Abstract
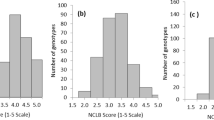
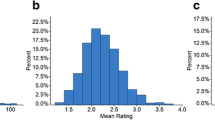
The Northern corn leaf blight (NCLB) caused by the fungus Exserohilum turcicum is one of the oldest and most important leaf diseases of corn, occurring widely in Brazil and in the main producing regions of the world. The pathogen causes the devastating leaf disease that results in considerable losses in corn yield. The objective of this research was to identify genomic regions or associated SNPs involved in resistance to NCLB in a panel of field corn, popcorn, and sweet corn inbred lines. A genome-wide association study was carried out with phenotypic data collected in two environments on a panel of 320 maize inbred lines. The experiments were conducted in a 20 × 16 alpha-lattice experimental design, with three replications. The severity of NCLB was evaluated 25 days after the end of flowering. A set of 350, 643 high-quality polymorphic SNPs obtained using genotyping by sequencing were used, 14 of which were associated with E. turcicum resistance. The variation explained by each SNP ranged from 0.5 to 5.7%. In the first growing season, five SNPs explained 16.2% of the phenotypic variance, while during the second growing season, nine SNPs explained 16.5% of the total phenotypic variance. The candidate gene models GRMZM2G042920, GRMZM2G041774 and GRMZM2G056564 were the most promising, given that they were previously identified playing an important role in the response of corn to defense, abiotic and biotic stress through signaling mechanisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Agroceres (1996) Guia agroceres de sanidade. Sementes Agroceres, São Paulo, SP, p 72
Amaral AT, Ribeiro RM, Santos PHD, Poltronieri TPS, Vivas JMS et al (2016) Genetic variability affecting Exserohilum turcicum resistance in popcorn lines grown under high and low phosphorus conditions. Genet Mol Res 15(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.4238/gmr15049399
Bentolila S, Guitton C, Bouvet N, Sailland A, Nykaza S, Freyssinet G (1991) Identification of an RFLP marker tightly linked to the Ht1 gene in maize. Theor Appl Genet 82:393–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588588
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y et al (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23(19):2633–2635. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm308
Carson ML, Van Dyke CG (1994) Effect of light and temperature on expression of partial resistance of maize to Exserohilum turcicum. Plant Dis 78(5):519–522. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-78-0519
Chen D-H, Ronald PC (1999) A rapid DNA minipreparation method suitable for AFLP and other PCR applications. Plant Mol Biol Report 17(1):53–57
Chen G, Wang X, Long S, Jaqueth J, Li B et al (2016) Mapping of QTL conferring resistance to northern corn leaf blight using high-density SNPs in maize. Mol Breed 36(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0421-3
Coan MMD, Senhorinho HJC, Pinto RJB, Scapim CA, Tessmann DJ et al (2018) Genome-wide association study of resistance to ear rot by Fusarium verticillioides in a tropical field maize and popcorn core collection. Crop Sci 58(2):564–578. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2017.05.0322
Coelho AM (2006) Nutrição e adubação do milho. Sete Lagoas: EMBRAPA Milho e Sorgo (Circular técnica, 78)
de Souza Camacho LR, Coan MMD, Scapim CA, Barth Pinto RJ, Tessmann DJ et al (2019) A genome-wide association study for partial resistance to southern corn rust in tropical maize. Plant Breed. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12718
Ding J, Ali F, Chen G, Li H, Mahuku G et al (2015) Genome-wide association mapping reveals novel sources of resistance to northern corn leaf blight in maize. BMC Plant Biol 15: 206. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-015-0589-z
do Kurosawa RNF, Vivas M, do Junior ATA, Ribeiro RM, Miranda SB et al (2018) Popcorn germplasm resistance to fungal diseases caused by Exserohilum turcicum and bipolaris maydis. Bragantia 77(1):36–47. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4499.2017035
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K et al (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6(5):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019379
Fancelli AL, Dourado Neto D (2000) Produção de milho. Agropecuária, Guaíba, p 360
Galiano-Carneiro AL, Kessel B, Presterl T, Miedaner T (2021) Intercontinental trials reveal stable QTL for northern corn leaf blight resistance in Europe and in Brazil. Theor Appl Genet 134:63–79
Glaubitz JC, Casstevens TM, Lu F, Harriman J, Elshire RJ et al (2014) TASSEL-GBS: a high capacity genotyping by sequencing analysis pipeline. PLoS ONE 9(2):e90346. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090346
Holland JB (2007) Genetic architecture of complex traits in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2007.01.003
Ishfaq A, Dar ZA, Lone AA, Ali G, Gazal A, Hamid B, Mohiddin FA (2014) Disease reaction studies of maize (Zea mays L.) against turcicum leaf blight involving indigenously identified cytosterile source. African J Microbiol Res 8(27):2592–3259
