Abstract
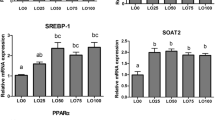
A feeding trial was conducted to evaluate the effect of linseed oil (LO) on growth, plasma biochemistry, hepatic metabolism enzymes, and antioxidant capacity of juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Four isonitrogenous (crude protein, 45%) and isoenergetic (gross energy, 18 MJ/kg) diets were formulated by replacing 0 (the control), 33.3%, 66.7%, and 100% of fish oil with linseed oil. Each diet was fed to three replicate groups of fish (initial body weight, 22.02 ± 0.61 g) for 8 weeks. The results indicated that fish fed diet with 100% LO substitution level had lower weight gain (WG), specific growth rate (SGR), and protein efficiency ratio (PER) than the other groups (P < 0.05), while feed conversion ratio (FCR) was higher compared to the other groups (P < 0.05). Feed intake (FI) and hepatosomatic index (HSI) of 66.7% LO substitution level were significantly lower than the control groups (P < 0.05). Glycogen, lipid, and non-esterified fatty acid content in the liver decreased significantly with increasing dietary LO levels (P < 0.05). Moreover, the replacement of fish oil (FO) with LO could significantly reduce the content of triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) and the activity of alanine amiotransferase (ALT) in plasma of M. salmoides (P < 0.05). There were significant differences in hepatic metabolism enzymes in fish fed diets with different dietary LO levels. Adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)–activated protein kinase (AMPK) and peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR-α) activities in liver significantly increased with increasing dietary LO level (P < 0.05). In addition, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) activities in the liver significantly increased with decreasing dietary LO level (P < 0.05). Both the lowest superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities in the liver were recorded in the control group (P < 0.05). Moreover, nitric oxide content, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) activities in the liver significantly increased with increasing dietary LO level, while malondialdehyde (MDA) content significantly reduced. These findings demonstrated that LO can improve liver function and antioxidant ability of M. salmoides. In addition, replacing partial FO with LO cannot affect growth performance, but all substitutions inhibit growth performance of M. salmoides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akrami R, Gharaei A, Mansour MR, Galeshi A (2015) Effects of dietary onion (Allium cepa) powder on growth, innate immune response and hemato-biochemical parameters of beluga (Huso huso linnaeus, 1754) juvenile. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45(2):828–834
Akrami A, Nikaein F, Babajafari S, Faghih S, Yarmohammadi H (2018) Comparison of the effects of flaxseed oil and sunflower seed oil consumption on serum glucose, lipid profile, blood pressure, and lipid peroxidation in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Clin Lipidol 12:70–77
Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) (2005) Official methods of analysis, 18th edn. Gaithersburg
Benítez-Dorta V, Caballero MJ, Izquierdo M, Manchado M, Infante C, Zamorano MJ, Montero D (2013) Total substitution of fish oil by vegetable oils in Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) diets: effects on fish performance, biochemical composition, and expression of some glucocorticoid receptor-related gene. Fish Physiol Biochem 39:335–349
Brauge C, Medale F, Corraze G (1994) Effect of dietary carbohydrate levels on growth, body composition and glycaemia in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, reared in seawater. Aquaculture 123(1–2):109–120
Chakrabarti R, Srivastava PK, Verma N, Sharma JG (2014) Effect of seeds of Achyranthes aspera, on the immune responses and expression of some immune-related genes in carp Catla catla. Fish Shellfish Immunol 41(1):64–69
Corino C, Rossi R, Cannata S, Ratti S (2014) Effect of dietary linseed on the nutritional value and quality of pork and pork products: systematic review and meta-analysis. Meat Sci 98:679–688
Du ZY (2014) Causes of fatty liver in farmed fish: a review and new perspectives. J Fish China 38(9):1628–1638 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Francis DS, Turchini GM, Jones PL, De Silva SS (2006) Effects of dietary oil source on growth and fillet fatty acid composition of Murray cod, Maccullochella peelii peelii. Aquaculture 253:547–556
Geurden I, Cuvier A, Gondouin E, Olsen RE, Ruohonen K, Kaushik S, Boujard T (2005) Rainbow trout can discriminate between feeds with different oil sources. Physiol Behav 85(2):107–114
Goyal A, Sharma V, Upadhyay N, Gill S, Sihag M (2014) Flax and flaxseed oil: an ancient medicine & modern functional food. J Food Sci Technol 51(9):1633–1653
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1985) Free radical in biology and medicine. Clarendon Pr 318(6044):332–332
Izquierdo MS, Montero D, Robaina L, Caballero R, Rosenlund G, Ginés R (2005) Alterations in fillet fatty acid profile and flesh quality in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) fed vegetable oils for a long term period. Recovery of fatty acid profiles by fish oil feeding. Aquaculture 250:431–444
