7# and 8# unit upstream side wall. The study on the deformation mechanism of underground powerhouse in Wudongde Hydropower Station can provide experience reference for projects with similar geological conditions.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang L, Feng D, Nuwen X et al (2017) Failure mechanism and mode of surrounding rock of underground powerhouse at the right bank of Wudongde hydropower station subjected to excavation. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 36(04):781–793
Biao L, Nuwen X, Feng D et al (2017) Microseismic monitoring and large deformation forecasting research during excavation of underground powerhouse at Wudongde hydropower station. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 36(S2):4102–4112
Changgen Y, Tong L, Faquan W (2008) Deformation and stablity analysis of large-scale underground cavity group under complicated geological conditions. J Eng Geol 16(01):84–88
Chonglin J, Jilin F (2017) Deformation and treatment of the underground powerhouse at the right bank of Wudongde hydropower station subjected to excavation. China Water Resour S1:96–99
Cunhui Z, Huibo L, Lingli Z (2015) Special report on stability evaluation and support design optimization of underground powerhouse group surrounding rock of Wuddong hydropower station on Jinsha River. Wuhan Changjiang Surv Plan Des Res Inst
Hu Zhonghua Xu, Nuwen DF et al (2017) Stability analysis of layered and jointed rock masses at rigth bank underground powerhouse of Wudongde hydropower station. Eng Sci Technol 49(S1):103–111
Hu Zhonghua Xu, Nuwen DF et al (2018) Stability and deformation mechanism of bedding rock masses at the underground powerhouse of Wudongde hydropower station. Rock Soil Mech 39(10):3794–3802 (in Chinese)
Jiang S, Wang YF, Tang CA et al (2018) Long-term kinematics and mechanism of a deep-seated slow-moving debris slide near Wudongde hydropower station in Southwest China. J Mt Sci 15(2):364–379
Kai Ai, Xiaoyu H, Yongsong Li (2006) Regression analysis of in-situ stress for Wudongde hydropower station, Jinsha river. Chin J Undergr Space Eng 2(06):930–933
Li YY, Chen JP, Shang YJ (2017a) An RVM-based model for assessing the failure probability of slopes along the jinsha river, close to the wudongde dam site, china. Sustainability 9(321):1–15
Li YY, Wang HG, Chen JP et al (2017b) Debris flow susceptibility assessment in the wudongde dam area, china based on rock engineering system and fuzzy c-means algorithm. Water 9(6699):1–15
Li A, Xu NW, Dai F et al (2018) Stability analysis and failure mechanism of the steeply inclined bedded rock masses surrounding a large underground opening. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 77:45–58
Li B, Xu NW, Dai F et al (2020) Microseismic monitoring and stability analysis for the large-scale underground caverns at the Wudongde hydropower station. Bull Eng Geol Env 79(7):3559–3573
Niu CC, Wang Q, Chen JP et al (2015) Hazard assessment of debris flows in the reservoir region of wudongde hydropower station in china. Sustainability 7(11):15099–15118
Peng L, Cheng W, Yonghong W et al (2014) Analysis of interaction of overall stability of Wudongde super-high arch dam and underground powerhouse. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 33(11):2236–2246
Qi P, Dikai W, Jianhui D et al (2007) Analysis of surrounding rock deformation characteristics in underground powerhouse. Rock Mech Eng 26(12):2583–2587
Qi Xu, Jiliang W, Wenzhong H et al (2019) Correlation between deformation modulus and wave velocity of Wudongde dam foundation rock mass and its application. Chin J Undergr Space Eng 15(05):1434–1441
Qiuxiang H, Jianhui D, Pengyun S et al (2011) Displacement characteristics analysis of surrounding rock in underground powerhouse chambers at Pubugou hydropower station during construction. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 30(S1):3032–3042
Qixiang F, Yifeng W (2010) Stability analysis of layered surrounding rock mass of large underground powerhouse of Xiangjiaba hydropower station. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 29(07):1307–1313
Ruilian Y, Wen L, Tao O et al (2010) Construction control technology for surrounding rock of underground house high side wall of Pengshui hydropower station. Yangtze River 41(19):18–23
Shi MY, Chen JP, Sun DY et al (2015) Hazard assessment of debris flows based on the catastrophe progression method: a case study from the wudongde dam site. Int J Heat Technol 33(4):217–220
Wang GJ, Xie MW, Chai XQ et al (2013) D-InSAR-based landslide location and monitoring at Wudongde hydropower reservoir in China. Environ Earth Sci 69(8):2763–2777
Xiuli D, Zhihong D, Bo L et al (2008) Deformation characteristics and feedback analysis of surrounding rock of large underground powerhouses excavated in steeply dipped sedimentary rock strata. Rock Mech Eng 27(10):2019–2026
Xu WY, Zhang JC, Wang W et al (2014) Investigation into in situ stress fields in the asymmetric V-shaped river valley at the Wudongde dam site, southwest China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 73(2SI):465–477
Zhang W, Li HZ, Chen JP et al (2011) Comprehensive hazard assessment and protection of debris flows along Jinsha river close to the Wudongde dam site in China. Nat Hazards 58(1):459–477
Zhang JC, Xu WY, Wang HL et al (2016) Testing and modeling of the mechanical behavior of dolomite in the Wudongde hydropower plant. Geomech Geoeng 11(4):270–280
Zhao H, Li X, Zhang X (2004) Stability study of surrounding rock mass excavations for the underground powerhouse in Longtan hydropower station. Water Power 30(6):37–40
Zhao CY, Kang Y, Zhang Q, et al (2018) Landslide identification and monitoring along the Jinsha river catchment (wudongde reservoir area), china, using the insar method. Remote Sens
Funding
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (No. 20210302124633) and Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 20212BAB214003), supported by Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (STIP) (No. 2021L570), Supported by the State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for Gas Geology and Gas Control (Henan Polytechnic University) (No. WS2021B07), Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Bridge Structures, Jiangxi Transportation Institute (No. JXBS2020003) and the Luliang Platform base construction project (No.2021GCZX-1–46).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiyong, L., Changchun, H. Deformation Characteristics and Mechanism of Side Walls of Wudongde Hydropower Station. Geotech Geol Eng 40, 4657–4671 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02176-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02176-9