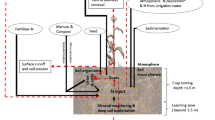
Abstract
An in-depth understanding of nutrient management variability on the regional scale is urgently required due to rapid changes in cropping patterns and farmers’ resource use in peri-urban areas of China. The soil surface nitrogen (N) balances of cereal, orchard and vegetable systems were studied over a 2-year period on smallholder fields in a representative peri-urban area of Beijing. Positive soil surface N balances were obtained across all three cropping systems. The mean annual N surplus of the vegetable system was 1,575 kg N ha−1 year−1, or approximately 3 times the corresponding values in the cereal (531 kg N ha−1 year−1) and orchard systems (519 kg N ha−1 year−1). In the vegetable system, animal manure (1,443 kg N ha−1 year−1 on average) was the major source of N input (65 % of the total N input) and the factor with strongest impact on the N surplus. In the cereal system, however, about 74 % of the total N input originated from mineral fertilizer application which was the major contributor to the N surplus, while in the orchard system, the N surplus was strongly and positively correlated with both mineral fertilizer and animal manure applications. Furthermore, within each cropping system, N fertilization, crop yields and N balances showed large variations among different smallholder fields, especially in orchard and vegetable systems. This study highlights that differences in farming practices within or among cropping systems should be taken into account when calculating nutrient balances and designing strategies of integrated nutrient management on a regional scale.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai YA (2003) Studies on nutrient uptake nitrogen balance in protected-field tomato in Beijing suburb. Dissertation, China Agricultural University (in Chinese)
Brouwer F (1998) Nitrogen balances at farm level as a tool to monitor effects of agri-environmental policy. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 52:303–308. doi:10.1023/A:1009783302364
Cai Z, Qin SW (2006) Crop yield, N use efficiency and environmental impact of a long-term fertilization experiment in fluvo aquic soil in North China. Acta Pedol Sin 43:885–891 (in Chinese)
Cai GX, Chen DL, Ding H, Pacholski A, Fan XH, Zhu ZL (2002) Nitrogen losses from fertilizers applied to maize, wheat and rice in the North China Plain. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 63:187–195. doi:10.1023/A:1021198724250
Cao WZ, Zhu HJ, Chen SL (2007) Impact of urbanization on topsoil nutrient balances—a case study at a provincial scale from Fujian, China. Catena 69:36–43. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2006.04.014
Chen J (2007) Rapid urbanization in China: a real challenge to soil protection and food security. Catena 69:1–15. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2006.04.019
Chen Q, Zhang HY, Zhang XS, Wu JF, Li XL (2002) Characteristics of N uptake and N recommendation for autumn Chinese cabbage in Beijing suburb. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 8:404–408 (in Chinese)
Chen Q, Zhang XS, Zhang HY, Christie P, Li XL, Horlacher D, Liebig HP (2004) Evaluation of current fertilizer practice and soil fertility in vegetable production in the Beijing region. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 69:51–58. doi:10.1023/B:FRES.0000025293.99199.ff
Chen JY, Tang CY, Sakura Y, Yu JJ, Fukushima Y (2005) Nitrate pollution from agriculture in different hydrogeological zones of the regional ground water flow system in the North China Plain. J Hydrol 13:481–492. doi:10.1007/s10040-004-0321-9
Du LF, Zhao TK, Zhang CJ, An ZZ, Wu Q, Liu BC, Peng L, Ma MT (2009) Investigation on nitrate pollution in soils, ground water and vegetables of three typical farmlands in Beijing region. Sci Agric Sin 42:2837–2843 (in Chinese)
FAO (2006) World reference base for soil resources. A framework for international classification, correlation and communication. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
Huang SW, Jin JY, Zuo YB, Yang LP, Cheng MF (2000) Nutrient balance of agricultural soils and their evaluation. Soil Fertil 6:14–19 (in Chinese)
IFA (2007) Medium-term outlook for world agriculture and fertilizer demand. 2006/07–2011/12 IFA annual conference. http://www.fertilizer.org. Accessed 26 Oct 2009
