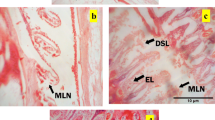
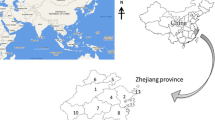
Abstract
Ibuprofen as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug can be detected in the aquatic environments all over the world. This study evaluated the effects of ibuprofen on the immune parameters of juvenile grass carp at the concentration in real environments which were determined by detecting its concentrations in the surface water of local rivers. The concentration of ibuprofen ranged from 13.2 to 95.5 ng/L with a mean value of 47.9 ng/L in the surface water of local rivers detected by solid-phase extraction followed by LC-MS/MS analysis. Accordingly, juvenile grass carp were exposed to 4.8, 48.0 and 480.0 ng/L of ibuprofen for 14 days. The serum lysozyme activity of these fish decreased, while the serum creatinine levels were not affected after the exposure. Moreover, the mRNA expression of interleukin 6 in the skin and interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha in the gills was enhanced by this exposure. These results collectively suggest that ibuprofen at environmentally relevant concentration can affect the immune parameters of juvenile grass carp, providing an insight into the possibility of this contaminant to modify the immunostatus of fish.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bendz D, Paxeus NA, Ginn TR, Loge FJ (2005) Occurrence and fate of pharmaceutically active compounds in the environment, a case study: Hoje River in Sweden. J Hazard Mater 122:195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.03.012
Bhandari K, Venables B (2011) Ibuprofen bioconcentration and prostaglandin E2 levels in the bluntnose minnow Pimephales notatus. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 153:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2010.11.004
Brozinski JM, Lahti M, Oikari A, Kronberg L (2013a) Identification and dose dependency of ibuprofen biliary metabolites in rainbow trout. Chemosphere 93:1789–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.018
Brozinski JM, Lahti M, Meierjohann A, Oikari A, Kronberg L (2013b) The anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, naproxen and ibuprofen are found in the bile of wild fish caught downstream of a wastewater treatment plant. Environ Sci Technol 47:342–348. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303013j
Buser H-R, Poiger T, Müller MD (1999) Occurrence and environmental behavior of the chiral pharmaceutical drug ibuprofen in surface waters and in wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 33:2529–2535
Cleuvers M (2004) Mixture toxicity of the anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetylsalicylic acid. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0147-6513(03)00141-6
Constantine LA, Green JW, Schneider SZ (2020) Ibuprofen: fish short-term reproduction assay with zebrafish (Danio rerio) based on an extended OECD 229 protocol. Environ Toxicol Chem 39:1534–1545. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4742
Ershad M, Ameer MA, Vearrier D (2020) Ibuprofen toxicity. StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL)
Gonzalez-Mira A, Torreblanca A, Hontoria F, Navarro JC, Mananos E, Varo I (2018) Effects of ibuprofen and carbamazepine on the ion transport system and fatty acid metabolism of temperature conditioned juveniles of Solea senegalensis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:693–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.11.023
Goyal A, Daneshpajouhnejad P, Hashmi MF, Bashir K (2021) Acute kidney injury. StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL)
Gutierrez-Noya VM, Gomez-Olivan LM, Ramirez-Montero MDC, Islas-Flores H, Galar-Martinez M, Dublan-Garcia O, Romero R (2020) Ibuprofen at environmentally relevant concentrations alters embryonic development, induces teratogenesis and oxidative stress in Cyprinus carpio. Sci Total Environ 710:136327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136327
Han S, Choi K, Kim J, Ji K, Kim S, Ahn B, Yun J, Choi K, Khim JS, Zhang X, Giesy JP (2010) Endocrine disruption and consequences of chronic exposure to ibuprofen in Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes) and freshwater cladocerans Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa. Aquat Toxicol 98:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.02.013
Haneberg B, Sornes S, Bakke O, Solberg CO (1987) Inhibition of in vitro lysozyme release from human granulocytes and monocytes by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C 95:149–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00023.x
