Abstract
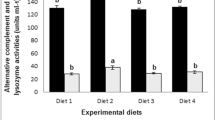
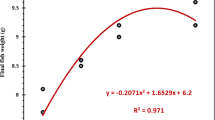
A 30-day feeding trial was conducted to investigate the effects of supplemental ferulic acid (FA) on survival, growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of the large yellow croaker larvae (initial weight: 2.58 ± 0.30 mg). Four isonitrogenous and isolipidic micro-diets were formulated with graded levels of FA (0, 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg) and fed to the experimental larvae seven times daily. Results showed that larvae fed the diet with 40 mg/kg FA had significantly higher survival rate, while the specific growth rate was higher in larvae fed diets with 40 and 80 mg/kg FA than the control group (P < 0.05). Activities of trypsin in pancreatic segments (PS) and intestinal segments, lipase in PS and alkaline phosphatase in brush border membrane were significantly increased by supplementation of FA compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Supplementation of FA significantly increased activities of total superoxide dismutase and catalase, and reduced the malondialdehyde content compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, activities of lysozyme, total nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide content were significantly improved by supplemental FA in diets. Furthermore, supplementation of 40 mg/kg FA reduced the triglyceride content in larval visceral mass probably through down-regulating expression of lipogenesis-related genes (scd1, fas and dgat2) and up-regulating expression of lipid catabolism-related genes (aco, cpt-1 and hl). In conclusion, appropriate supplementation of 40 mg/kg FA could improve the survival and growth performance of large yellow croaker larvae through increasing digestive function, antioxidant capacity and promoting lipid metabolism.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmadifar E, Moghadam MS, Dawood MAO, Hoseinifar SH (2019) Lactobacillus fermentum and/or ferulic acid improved the immune responses, antioxidative defence and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) fingerlings. Fish Shellfish Immunol 94:916–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.10.019
Ai QH, Zhao JZ, Mai KS, Xu W, Tan BP, Ma HM, Liufu ZG (2008) Optimal dietary lipid level for large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquac Nutr 14:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2007.00557.x
AOAC (2003) Official methods of analysis of the association of analytical chemistry, 15th edn. Arlington, VA, USA., AOAC
Birnie-Gauvin K, Costantini D, Cooke SJ, Cooke SJ, Willmore WG (2017) A comparative and evolutionary approach to oxidative stress in fish: a review. Fish Fish 18:928–942. https://doi.org/10.1111/faf.12215
Cai ZN, Mai KS, Ai QH (2017) Regulation of hepatic lipid deposition by phospholipid in large yellow croaker. Br J Nutr 118:999–1009. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451700294X
Cahu C, Infante J (1994) Early weaning of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae with a compound diet: effect on digestive enzymes. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A: Mol Integr Physiol 109(2):213–222
Carobbio S, Hagen RM, Lelliott CJ, Tan CY, Virtue S, Oresic M, Griffin JL, Sethi JK, Lopez M, Vidal-Puig A (2013) Adaptive changes of the Insig1/SREBP1/ SCD1 set point help adipose tissue to cope with increased storage demands of obesity. Diabetes 62:3697–3708. https://doi.org/10.2337/db12-1748
Cedo L, Santos D, Roglans N, Julve J, Pallarès V, Rivas-Urbina A, Llorente-Cortes V, Laguna JC, Blanco-Vacal F, Escolà-Gil JC (2017) Human hepatic lipase overexpression in mice induces hepatic steatosis and obesity through promoting hepatic lipogenesis and white adipose tissue lipolysis and fatty acid uptake. PLoS ONE 12:e0189834. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189834
Chaudhary A, Choudhary S, Sharma U, Vig AP, Singh B, Arora S (2018) Purple head broccoli (Brassica oleracea L var italica Plenck), a functional food crop for antioxidant and anticancer potential. J Food Sci Technol (New Delhi, India) 55:1806–1815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3095-0
Chaudhary A, Jaswal VS, Choudhary S, Sonika SA, Beniwal V, Tuli HS, Sharma S (2019) Ferulic acid: a promising therapeutic phytochemical and recent patents advances. Recent Pat Inflammation Allergy Drug Discovery 13:115–123. https://doi.org/10.2174/1872213X13666190621125048