Jiang Y, Zhao PF, Lin SM, Tang RJ, Chen YJ, Luo L (2018) Partial substitution of soybean meal with fermented soybean residue in diets for juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Aquac Nutr 24:1213–1222
Li FJ, Lin X, Lin SM, Chen WY, Guan Y (2016) Effects of dietary fish oil substitution with linseed oil on growth, muscle fatty acid and metabolism of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac Nutr 22(3):499–508
Liu C, Wang J, Ma Z, Li T, Xing W, Jiang N (2018) Effects of totally replacing dietary fish oil by linseed oil or soybean oil on juvenile hybrid sturgeon, acipenser baeri brandt ♀ × a. schrenckii brandt. Aquac Nutr 24(1):184–194
Menoyo D, López-Bote CJ, Obach A, Bautista JM (2005) Effect of dietary fish oil substitution with linseed oil on the performance, tissue fatty acid profile, metabolism, and oxidative stability of Atlantic salmon. J Anim Sci 83(12):2853–2862
Nayak M, Saha A, Pradhan A, Samanta M, Giri SS (2017) Dietary fish oil replacement by linseed oil: effect on growth, nutrient utilization, tissue fatty acid composition and desaturase gene expression in silver barb (Puntius gonionotus) fingerlings. Comp Biochem Physiol B 205:1–12
Nutrient Requirements of Fish Shrimp (NRC) (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp
Oakhill JS, Steel R, Chen ZP, Scott JW, Ling N, Tam S (2011) AMPK is a direct adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. Science 332(6036):1433–1435
Pan Y, Mao SH, Guan Y, Lin X, Lin SM, Gao QP, Luo L (2012) Effects of different lipid sources in diets on growth performance, lipid metabolism and antioxidant ability of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Chin J Anim Nutr 24(07):1368–1375 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Peng M, Xu W, Tan P, Du J, Mai K, Zhou H (2017) Effect of dietary fatty acid composition on growth, fatty acids composition and hepatic lipid metabolism in juvenile turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) fed diets with required n3 LC-PUFAs. Aquaculture 479:591–600
Piedecausa MA, Mazon MJ, Garcia GB, Hernandez MD (2007) Effects of total replacement of fish oil by vegetable oils in the diets of sharpsnout seabream (Diplodus puntazzo). Aquaculture 263(1):211–219
Rakhshandehroo M, Knoch B, Müller MR, Kersten S (2010) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes. PPAR Res 2010(4):393–416
Rosenlund G, Obach A, Sandberg MG, Standal H, Tveit K (2015) Effect of alternative lipid sources on long-term growth performance and quality of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquac Res 32(s1):323–328
Tang CC, Huang HP, Lee YJ, Tang YH, Wang CJ (2013) Hepatoprotective effect of mulberry water extracts on ethanol-induced liver injury via anti-inflammation and inhibition of lipogenesis in C57BL/6J mice. Food Chem Toxicol 62:786–796
Turchini GM, Francis DS (2009) Fatty acid metabolism (desaturation, elongation and β-oxidation) in rainbow trout fed fish oil- or linseed oil-based diets. Br J Nutr 102:69–81
Turchini GM, Torstensen BE, Ng WK (2009) Fish oil replacement in finfish nutrition. Rev Aquac 1:10–57
Vestergren ALS, Trattner S, Pan J, Johnsson P, Kamal-Eldin A, Eva B (2013) The effect of combining linseed oil and sesamin on the fatty acid composition in white muscle and on expression of lipid-related genes in white muscle and liver of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquac Int 21(4):843–859
Wei BH, Yang ZG, Cheng YX, Wang JY, Zhou JY (2018) Effects of the complete replacement of fish oil with linseed oil on growth, fatty acid composition, and protein expression in the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Proteome Sci 16:6
Yang W, Fu J, Yu M, Huang QD, Wang D, Xu JQ, Deng QC, Yao P, Huang FH, Liu LG (2012) Effects of flaxseed oil on anti-oxidative system and membrane deformation of human peripheral blood erythrocytes in high glucose level. Lipids Health Dis 11:88
Yao CL, Ji PF, Wang ZY, Li FH, Xiang JH (2010) Molecular cloning and expression of NOS in shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol 28(3):0–460
Yildiz M, Eroldogan T, Ofori-Mensah S, Engin K, Baltacı M (2017) The effects of fish oil replacement by vegetable oils on growth performance and fatty acid profile of rainbow trout: re-feeding with fish oil finishing diet improved the fatty acid composition. Aquaculture 488:123–133
Zhu HY, Li Q, Wang HW, Zhu TT, Qin JG, Li EC, Chen LQ (2016) Growth, fatty acid composition and lipid deposition of Russian sturgeon (Acipenser gueldenstaedtii ) fed different lipid sources. Aquac Res 48(9):5126–5132
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. L. Zhou and Y. Jiang for their help during the experiment. Thanks are also due to M. M. Mou and M. Q. Song for helping with the chemical analysis.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31672659), the Science and Technology Council of Chongqing, China (No.cstc2015jcyjA80027), Chongqing Ecological Fishery Technology System (2018-2019), China, and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2018D007), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, CM., Zhao, H., Zhai, XL. et al. Linseed oil can decrease liver fat deposition and improve antioxidant ability of juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Fish Physiol Biochem 45, 1513–1521 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00636-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00636-3