Abstract
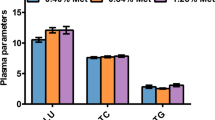
Little information is available on how exogenous bile acids alter lipid metabolism in muscle of fish. In the present study, an 8-week feeding trial were used to investigate the impacts of bile acids on lipid deposition, lipid metabolism, lipidomics, and transcriptomics in muscle of pearl gentian grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × E. lanceolatus♂) fed a high-fat diet (HD). The HD treatment significantly increased the crude lipid content, while bile acids diet (BD) treatment decreased it (p = 0.057). BD treatment significantly decreased triglycerides level and significantly increased phosphatidylcholines, phosphatidylethanolamines, and phosphatidylglycerol levels. The contents of TG (17:0/18:2/18:2), TG (17:1/18:2/22:6), PC (6:0/22:1), PC (9:0/26:1), PC (26:1/6:0), PC (17:2/18:2), PE (16:0/18:1), PE (18:0/17:1), PG (18:0/20:5), PG (18:3/20:5), PG (19:0/16:1), and PG (18:0/18:1) in muscle were well response to dietary lipid level and bile acids supplementation. HD and BD groups induced a variety of adaptive metabolic responses in transcriptomics. HD treatment increased the lipogenesis and decreased lipolysis, whereas BD treatment decreased the lipogenesis and increased lipolysis. Present study revealed the improvement of muscular lipid metabolism and lipid composition in response to bile acids administration in pearl gentian grouper.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The original data of lipidomics (accession ID: MTBLS4808) were deposited in MetaboLights database. The original transcriptomics reads were deposited in NCBI database (accession ID: PRJNA833953).
Abbreviations
- 4ebp :
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E binding protein
- aco :
-
Acyl-CoA oxidase 1
- atgl :
-
Adipose triglyceride lipase
- BD:
-
HD with 0.09% bile acids
- CD:
-
Control diet
- CE:
-
Cholesterol ester
- Cer:
-
Ceramides
- eif4b :
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4B
- HD:
-
High-fat diet
- LPC:
-
Lysophosphatidylcholine
- LPE:
-
Lysophosphatidylethanolamine
- LPG:
-
Lysophosphatidylglycerol
- mtor :
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- mlst8 :
-
Target of rapamycin complex subunit LST8
- PC(O):
-
Alkylphosphatidylcholine
- PC(P):
-
Alkenylphosphatidylcholine
- PE:
-
Phosphatidylethanolamines
- PE(P):
-
Alkenylphosphatidylethanolamine
- PG:
-
Phosphatidylglycerol
- PhytoCer:
-
Phytoceramides
- PI:
-
Phosphatidylinositol
- ppara :
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
- ragab :
-
Ragulator-Rag complex A/B
- ragcd :
-
Ragulator-Rag complex C/D
- raptor :
-
Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR
- s6 :
-
Ribosomal protein S6
- s6k :
-
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase
- srebp1 :
-
Sterol-regulator element-binding protein 1
- tel2 :
-
Telomere length regulation protein
References
An W, Li W, Tan B, Yang Q, Dong X, Liu H, Zhang S, Yang Y, Zhang H (2018) Optimum calcium and phosphorus supplemental levels in diets of large size Litopenaeus vannamei. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 38:8–19
Bai F, Wang X, Niu X, Shen G, Ye J (2021) Lipidomic profiling reveals the reducing lipid accumulation effect of dietary taurine in groupers (Epinephelus coioides). Front Mol Biosci. 8:814318. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.814318
Chao L, Zhe Z, Qing-heng W, Rong-lian H, Yue-wen D, Jun-hui L (2017) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of Pm-ApoL2 gene from. Pinctada fucata martensii Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 37:7
Chao S, Xiaojun L, Haizhen W, Ludi F, Shaozhen L, Zhiwen S, Weiliang H, Chunhong J, Ying W, Fan W, Yunfei G (2019) Lithocholic acid activates mTOR signaling inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress in placenta during intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Life Sci. 218:300–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.12.050