Crane RK, Boge G, Rigal A (1979) Isolation of brush border membranes in vesicular form from the intestinal spiral valve of the small dogfish (Scyliorhinus canicula). Biochim Biophys Acta 554:264–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(79)90024-5
Dawood MAO, Metwally AS, El-Sharawy ME, Ghozlan AM, Abdel-Latif HMR, Van Doan H, Ali MAM (2020) The influences of ferulic acid on the growth performance, haemato-immunological responses, and immune-related genes of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to heat stress. Aquaculture 525:735320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735320
Del RD, Stewart AJ, Pellegrini N (2005) A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 15:316–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2005.05.003
Feng SH, Cai ZN, Zuo RT, Mai KS, Ai QH (2017) Effects of dietary phospholipids on growth performance and expression of key genes involved in phosphatidylcholine metabolism in larval and juvenile large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquaculture 469:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.12.002
Galina J, Yin G, Ardo L, Jeney Z (2009) The use of immunostimulating herbs in fish: an overview of research. Fish Physiol Biochem 35:669–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-009-9304-z
Giri SS, Sukumaran V, Park SC (2019) Effects of bioactive substance from turmeric on growth, skin mucosal immunity and antioxidant factors in common carp Cyprinus Carpio. Fish Shellfish Immunol 92:612–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.06.053
Guo XX, Zeng Z, Qian YZ, Qiu J, Wang K, Wang Y, Ji BP, Zhou F (2019) Wheat flour, enriched with γ-oryzanol, phytosterol, and ferulic acid, alleviates lipid and glucose metabolism in high-fat-fructose-fed rats. Nutrients 11:1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071697
Habte-Tsion HM (2020) A review on fish immuno-nutritional response to indispensable amino acids T in relation to TOR NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways trends and prospects. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 241:110389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2019.110389
Harris CA, Haas JT, Streeper RS, Stone SJ, Kumari M, Yang K, Han XL, Brownell N, Gross RW, Zechner R, Farese RV (2011) DGAT enzymes are required for triacylglycerol synthesis and lipid droplets in adipocytes. J Lipid Res 52:657–667. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M013003
Holm H, Hanssen LE, Krogdahl A, Florholmen J (1988) High and low inhibitor soybean meals affect human duodenal proteinase activity differently in vivo comparison with bovine serum albumin. J Nutr 118:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/118.4.515
Huang WX, Yao CW, Liu YT, Xu N, Yin ZY, Xu WX, Miao YQ, Mai KS, Ai QH (2020) Dietary allicin improved the survival and growth of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae via promoting intestinal development, alleviating inflammation and enhancing appetite. Front Physiol 11:587674. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.587674
Huang WX, Yao CW, Liu YT, Xu N, Yin ZY, Xu WX, Miao YQ, Mai KS, Ai QH (2021) Effects of dietary eucommia ulmoides leaf extract (ELE) on growth performance, expression of feeding-related genes, activities of digestive enzymes, antioxidant capacity, immunity and cytokines expression of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Br J Nutr 1:29. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521004621
Imentai A, Rašković B, Steinbach C, Rahimnejad S, Yanes-Roca C, Policar T (2020) Effects of first feeding regime on growth performance, survival rate and development of digestive system in pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) larvae. Aquaculture 529:735636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735636
Izquierdo MS, Socorro J, Arantzamendi L, Hernandez-Cruz CM (2000) Recent advances in lipid nutrition in fish larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 22:97–107. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007810506259
Ji M, Yao LY, Zhang JH (2013) Continuous monitoring assay for leucine aminopeptidase in serum and its clinical value. Guide China Med 319:7. https://doi.org/10.15912/j.cnki.gocm.2013.07.116
Katayama S, Ohno F, Mitani T, Akiyama H, Nakamura S (2017) Rutinosylated ferulic acid attenuates food allergic response and colitis by upregulating regulatory T cells in mouse models. J Agric Food Chem 65:10730–10737. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03933
