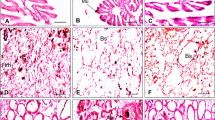
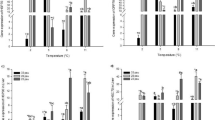
Abstract
In aquaculture, fish species may experience stressful episodes caused by poor farming conditions. The exponential increase of global aquaculture has raised the number of research studies aimed at demonstrating the sensitivity of aquatic animals in confined environments. The development of a real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry methods were investigated to evaluate the presence, localization, and quantity of biomarkers of oxidative stress in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). In particular, stress tests such as manipulation and temperature changes were conducted through molecular methods to identify the expression level of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) in stressed animals compared with a control group. The immunohistochemical technique was also applied to locate and study the trends-levels of nitrotyrosine (NT), heat shock protein 70 (HSP70), malondialdehyde (MDA), and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) in different tissues from stressed animals and control group. The presence of the rodlet cell (RCs) was evaluated by histology in both a control and stressed group. Our results show that the real-time PCR method developed is specific for the evaluated target gene and that manipulation and temperature increase are strong stressors for animals. Relative quantification data revealed a gene expression increase of HSP70 in the stressed group of animals compared to the control group. The antibodies used for the immunohistochemical staining were efficient, and it was possible to appreciate the increase of immunoprecipitates in European sea bass either manipulated or stressed by temperature increase. The present study can be a starting point to allow the quantification of HSP70 and the identification of other stress biomarkers in D. labrax.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HSP70:
-
heat shock protein 70
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- HNE:
-
4-hydroxy-2-nonenal
- NT:
-
nitrotyrosine
- RCs:
-
rodlet cells
- PUFAs:
-
polyunsaturated fatty acids
References
Aldini G, Dalle-Donne I, Facino RM, Milzani A, Carini M (2007) Intervention strategies to inhibit protein carbonylation by lipoxidation-derived reactive carbonyls. Med Res Rev 27(6):817–868. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.20073
Bancroft J, Gamble M (2002) Theory and practice of histological techniques. C. Livingstone, New York
Boscolo Papo M, Bertotto D, Quaglio F, Vascellari M, Pascoli F, Negrato E, Binato G, Radaelli G (2014) Histopathology and stress biomarkers in the clam Venerupis philippinarum from the Venice Lagoon (Italy). Fish Shellfish Immunol 39(1):42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.04.016
Conover WJ, Johnson ME, Johnson MM (1981) A comparative study of tests for homogeneity of variances, with applications to the outer continental shelf bidding data. Technometrics 23(4):351–361 https://www.jstor.org/stable/1268225
Decreto legislativo 26/14 (2014) Decreto Legislativo per l’attuazione Della Direttiva 2010/63/UE Sulla Protezione Degli Animali Utilizzati a Fini Scientifici. 1–24
Dezfuli BS, Simoni E, Giari L, Manera M (2006) Effects of experimental terbuthylazine exposure on the cells of Dicentrarchus labrax (L.). Chemosphere 64(10):1684–1694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.023
Feder ME, Hofmann GE (2002) Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu Rev Physiol 61:243–282. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.61.1.243
Giari L, Simoni E, Manera M, Dezfuli BS (2008) Histo-cytological responses of Dicentrarchus labrax (L.) following mercury exposure. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70(3):400–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.08.013
Gornati R, Papis E, Rimoldi S, Terova G, Saroglia M, Bernardini G (2004) Rearing density influences the expression of stress-related genes in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.). Gene 341:111–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2004.06.020
Grutter A (2002) The effects of capture, handling, confinement and ectoparasite load on plasma levels of cortisol, glucose and lactate in the coral reef fish Hemigymnus melapterus. J Fish Biol 57(2):391–401. https://doi.org/10.1006/jfbi.2000.1312