Chen YY, Chang-Ling LI, Huang XH (2015) Effects of microcystin on activities of immune enzymes in the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 3:13–20
Chen Q, Liu H, Tan B, Dong X, Chi S, Yang Q, Zhang S (2016) Effects of dietary cholesterol level on growth performance, blood biochemical parameters and lipid metabolism of juvenile cobia (Rachycentron canadum). Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 36:35–43
Dai Y-J, Jiang G-Z, Yuan X-Y, Liu W-B (2018) High-fat-diet-induced inflammation depresses the appetite of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) through the transcriptional regulation of leptin/mammalian target of rapamycin. Br J Nutr. 120:1422–1431
Ding T, Xu N, Liu Y, Du J, Xiang X, Xu D, Liu Q, Yin Z, Li J, Mai K, Ai Q (2020) Effect of dietary bile acid (BA) on the growth performance, body composition, antioxidant responses and expression of lipid metabolism-related genes of juvenile large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) fed high-lipid diets. Aquaculture. 518:734768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734768
Eisinger K, Krautbauer S, Hebel T, Schmitz G, Aslanidis C, Liebisch G, Buechler C (2014) Lipidomic analysis of the liver from high-fat diet induced obese mice identifies changes in multiple lipid classes. Exp Mol Pathol. 97:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2014.05.002
El-Shenawy AM, Abeer EK, Alsokary ET, Gad DM (2020) Impact of carbohydrate to lipid ratio and bile salts supplementation on performance, body gain and body composition of Nile tilapia fish. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. 8:88–97
Feng H, Yi K, Qian X, Niu X, Sun Y, Ye J (2020a) Growth and metabolic responses of juvenile grouper (Epinephelus coioides) to dietary methionine/cystine ratio at constant sulfur amino acid levels. Aquaculture. 518:734869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734869
Feng K, Lan Y, Zhu X, Li J, Chen T, Huang Q, Ho C-T, Chen Y, Cao Y (2020b) Hepatic lipidomics analysis reveals the antiobesity and cholesterol-lowering effects of tangeretin in high-fat diet-fed rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68:6142–6153. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01778
Gui L, Mai H, Chi S, Zhou W, Li Y, Tan B (2019) Effects of yeast culture on growth performance, hematological parameters, immunity and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 39:30–37
Han S-L, Wang J, Li L-Y, Lu D-L, Chen L-Q, Zhang M-L, Du Z-Y (2020) The regulation of rapamycin on nutrient metabolism in Nile tilapia fed with high-energy diet. Aquaculture. 520:734975
Haug K, Cochrane K, Nainala VC, Williams M, Chang J, Jayaseelan KV, O’Donovan C (2020) MetaboLights: a resource evolving in response to the needs of its scientific community. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:D440–D444. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1019
Hu J, Hong W, Yao KN, Zhu XH, Chen ZY, Ye L (2019) Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates hepatic lipid metabolism in LO2 cells by regulating the AKT/mTOR/SREBP-1 signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 25:1492–1501. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1492
Huang X, Zeng Y, Wang X, Ma X, Li Q, Li N, Su H, Huang W (2016) FXR blocks the growth of liver cancer cells through inhibiting mTOR-s6K pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:351–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.04.106
Ka J, Pak B, Han O, Lee S, Jin SW (2020) Comparison of transcriptomic changes between zebrafish and mice upon high fat diet reveals evolutionary convergence in lipid metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 530:638–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.042
Kong Y, Li M, Xia C, Liu X, Wang G (2021) A novel model construction of lithocholic acid-induced cholestasis and transcriptome analysis in snakehead fish (Channa argus). Aquaculture. 543:737014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737014