Khoa TND, Hayasaka O, Matsui H, Waqalevu V, Honda A, Nakajima K, Yamashita H, Ishikawa M, Shiozaki K, Kotani T (2021) Changes in early digestive tract morphology, enzyme expression and activity of Kawakawa tuna (Euthynnus affinis). Aquaculture 530:735–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735935
Koh EJ, Kim KJ, Seo YJ, Choi J, Lee BY (2017) Modulation of HO-1 by ferulic acid attenuates adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 Cells. Molecules 22:745. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22050745
Li LY, Stasiak M, Li L, Xie BZ, Fu YM, Gidzinski D, Dixon MK, Liu H (2016) Rearing Tenebrio molitor in BLSS: dietary fiber affects larval growth, development, and respiration characteristics. Acta Astronaut 118:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.10.003
Liu YT, Miao YQ, Xu N, Ding T, Cui K, Chen QC, Zhang JZ, Fang W, Mai KS, Ai QH (2020) Effects of dietary Astragalus polysaccharides (APS) on survival, growth performance, activities of digestive enzyme, antioxidant responses and intestinal development of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquaculture 517:734752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734752
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ma YC, Chen K, Lv L, Wu SY, Guo ZJ (2019) Ferulic acid ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and modulates the gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet fed ApoE mice. Biomed Pharmacother 113:108753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108753
Macías-Cruz U, Perard S, Vicente R, Alvarez FD, Torrentera-Olivera NG, Gonzalez-Rios H, Soto-Navarro SA, Rojo R, Meza-Herrera CA, Avendano-Reyes L (2014) Effects of free ferulic acid on productive performance, blood metabolites, and carcass characteristics of feedlot finishing ewe lambs. J Anim Sci 92:5762–5768. https://doi.org/10.2527/jas.2014-8208
Management rule of laboratory animals (Chinese Order No. 676 of the State Council, revised 1 March 2017). http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2017/content_5219148.htm
Maoka T, Tanimoto F, Sano M, Tsurukawa K, Tsuno T, Tsujiwaki S, Ishimaru K, Takii K (2008) Effects of dietary supplementation of ferulic acid and gamma-oryzanol on integument color and suppression of oxidative stress in cultured red sea bream (Pagrus major). J Oleo Sci 57:133–137. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.57.133
Maroux S, Louvard D, Barath J (1973) The aminopeptidase from hog intestinal brush border. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Enzymol 321:282–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2744(73)90083-1
Martínez-Álvarez RM, Morales AE, Sanz A (2005) Antioxidant defenses in fish: biotic and abiotic factors. Rev.: Methods Technol. Fish Biol Fish 15:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-005-7846-4
Middleton E, Kandaswami C, Theoharides TC (2000) The effects of plants flavonoids on mammalian cells: implication for inflammation, heart diseases and cancer. Pharmacol Rev 52:673–751. https://doi.org/10.1006/phrs.2000.0734
Nootash S, Sheikhzadeh N, Baradaran B, Oushani AK, Moghadam MRM, Nofouzi K, Monfaredan A, Aghebati L, Zare F, Shabanzadeh S (2013) Green tea (Camellia sinensis) administration induces expression of immune relevant genes and biochemical parameters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:1916–1923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.09.030
Pena-Torres EF, Davila-Ramirez JL, Pena-Ramos EA, Valenzuela-Melendres M, Pinelli-Saavedra A, Avendano-Reyes L, Gonzalez-Rios H (2021) Effects of dietary ferulic acid on growth performance, carcass traits and meat quality of heifers. J Sci Food Agric 101:548–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10666
Punitha SMJ, Babu MM, Sivaram V, Shankar VS, Dhas SA, Mahesh TC, Immanuel G, Citarasu T (2008) Immunostimulating influence of herbal biomedicines on nonspecific immunity in Grouper Epinephelus tauvina juvenile against Vibrio harveyi infection. Aquacult Int 16:511–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-007-9162-6
Reverter M, Bontemps N, Lecchini D, Banaigs B, Sasal P (2014) Use of plant extracts in fish aquaculture as an alternative to chemotherapy: current status and future perspectives. Aquaculture 433:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.05.048