Islas-Flores H, Gomez-Olivan LM, Galar-Martinez M, Garcia-Medina S, Neri-Cruz N, Dublan-Garcia O (2014) Effect of ibuprofen exposure on blood, gill, liver, and brain on common carp (Cyprinus carpio) using oxidative stress biomarkers. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:5157–5166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2477-0
Jones HS, Trollope HT, Hutchinson TH, Panter GH, Chipman JK (2012) Metabolism of ibuprofen in zebrafish larvae. Xenobiotica 42:1069–1075
Kim SD, Cho J, Kim IS, Vanderford BJ, Snyder SA (2007) Occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and endocrine disruptors in South Korean surface, drinking, and waste waters. Water Res 41:1013–1021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.034
Kunkel SL, Spengler M, May MA, Spengler R, Larrick J, Remick D (1988) Prostaglandin E2 regulates macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor gene expression. J Biol Chem 263:5380–5384
Lee YJ, Chuang YC (2010) Ibuprofen augments pro-inflammatory cytokine release in a mouse model of Vibrio vulnificus infection. Microbiol Immunol 54:542–550. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2010.00249.x
Ma R, Qu H, Wang B, Wang F, Yu Y, Yu G (2019) Simultaneous enantiomeric analysis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environment by chiral LC-MS/MS: a pilot study in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.122
Mackay D, Fraser A (2000) Kenneth Mellanby Review Award. Bioaccumulation of persistent organic chemicals: mechanisms and models. Environ Pollut 110:375–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(00)00162-7
Magnadottir B (2006) Innate immunity of fish (overview). Fish Shellfish Immunol 20:137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2004.09.006
Mathias FT, Fockink DH, Disner GR, Prodocimo V, Ribas JLC, Ramos LP, Cestari MM, Silva de Assis HC (2018) Effects of low concentrations of ibuprofen on freshwater fish Rhamdia quelen. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 59:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2018.03.008
Milan M, Pauletto M, Patarnello T, Bargelloni L, Marin MG, Matozzo V (2013) Gene transcription and biomarker responses in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum after exposure to ibuprofen. Aquat Toxicol 126:17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.10.007
Morthorst JE, Lister A, Bjerregaard P, Van Der Kraak G (2013) Ibuprofen reduces zebrafish PGE(2) levels but steroid hormone levels and reproductive parameters are not affected. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 157:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2012.12.001
Nallani GC, Paulos PM, Constantine LA, Venables BJ, Huggett DB (2011) Bioconcentration of ibuprofen in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) and channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Chemosphere 84:1371–1377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.008
Narra MR, Rajender K, Reddy RR, Murty US, Begum G (2017) Insecticides induced stress response and recuperation in fish: biomarkers in blood and tissues related to oxidative damage. Chemosphere 168:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.10.066
Neal TM, Vissers MC, Winterbourn CC (1987) Inhibition by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs of superoxide production and granule enzyme release by polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated with immune complexes or formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. Biochem Pharmacol 36:2511–2517. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(87)90524-7
Nielsen VG, Webster RO (1987) Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions by ibuprofen. Immunopharmacology 13:61–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/0162-3109(87)90027-0
Patel A, Panter GH, Trollope HT, Glennon YC, Owen SF, Sumpter JP, Rand-Weaver M (2016) Testing the "read-across hypothesis" by investigating the effects of ibuprofen on fish. Chemosphere 163:592–600
Santos LH, Araujo AN, Fachini A, Pena A, Delerue-Matos C, Montenegro MC (2010) Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 175:45–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.100
Saravanan M, Devi KU, Malarvizhi A, Ramesh M (2012) Effects of Ibuprofen on hematological, biochemical and enzymological parameters of blood in an Indian major carp, Cirrhinus mrigala. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 34:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2012.02.005
Scales WE, Chensue SW, Otterness I, Kunkel SL (1989) Regulation of monokine gene expression: prostaglandin E2 suppresses tumor necrosis factor but not interleukin-1 alpha or beta-mRNA and cell-associated bioactivity. J Leukoc Biol 45:416–421