Jiang YM, Zhang HY, Zhang FS (2007) Theories and practices of integrated nutrient resources management. China Agricultural University Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ju XT, Liu XJ, Zhang FS, Roelcke M (2004) Nitrogen fertilization, soil nitrate accumulation, and policy recommendations in several agricultural regions of China. Ambio 33:300–305. doi:10.1579/0044-7447-33.6.300
Ju XT, Zhang FS, Bao XM, Römheld V, Roelcke M (2005) Utilization and management of organic wastes in Chinese agriculture: past, present and perspectives. Sci China Ser C Life Sci 48:965–979 (special issue). doi:10.1007/BF03187135
Ju XT, Kou CL, Zhang FS, Christie P (2006) Nitrogen balance and groundwater nitrate contamination: Comparison among three intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ Pollut 43:117–125. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.11.005
Ju XT, Xing GX, Chen XP, Zhang SL, Zhang LJ, Liu XJ, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu ZL, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:3041–3046. doi:0813417106
Khai NM, Ha PQ, Öborn I (2007) Nutrient flows in small-scale peri-urban vegetable farming systems in Southeast Asia—a case study in Hanoi. Agric Ecosyst Environ 122:192–202. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2007.01.003
Li X (2007) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen and gaseous N loss in winter wheat-summer maize rotation system in North China Plain. Dissertation, Agricultural University of Hebei (in Chinese)
Li YT, Zhen GX, Chen DW, Wang RX, Huang XF, Wei JR, Zhang JL (2007) The distribution of ammonia nitrogen in groundwater of Shunyi and its influencing factors. J Environ Health 24:706–708 (in Chinese)
Liang J (2011) Study on the situation of nitrogen input and output and the potential of fertilizer saving in vegetable system in China. Dissertation, China Agricultural University (in Chinese)
Liu HB, Lei BK, Zhang YG, Zhang WL, Lin B (2001) Investigation and evaluation on nitrate pollution in groundwater of Shunyi District. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci 7:385–390 (in Chinese)
Liu GD, Wu WL, Zhang J (2005) Regional differentiation of non-point source pollution of agriculture-derived nitrate nitrogen in ground water in Northern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 107:211–220. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2004.11.010
Lu RK, Liu HX, Wen DZ, Qin SW, Zhen JY, Wang ZH (1996a) Nutrient cycle and balance research of farmland ecosystem in typical area of China, II. Farmland nutrient income parameter. Chin J Soil Sci 27:151–154 (in Chinese)
Lu RK, Liu HX, Wen DZ, Qin SW, Zhen JY, Wang ZH (1996b) Nutrient cycle and balance research of farmland ecosystem in typical area of China, I. Farmland nutrient outcome parameter. Chin J Soil Sci 27:145–151 (in Chinese)
Ma L (2010) Mechanism and regulatory strategies of nitrogen flow in food chain of China. Dissertation, Agricultural University of Hebei (in Chinese)
Ma L, Wei J, Wang FH, Gao LW, Zhao L, Ma WQ, Zhang FS (2009) Nitrogen flow in food chain among regions based on MFA and model: a case of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. Acta Ecol Sin 29:475–483 (in Chinese)
Ma L, Ma WQ, Velthof GL, Wang FH, Qin W, Zhang FS, Oenema O (2010) Modeling nutrient flows in the food chain of China. J Environ Qual 39:1279–1289. doi:10.2134/jeq2009.0403
NATESC (National Agro-Technical Extension and Service Centre) (1999a) Nutrient content in organic fertilizer of China. China Agricultural Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
NATESC (National Agro-Technical Extension and Service Centre) (1999b) Nutrient resource in organic fertilizer of China. China Agricultural Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
NBSC (National Bureau of Statistics of China) (1999–2010) China statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Oenema O (2004) Governmental policies and measures regulating nitrogen and phosphorus from animal manure in European agriculture. J Anim Sci 82(E-Suppl):E196–E206
Oenema O, Kros H, De VW (2003) Approaches and uncertainties in nutrient budgets: implications for nutrient management and environmental policies. Eur J Agron 20:3–16. doi:10.1016/S1161-0301(03)00067-4
Oenema O, Van LL, Schoumans O (2005) Effects of lowering nitrogen and phosphorus surpluses in agriculture on the quality of groundwater and surface water in The Netherlands. J Hydrol 304:289–301. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2004.07.044