Li W, Li L, Liu H, Tan B, Dong X, Yang Q, Chi S, Zhang S, Xie R (2022) Effects of Clostridium butyricum on growth, antioxidant capacity and non-specific immunology of Litopenaeus vannamei fed with concentrated cottonseed protein replacement of fishmeal. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 42:29–37
Liang H, Huang D, Wu Y, Wang C, Zhong W (2013) Effects of temperature and salinity on survival and food intake of grouper hybrid (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂× E. fuscoguttatus♀). Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 33:22–26
Liao ZB, Sun B, Zhang QG, Jia LL, Wei YL, Liang MQ, Xu HG (2020) Dietary bile acids regulate the hepatic lipid homeostasis in tiger puffer fed normal or high-lipid diets. Aquaculture. 519:734935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.734935
Liu Y, Jiao JG, Gao S, Ning LJ, McHele Limbu S, Qiao F, Chen LQ, Zhang ML, Du ZY (2019) Dietary oils modify lipid molecules and nutritional value of fillet in Nile tilapia: a deep lipidomics analysis. Food Chem. 277:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.020
Liu D, Gu Y, Pang Q, Yu H, Zhang J (2021a) Dietary betaine regulates the synthesis of fatty acids through mTOR signaling in the muscle of zebrafish. J. Funct. Foods 85:104610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2021.104610
Liu H, Li L, Stephen A, Tang Z, Fan W, Tan B, Dong X, Chi S, Yang Q, Zhang S (2021b) Effects of dietary yeast culture supplementation on growth, intestinal morphology, immunity, and disease resistance in Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatu♂. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 41:1–11
Masoodi M, Gastaldelli A, Hyotylainen T, Arretxe E, Alonso C, Gaggini M, Brosnan J, Anstee QM, Millet O, Ortiz P, Mato JM, Dufour JF, Oresic M (2021) Metabolomics and lipidomics in NAFLD: biomarkers and non-invasive diagnostic tests. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:835–856. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-021-00502-9
Nam M, Choi MS, Jung S, Jung Y, Choi JY, Ryu DH, Hwang GS (2015) Lipidomic profiling of liver tissue from obesity-prone and obesity-resistant mice fed a high fat diet. Sci Rep. 5:16984. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16984
Nie Q, Xing M, Chen H, Hu J, Nie S (2019) Metabolomics and lipidomics profiling reveals hypocholesterolemic and hypolipidemic effects of arabinoxylan on type 2 diabetic rats. J Agric Food Chem. 67:10614–10623. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03430
Pan J, Han Y, Huo Y, Su P, Jiang Z (2016) Effects of dietary alginate oligosaccharide on intestinal morphology, activities of digestive enzymes and apparent digestibility of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus l). Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 36:39–44
Peng XR, Feng L, Jiang WD, Wu P, Liu Y, Jiang J, Kuang SY, Tang L, Zhou XQ (2019) Supplementation exogenous bile acid improved growth and intestinal immune function associated with NF-kappaB and TOR signalling pathways in on-growing grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): enhancement the effect of protein-sparing by dietary lipid. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 92:552–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.06.047
Petersen MC, Shulman GI (2017) Roles of diacylglycerols and ceramides in hepatic insulin resistance. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 38:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.04.004
Press CA (2021) Fisheries and Fishery Administration Bureau of The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, National Fishery Technology Promotion Station, China Society of Fisheries. In: China Fishery Statistics Yearbook 2020. China Agriculture Press
Qiang J, Tao F, Bao W, He J, Li X, Chen J, Xu P (2021) Responses of functional miRNA-mRNA regulatory modules to a high-fat diet in the liver of hybrid yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco x P. vachelli). Genomics. 113:1207–1220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.12.007