Sadar SS, Vyawahare NS, Bodhankar SL (2016) Ferulic acid ameliorates TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis through modulation of cytokines, oxidative stress, iNOs, COX-2, and apoptosis in laboratory rats. Excil J 15:482–499. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2016-393
Saeij JPJ, Van Muiswinkel WB, Groeneveld A, Wiegertjes GF (2002) Immune modulation by fish kinetoplastid parasites: a role for nitric oxide. Parasitology 124:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182001008915
Sarker U, Oba S (2020) Phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities in selected drought-tolerant leafy vegetable amaranth. Sci Rep 10:18287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71727-y
Saurabh S, Sahoo PK (2008) Lysozyme: an important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquacult Res 39:223–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2007.01883.x
Silva ED, Batista R (2017) Ferulic acid and naturally occurring compounds bearing a feruloyl moiety: a review on their structures, occurrence, and potential health benefits. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 16:580–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12266
Soobrattee MA, Neergheen VS, Luximon-Ramma A, Aruoma OI, Bahorun T (2005) Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: mechanism and actions. Mutat Res 579:200–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.03.023
Valadez-García KM, Avendaño-Reyes L, Díaz-Molina R, Mellado M, Meza-Herrera CA, Correa-Calderon A, Macias-Cruz U (2021) Free ferulic acid supplementation of heat-stressed hair ewe lambs: oxidative status, feedlot performance, carcass traits and meat quality. Meat Sci 173:108395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108395
Wang JL, Meng XL, Lu RH, Wu C, Luo YT, Yan X, Li XJ, Kong XH, Nie GX (2015) Effects of Rehmannia glutinosa on growth performance, immunological parameters and disease resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquaculture 435:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.10.004
Wang WW, Pan Y, Wang L, Zhou H, Song G, Wang YW, Liu JX, Li AK (2019) Optimal dietary ferulic acid for suppressing the obesity-related disorders in leptin-deficient obese C57BL/6J -ob/ob mice. J Agric Food Chem 67:4250–4258. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06760
Wang YX, Chen XL, Huang ZQ, Chen DW, Yu B, Yu J, Chen H, He J, Luo YH, Zheng P (2020) Dietary ferulic acid supplementation improves antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism in weaned piglets. Nutrients 12:3811. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123811
Wen Y, Ushi H (2017) Ferulic acid promotes hypertrophic growth of fast skeletal muscle in zebrafish model. Nutrients 9:1066. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101066
Wiegertjes GF, Wentzel AS, Spaink HP, Elks PM, Fink IR (2016) Polarization of immune responses in fish: the macrophages first point of view. Mol Immunol 69:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2015.09.026
Xu H, Zhang DL, Lv CH, Luo HY, Wang ZY (2015) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of scd1 gene from large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea under cold stress. Gene 568:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.05.027
Xu WX, Liu YT, Huang WX, Yao CW, Yin ZY, Mai KS, Ai QH (2022) Effects of dietary supplementation of astaxanthin (Ast) on growth performance, activities of digestive enzymes, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquacult Res 00:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.15933
Yan J, Liao K, Wang TJ, Mai KS, Xu W, Ai QH (2015) Dietary lipid levels influence lipid deposition in the liver of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) by regulating lipoprotein receptors, fatty acid uptake and triacylglycerol synthesis and catabolism at the transcriptional level. PLoS ONE 10:6-e0129937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0129937
Yao CW, Huang WX, Liu YT, Yin ZY, Xu N, He YL, Wu XF, Mai KS, Ai QH (2020) Effects of dietary silymarin (SM) supplementation on growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism gene expression in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Aquacult Nutr 26:2225–2234. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13159
Yu LJ, Wu F, Jiang M, Yang CG, Liu W, Tian J, Lu X, Wen H (2016) Ferulic acid: a natural compound as an efficient feed additive for GIFT (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquacult Nutr 24:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12529