Sebok A, Vasanits-Zsigrai A, Palko G, Zaray G, Molnar-Perl I (2008) Identification and quantification of ibuprofen, naproxen, ketoprofen and diclofenac present in waste-waters, as their trimethylsilyl derivatives, by gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Talanta 76:642–650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.04.008
Song Y, Chai T, Yin Z, Zhang X, Zhang W, Qian Y, Qiu J (2018) Stereoselective effects of ibuprofen in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) using UPLC-TOF/MS-based metabolomics. Environ Pollut 241:730–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.009
Stevens DL (1995) Could nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) enhance the progression of bacterial infections to toxic shock syndrome? Clin Infect Dis 21:977–980. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinids/21.4.977
Tixier C, Singer HP, Oellers S, Müller SR (2003) Occurrence and fate of carbamazepine, clofibric acid, diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, and naproxen in surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 37:1061–1068
Wang L, Ying GG, Zhao JL, Yang XB, Chen F, Tao R, Liu S, Zhou LJ (2010) Occurrence and risk assessment of acidic pharmaceuticals in the Yellow River, Hai River and Liao River of north China. Sci Total Environ 408:3139–3147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.04.047
Wang X, Guo Y, Wen C, Lv M, Gan N, Zhou H, Zhang A, Yang K (2019) Molecular characterization of grass carp interleukin-6 receptor and the agonistic activity of its soluble form in head kidney leucocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol 86:1072–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.12.031
Weigel S, Kuhlmann J, Huhnerfuss H (2002) Drugs and personal care products as ubiquitous pollutants: occurrence and distribution of clofibric acid, caffeine and DEET in the North Sea. Sci Total Environ 295:131–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(02)00064-5
Wen C, Gan N, Zeng T, Lv M, Zhang N, Zhou H, Zhang A, Wang X (2020) Regulation of Il-10 gene expression by Il-6 via Stat3 in grass carp head kidney leucocytes. Gene 741:144579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.144579
Xia L, Zheng L, Zhou JL (2017) Effects of ibuprofen, diclofenac and paracetamol on hatch and motor behavior in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 182:416–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.054
Yang X, Xu X, Wei X, Wan J, Zhang Y (2019) Biomarker effects in Carassius auratus exposure to ofloxacin, sulfamethoxazole and ibuprofen. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16091628
Zhang K, Yuan G, Werdich AA, Zhao Y (2020a) Ibuprofen and diclofenac impair the cardiovascular development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) at low concentrations. Environ Pollut 258:113613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113613
Zhang W, Song Y, Chai T, Liao G, Zhang L, Jia Q, Qian Y, Qiu J (2020b) Lipidomics perturbations in the brain of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) after exposure to chiral ibuprofen. Sci Total Environ 713:136565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136565
Zhao JL, Ying GG, Liu YS, Chen F, Yang JF, Wang L, Yang XB, Stauber JL, Warne MS (2010) Occurrence and a screening-level risk assessment of human pharmaceuticals in the Pearl River system, South China. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:1377–1384. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.161
Funding
This work was funded by the grants from the Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2019JDRC0007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.Z.: investigation, methodology, visualization, X.L.: investigation, formal analysis, L.P.: investigation, X.Z.: investigation, L.Z.: investigation, X.M.: investigation, H.Z.: writing—review & editing, J.L.: methodology, investigation, X.W.: project administration, writing—original draft, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The animal experiments performed were allowed by the ethics committee of the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, under permit number 1061420210305007.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary table 1A
HPLC parameters for quantification of ibuprofen (PNG 183 kb)
Supplementary table 1B
MS parameters for quantification of ibuprofen (PNG 45 kb)
Supplementary table 2
Primer used in the present study (PNG 154 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, N., Liu, X., Pan, L. et al. Evaluation of ibuprofen contamination in local urban rivers and its effects on immune parameters of juvenile grass carp. Fish Physiol Biochem 47, 1405–1413 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-00987-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-00987-w