Rahimnejad S, Bang IC, Park J-Y, Sade A, Choi J, Lee S-M (2015) Effects of dietary protein and lipid levels on growth performance, feed utilization and body composition of juvenile hybrid grouper, Epinephelus fuscoguttatus×E. lanceolatus. Aquaculture. 446:283–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.05.019
Shao-hong M, Yu-chong H, Ji-chang J, Shuang-hu C (2019) Cloning and prokaryotic expression of PspF gene from Vibrio harveyi. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 39:1–7
Wang G, Sun Y, Niu F, He F, Mo W, Zhu X, Cao J, Huang Y (2017) Effects of exogenous enzyme supplementation on digestive enzyme activity, apparent digestibility and fecal nitrogen and phosphorus content of juvenile yellow catfish. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 37:19–25
Wang A, Yang Q, Tan B, Xiao W, Jia J, Dong X, Zhang S (2018) Effects of enzymolytic soybean meal on growth performance, serum biochemical indices, non-specific immunity and disease resistance of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 38:14–21
Wu Y, Li R, Shen G, Huang F, Yang Q, Tan B, Chi S (2021a) Effects of dietary small peptides on growth, antioxidant capacity, nonspecific immunity and ingut microflora structure of Litopenaeus vannamei. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 41:1–9
Wu Z, Wu B, Lv X, Xie Y, Xu S, Ma C, Xu J, Tu X, Wei F, Chen H (2021b) Serumal lipidomics reveals the anti-inflammatory effect of flax lignans and sinapic acid in high-fat-diet-fed mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 69:9111–9123. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07291
Xie J, Qiu D, Liu C, Zhu W, Zeng L (2013) Effcets of Vibrio alginolyticus peptidoglycan on astaxanthin level, immune indicators and protection in Litopenaeus vannamei. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University 33:50–55
Xiong F, Wu S, Qin L, Shi M, Li W, Zou H, Li M, Wang G (2019) Transcriptome analysis of grass carp provides insights into disease-related genes and novel regulation pattern of bile acid feedback in response to lithocholic acid. Aquaculture. 500:613–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.10.015
Xiu-ping F, Xiao-ming Q, Chao-hua Z, Jian-ping C, Qian-feng Z (2018) Nutritional and volatile flavor components of dorsal and ventral muscle from hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀ × E. lanceolatus♂). Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 38:8
Xu J, He G, Chen L, Xie S, Chi S, Zhang S, Cao J, Tan B (2022a) Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 (TGR5) signaling pathways improved the hepatic lipid metabolism in hybrid grouper. Aquac. Res. 22:100997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100997
Xu J, Li X, Yao X, Xie S, Chi S, Zhang S, Cao J, Tan B (2022b) Protective effects of bile acids against hepatic lipid accumulation in hybrid grouper fed a high-lipid diet. Front Nutr. 9:813249. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.813249
Xu J, Xie S, Chi S, Zhang S, Cao J, Tan B (2022c) Protective effects of taurocholic acid on the excessive hepatic lipid accumulation via regulation of bile acids metabolism in grouper. Food & Function. 13:3050–3062. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo04085e
Xu J, Xie S, Chi S, Zhang S, Cao J, Tan B (2022d) Short-term dietary antibiotics altered the intestinal microbiota and improved the lipid metabolism in hybrid grouper fed medium and high-lipid diets. Aquaculture. 547:737453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737453
Yin P, Xie S, Zhuang Z, He X, Tang X, Tian L, Liu Y, Niu J (2021) Dietary supplementation of bile acid attenuate adverse effects of high-fat diet on growth performance, antioxidant ability, lipid accumulation and intestinal health in juvenile largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). Aquaculture. 531:735864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735864