Hightower LE (1990) Stress proteins in biology and medicine. Richard I. Morimoto, Alfred Tissieres, and Costa Georgopoulos, Eds. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 1990. x, 450 Pp., Illus. $97. Cold Spring Harbor Monograph Series 19. Science 249(4968):572–574 https://doi.org/10.1126/science.249.4968.572-a
Iger Y, Abraham M (1997) Rodlet cells in the epidermis of fish exposed to stressors. Tissue Cell 29(4):431–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-8166(97)80029-8
Ischiropoulos H, Zhu L, Chen J, Tsai M, Martin JC, Smith CD, Beckman JS (1992) Peroxynitrite-mediated tyrosine nitration catalyzed by superoxide dismutase. Arch Biochem Biophys 298(2):431–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(92)90431-U
Iwama GK, Thomas PT, Forsyth RB, Mathilakth MV (1998) Heat shock protein expression in fish. Rev Fish Biol Fish 8:35–56. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008812500650
Kenneth J, Livak A, Thomas D (2001) Schmittgen analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Manera M, Dezfuli BS (2004) Rodlet cells in teleosts: a new insight into their nature and functions. J Fish Biol 65(3):597–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0022-1112.2004.00511.x
Mosca F, Ciulli S, Volpatti D, Romano N, Volpe E, Bulfon C, Massimini M, Caccia E, Galeotti M, Tiscar PG (2014) Defensive response of european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) against Listonella anguillarum or Photobacterium damselae subsp. piscicida experimental infection. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 162(3–4):83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetimm.2014.10.002
Neuhäuser M (2011) Wilcoxon--Mann--Whitney test. International Encyclopedia of Statistical Science 1656–1658. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04898-2_615
Noga EJ (1996) Fish disease: diagnosis and treatment. Mosby-Year Book, Saint Louis, MO
Pascoli F, Negrato E, Di Giancamillo A, Bertotto D, Domeneghini C, Simontacchi C, Mutinelli F, Radaelli G (2011) Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in Zosterisessor ophiocephalus from the Venice lagoon, Italy. Aquat Toxicol 101(3–4):512–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.12.003
Patruno M, Maccatrozzo L, Funkenstein B, Radaelli G (2006) Cloning and expression of insulin-like growth factors i and ii in the shi drum (Umbrina cirrosa). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 144(2):137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2006.02.003
Poltronieri C, Maccatrozzo L, Simontacchi C, Bertotto D, Funkenstein B, Patruno M, Radaelli G (2007) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis and immunohistochemical localization of HSP70 in sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax exposed to transport stress. Eur J Histochem 51(2):125–136. https://doi.org/10.4081/1134
Reite OB (2005) The rodlet cells of teleostean fish: their potential role in host defence in relation to the role of mast cells/eosinophilic granule cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol 19(3):253–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.01.002
Reite OB, Evensen Ø (2006) Inflammatory cells of teleostean fish: a review focusing on mast cells/eosinophilic granule cells and rodlet cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol 20(2):192–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.01.012
Schreck CB, Ola BL, Davis MW (1997) Behavioral responses to stress. Fish Stress Health Aquac:145–170
Slaninova A, Smutna M, Modra H, Svobodova Z (2009) A review : oxidative stress in fish induced by pesticides. Neuro Endocrinol Letters 30(Suppl 1):2–12
Vazzana M, Cammarata M, Cooper EL, Parrinello N (2002) Confinement stress in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) depresses peritoneal leukocyte cytotoxicity. Aquaculture 210(1–4):231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0044-8486(01)00818-3
Welch WJ (1993) How cells respond to stress. Sci Am 268(5):56–62
Zapata-Vìvenes E, Nusetti O (2007) Protection of glycolytic enzymes by metallothioneins from oxidative damage in the digestive gland of green lipped mussel perna viridis. J Shellfish Res 26(2):335–344. https://doi.org/10.2983/0730-8000(2007)26[335:POGEBM]2.0.CO;2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiocchi, E., Civettini, M., Carbonara, P. et al. Development of molecular and histological methods to evaluate stress oxidative biomarkers in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Fish Physiol Biochem 46, 1577–1588 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00811-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-020-00811-x