Yu LJ, Wen H, Jiang M, Wu F, Tian J, Lu X, Xiao JR, Liu W (2020) Effects of ferulic acid on growth performance, immunity and antioxidant status in genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed oxidized fish oil. Aquacult Nutr 26:1431–1442. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13087
Yu LJ, Wen H, Jiang M, Wu F, Tian J, Lu X, Xiao JR, Liu W (2020) Effects of ferulic acid on intestinal enzyme activities, morphology, microbiome composition of genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed oxidized fish oil. Aquaculture 528:735543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735543
Yuan XY, Wang CC, Huang YY, Dai YJ, Desouky HE (2020) A comparative study on intestinal morphology and function of normal and injured intestines of Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var Jian). Aquaculture 528:735496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735496
Zemheri-Navruz F, Acar U, Yılmaz S (2019) Dietary supplementation of olive leaf extract increases haematological, serum biochemical parameters and immune related genes expression level in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) juveniles. Fish Shellfish Immunol 89:672–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2019.04.037
Zhao JZ, Ai QH, Mai KS, Zuo RT, Luo YW (2013) Effects of dietary phospholipids on survival, growth, digestive enzymes and stress resistance of large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) larvae. Aquaculture 410:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.05.018
Zheng XX, Cheng Y, Chen YW, Yue YS, Li YC, Xia SZ, Li Y, Deng HH, Zhang JL, Cao YJ (2019) Ferulic acid improves depressive-like behavior in prenatally-stressed offspring rats via anti-inflammatory activity and HPA axis. Int J Mol Sci 20:493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030493
Zhou ZK, Shi TX, Hou J, Li M (2020) Ferulic acid alleviates atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in mice via its potent anti-inflammatory effect. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 42:156–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923973.2020.1733012
Zhu LJ, Zhang ZS, Xia NN, Zhang WF, Wei YL, Huang JS, Ren ZJ, Meng FL, Yang L (2020) Anti-arthritic activity of ferulic acid in complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis in rats: JAK2 inhibition. Inflammopharmacology 28:463–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00642-0
Zuo RT, Ai QH, Mai KS, Xu W (2013) Effects of conjugated linoleic acid on growth, non-specific immunity, antioxidant capacity, lipid deposition and related gene expression in juvenile large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea) fed soyabean oilbased diets. Br J Nutr 110:1220–1232. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114513000378
Funding
This research was supported by the earmarked fund for CARS-47, Leading Talent of Technological Innovation of Ten-Thousands Talents Program (2018–29), and the Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong (CN) (2019JZZY010814).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors’ contributions were as follows: Qinghui Ai and Kangsen Mai formulated the research question; Wenxuan Xu, Wenxing Huang, Chuanwei Yao, Yongtao Liu and Zhaoyang Yin designed the study and conducted the research; Wenxuan Xu analysed the data, interpreted the findings and wrote the article. All authors revised the article. We appreciated Wencong Lai, Xiufei Cao, Ye Gong, and Dan Xu for their help in revising the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments in this study were in accordance with the Management Rule of Laboratory Animals (Chinese Order No. 676 of the State Council, revised 1 March 2017). The authors agree to collaborate and publish this article.
Consent for publication
We will transfer the copyright of the article to editorial office for publishing.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Huang, W., Yao, C. et al. Effects of supplemental ferulic acid (FA) on survival, growth performance, digestive enzyme activities, antioxidant capacity and lipid metabolism of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) larvae. Fish Physiol Biochem 48, 1635–1648 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01120-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-022-01120-1