Yu K, Huang K, Jiang S, Tang X, Huang X, Sun L, Pang L, Mo C (2021) Protective function on liver and proteomic analysis of the improvement mechanism of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture. 531:735977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735977
Yuan Y, Wang X, Jin M, Jiao L, Sun P, Betancor MB, Tocher DR, Zhou Q (2020) Modification of nutritional values and flavor qualities of muscle of swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus): application of a dietary lipid nutrition strategy. Food Chem. 308:125607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125607
Yuan Y, Xu F, Jin M, Wang X, Hu X, Zhao M, Cheng X, Luo J, Jiao L, Betancor MB, Tocher DR, Zhou Q (2021) Untargeted lipidomics reveals metabolic responses to different dietary n-3 PUFA in juvenile swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus). Food Chem. 354:129570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129570
Zhang D, Lu K, Jiang G, Liu W, Dong Z, Tian H, Li X (2015) A global transcriptional analysis of Megalobrama amblycephala revealing the molecular determinants of diet-induced hepatic steatosis. Gene. 570:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.06.025
Zhang W, Tan B, Pang A, Deng J, Yang Q, Zhang H (2022) Screening of potential biomarkers for soybean meal induced enteritis in pearl gentian grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀× Epinephelus lanceolatus♂). Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 42:1–12
Zhi-xin W, Hai-ying L, Xiao-dong D, Rong-lian H, Yue-wen D, Qing-heng W, Yu J (2013) Cloning and express characters of HSP60 gene from Pinctada martensii. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 33:14–23
Zhou JS, Chen HJ, Ji H, Shi XC, Li XX, Chen LQ, Du ZY, Yu HB (2018) Effect of dietary bile acids on growth, body composition, lipid metabolism and microbiota in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquacult Nutr. 24:802–813. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12609
Zhu W, Qiu D, Gan Z, Lu Y, Jian J (2015) Antivirus effects of Vibrio alginolyticus peptidoglycan on Litopenaeus vannamei against white spot syndrome virus. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University. 35:40–46
Zou C, Su N, Wu J, Xu M, Sun Z, Liu Q, Chen L, Zhou Y, Wang A, Ye C (2019) Dietary Radix Bupleuri extracts improves hepatic lipid accumulation and immune response of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatusmale symbol x Epinephelus fuscoguttatusfemale symbol). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 88:496–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.02.052
Muta K, Saito K, Kemmochi Y, Masuyama T, Kobayashi A, Saito Y, Sugai S (2022) Phosphatidylcholine (18: 0/20: 4), a potential biomarker to predict ethionamide-induced hepatic steatosis in rats. J Appl Toxicol.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Suzhou BioNovoGene for providing technical help.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFD0900200), the China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-47), the Science and technology project of Zhanjiang (2020A05003), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2018A030313154&2020A1515011129), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31772864).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Jia Xu, Menglin Shi, and Liutong Chen; methodology: Jia Xu, Menglin Shi, Liutong Chen, and Shiwei Xie; formal analysis and investigation: Jia Xu, Shuyan Chi, and Shuang Zhang; writing—original draft preparation: Jia Xu, Shuyan Chi, and Junming Cao; writing—review and editing: Jia Xu, Shuang Zhang, Junming Cao, and Shiwei Xie; funding acquisition: Beiping Tan and Shiwei Xie; resources: Junming Cao, Beiping Tan, and Shiwei Xie; supervision: Junming Cao, Beiping Tan, and Shiwei Xie. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Ethical and Welfare Committee of Guangdong Ocean University (Guangdong, China), processing ID: GDOU-AEWC-20180063.