Oenema O, Witzke HP, Klimont Z, Lesschen JP, Velthof GL (2009) Integrated assessment of promising measures to decrease nitrogen losses from agriculture in EU-27. Agric Ecosyst Environ 133:280–288. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2009.04.025
Parris K (1998) Agricultural nutrient balances as agri-environmental indicators: an OECD perspective. Environ Pollut 102(Sl):219–225. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(98)80036-5
SBSD (Statistics Bureau of Shunyi District) (1999–2010) Beijing Shunyi statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Schleef KH, Kleinhanss W (1994) Mineral balance in agriculture in the EU. Institute of Farm Economics, Federal Agricultural Research Centre, Braunschweig
Shen JL, Tang AH, Liu XJ, Fangmeier A, Goulding KTW, Zhang FS (2009) High concentrations and dry deposition of reactive nitrogen species at two sites in the North China Plain. Environ Pollut 157:3106–3113. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.05.016
Sun B, Shen RP, Bouwman AF (2008) Surface N balances in agricultural crop production systems in China for the period 1980–2015. Pedosphere 18:304–314. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(08)60020-X
Velthof GL, Oudendag D, Witzke HP, Asman WAH, Klimont Z, Oenema O (2009) Integrated assessment of nitrogen losses from agriculture in EU-27 using MITERRA-EUROPE. J Environ Qual 38:402–417. doi:10.2134/jeq2008.0108
Wang JQ, Ma WQ, Jiang RF, Zhang FS (2007) Development and application of nitrogen balance model of agro-ecosystem in China. Trans CSAE 28:210–215 (in Chinese)
Wang HJ, Huang B, Shi XZ, Darilek JL, Yu DS, Sun WX, Zhao YC, Chang Q, Öborn I (2008) Major nutrient balances in small-scale vegetable farming systems in peri-urban areas in China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 81:203–218. doi:10.1007/s10705-007-9157-8
Wei J (2008) Influence of urbanization on the nitrogen flow in food consumption system and nitrogen cycling in agro-ecosystem of China. Dissertation, Agricultural University of Hebei (in Chinese)
Zhang WL, Tian ZX, Zhang N, Li XQ (1996) Nitrate pollution of groundwater in northern China. Agric Ecosyst Environ 59:223–231. doi:10.1016/0167-8809(96)01052-3
Zhang WL, Wu SX, Ji HJ, Kolbe H (2004) Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China and the alleviating strategies. I. Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China in early 21 century. Sci Agric Sin 37:1008–1017 (in Chinese)
Zhang XS, Chen Q, He JD, Zhang HY, Li XL (2005) Building of target yield nutrients database for open field vegetable fertilizer recommendations in Beijing suburb. China Veg (Suppl 1):53–57 (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Zheng LX, Liu XJ, Jickells T, Cape JN, Goulding K, Fangmeier A, Zhang FS (2008) Evidence for organic N deposition and its anthropogenic sources in China. Atmos Environ 42:1035–1041. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.12.015
Zhao JY, Yu ZW (2006) Effects of nitrogen rate on nitrogen fertilizer use of winter wheat and content of soil nitrate N under different fertility condition. Acta Ecol Sin 26:815–822 (in Chinese)
Zhu ZL, Chen DL (2002) Nitrogen fertilizer use in China—contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 63:117–127. doi:10.1023/A:1021107026067
Zingore S, Murwira HK, Delve RJ, Giller KE (2007) Influence of nutrient management strategies on variability of soil fertility, crop yields and nutrient balances on smallholder farms in Zimbabwe. Agric Ecosyst Environ 119:112–126. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.06.019
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by two Sino-German projects funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF FKZ: 0330847B; 01RD1017A) together with the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST grant no. 2009DFA32710) and a special fund for agriculture profession of China (201103003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, Y., Gao, Z., Heimann, L. et al. Nitrogen balances of smallholder farms in major cropping systems in a peri-urban area of Beijing, China. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 92, 347–361 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-012-9494-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-012-9494-0