Consent for publication and consent to participate
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1:
Fig. S1 Quality control and lipid composition of lipidomics in groups. A: In PCA plot, the quality control sample is red and the tested sample is green. A smaller difference in quality control sample means a more stable system. B: the composition and numbers of lipid classes (n = 6). PC: phosphatidylcholines, PE: phosphatidylethanolamines, TG: triglycerides, DG: diacylglycerols, SM: sphingomyelins, CE: cholesterol ester, Cer: ceramides, LPC: lysophosphatidylcholine, LPE: lysophosphatidylethanolamine, LPG: lysophosphatidylglycerol, PC(O): alkylphosphatidylcholine, PC(P): alkenylphosphatidylcholine, PE: phosphatidylethanolamines, PE(P): alkenylphosphatidylethanolamine, PG: phosphatidylglycerol, PhytoCer: phytoceramides, PI: phosphatidylinositol. Fig. S2 PCA analysis of composition of SCM in TG (A), PC (B), PE (C) and PG (D) classes of muscle in CD, HD and BD groups (n = 6). TG: triglycerides, PC: phosphatidylcholines, PE: phosphatidylethanolamines, PG: phosphatidylglycerol. SCM: significantly changed metabolites. CD: control diet; HD: high-fat diet; BD: HD with 0.09% bile acids. Fig. S3 Heatmap analysis of composition of significantly changed metabolites in TG classes of muscle in CD, HD and BD groups (n = 6). TG: triglycerides. CD: control diet; HD: high-fat diet; BD: HD with 0.09% bile acids. Fig. S4 Heatmap analysis of composition of significantly changed metabolites in PC classes of muscle in CD, HD and BD groups (n = 6). PC: phosphatidylcholines. CD: control diet; HD: high-fat diet; BD: HD with 0.09% bile acids. Fig. S5 Heatmap analysis of composition of significantly changed metabolites in PE classes of muscle in CD, HD and BD groups (n = 6). PE: phosphatidylethanolamines. CD: control diet; HD: high-fat diet; BD: HD with 0.09% bile acids. Fig. S6 Heatmap analysis of composition of significantly changed metabolites in PG classes of muscle in CD, HD and BD groups (n = 6). PG: phosphatidylglycerol. CD: control diet; HD: high-fat diet; BD: HD with 0.09% bile acids. Fig. S7 KEGG enrichment pathways (top 20) of global DEGs profile of muscle in CD, HD and BD groups (n = 3). A: According to the p value, the results of DEGs profile in CD and HD groups. B: According to the p value, the results of DEGs profile in HD and BD groups. C: According to the FDR, the results of DEGs profile in CD and HD groups. D: According to the FDR, the results of DEGs profile in HD and BD groups. In C and D panels, the X-axis represents the Rich Factor, and Y-axis represents the name of a metabolic pathway. The Rich Factor is the ratio of a to b. a: the amount of DEGs in one pathway; b: the amount of all genes in this pathway. DEGs: differentially expressed genes; CD: control diet; HD: high-fat diet; BD: HD with 0.09% bile acids. Fig. S8 The WB original image of PPARA. Fig. S9 The WB original image of GAPDH. Fig. S10 The WB original image of SREBP1. Fig. S11 The WB original image of P-PPARA. (DOCX 3133 kb)
ESM 2:
Table S1 Composition and concentration of nutrients in diets (XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 3:
Table S2 Composition of fatty acids in diets (XLSX 12 kb)
ESM 4:
Table S3 Primers designed for qPCR (XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 5:
Table S4 The identified lipid species and composition in muscle of pearl gentian grouper in three groups (XLSX 465 kb)
ESM 6:
Table S5 The composition of lipid calsses in three groups (XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 7:
Table S6 Significantly changed metabolites in TG classes (XLSX 30 kb)
ESM 8:
Table S7 Significantly changed metabolites in PC classes (XLSX 59 kb)
ESM 9:
Table S8 Significantly changed metabolites in PE classes (XLSX 26 kb)
ESM 10:
Table S9 Significantly changed metabolites in PG classes (XLSX 17 kb)
ESM 11:
Table S10 Summary statistics of the muscle transcriptomics assembly of pearl gentian grouper (XLSX 9 kb)
ESM 12:
Table S11 Differentially expressed genes in all groups (XLSX 2351 kb)
ESM 13:
Table S12 KEGG enrichment pathways in three groups (XLSX 9 kb)
ESM 14:
Table S13 The differentially expressed genes related to lipid metabolism and amino acid metabolism in three groups (XLSX 10 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Shi, M., Chen, L. et al. Muscular lipidomics and transcriptomics reveal the effects of bile acids on lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-fed grouper. Fish Physiol Biochem 50, 127–143 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-023-01176-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-023-01176-7