Jamann TM, Luo X, Morales L, Kolkman JM, Chung CL et al (2016) A remorin gene is implicated in quantitative disease resistance in maize. Theor Appl Genet 129(3):591–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-015-2650-6
Jiao Y, Peluso P, Shi J, Liang T, Stitzer MC et al (2017) Improved maize reference genome with single-molecule technologies. Nat Publ Gr 546:524–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22971
Kaefer CA, Schuelter AR, Schuster I, Marcolin J et al (2017) Association mapping and genetic control for northern leaf blight (Exserohilum turcicum) resistance in maize lines. Aust J Crop Sci 11(10):1346–1353. https://doi.org/10.21475/ajcs.17.11.10.pne678
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis. Crop Sci 25:192–194. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1985.0011183X002500010046x
Kuki MC, Scapim CA, Rossi ES, Mangolin CA, Amaral Júnior ATd, Pinto RJB (2018) Genome wide association study for gray leaf spot resistance in tropical maize core. PLoS ONE 13(6):e0199539
Lipka AE, Tian F, Wang Q, Peiffer J, Li M et al (2012) GAPIT: Genome association and prediction integrated tool. Bioinformatics 28(18):2397–2399. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts444
Liu X, Huang M, Fan B, Buckler ES, Zhang Z (2016) Iterative usage of fixed and random effect models for powerful and efficient genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005767
Mendiburu F, Simon R (2015) Agricolae-Ten years of an open source statistical tool for experiments in breeding, agriculture and biology. PeerJ 3:1–17. https://doi.org/10.7287/peerj.preprints.1404v1
Montemarani A, Sartori M, Nesci A, Etcheverry M, Barros G (2018) Influence of crop residues, matric potential and temperature on growth of Exserohilum turcicum an emerging maize pathogen in Argentina. Lett Appl Microbiol 67(6):614–619. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13076
Moreira JUV, Bento DAV, De Souza AP, De Souza CL (2009) QTL mapping for reaction to Phaeosphaeria leaf spot in a tropical maize population. Theor Appl Genet 119(8):1361–1369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1140-0
Ogliari JB, Guimarães MA, Geraldi IO, Camargo LEA (2005) New resistance genes in the Zea mays-Exserohilum turcicum pathosystem. Genet Mol Biol 28(3):435–439. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572005000300017
Ogliari JB, Guimarães MA, Eduardo L, Camargo A (2007) Chromosomal locations of the maize (Zea mays L.) HtP and rt genes that confer resistance to Exserohilum turcicum. Genet Mol Biol 634(630):634
Olukolu BA, Tracy WF, Wisser R, De Vries B, Balint-Kurti PJ (2016) A genome-wide association study for partial resistance to maize common rust. Phytopathology 106(7):745–751. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-11-15-0305-R
Patterson HD, Williams ER (1976) A new class of resolvable incomplete block designs. Biometrika 63:83–92
Poland JA, Bradbury PJ, Buckler ES, Nelson RJ (2011) Genome-wide nested association mapping of quantitative resistance to northern leaf blight in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(17):6893–6898. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010894108
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA et al (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38(8):904–909. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1847
Ranganatha HM, Lohithaswa HC, Pandravada A (2021) Mapping and validation of major quantitative trait loci for resistance to Northern corn leaf blight along with the determination of the relationship between resistances to multiple foliar pathogens of maize (Zea mays L.). Front Genet 11:548407. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.548407
Rashid Z, Sofi M, Harlapur SI et al (2020) Genome-wide association studies in tropical maize germplasm reveal novel and known genomic regions for resistance to Northern corn leaf blight. Sci Rep 10:21949. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78928-5
Razzaq T, Khan MF, Awan SI (2019) Study of northern corn leaf blight (NCLB) on maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes and its effect on yield. Sarhad J Agri 35(4):1166–1174
Ribeiro RM, Amaral Junior AT, Pena GF, Vivas M, Kurosawa RN, Gonçalves L (2016) History of northern corn leaf blight disease in the seventh cycle of recurrent selection of an UENF-14 popcorn population. Acta Sci Agron 38:447–455. https://doi.org/10.4025/actasciagron.v38i4.30573
Rossi ES, Kuki MC, Pinto RJB, Scapim CA, Faria MV et al (2020) Genomic-wide association study for white spot resistance in a tropical maize germplasm. Euphytica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-019-2550-y
Shiomi HF, de Melo IS, de Minhoni MTA (2015) Avaliação de bactérias endofíticas para o controle biológico da mancha foliar de Exserohilum turcicum em milho. Arq Inst Biol (sao Paulo) 82:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1590/1808-1657000642013
Sibiya J, Tongoona P, Derera J, van Rij N, Makanda I (2011) Combining ability analysis for Phaeosphaeria leaf spot resistance and grain yield in tropical advanced maize inbred lines. F Crop Res 120(1):86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2010.09.001
Stich B, Möhring J, Piepho HP, Heckenberger M, Buckler ES et al (2008) Comparison of mixed-model approaches for association mapping. Genetics 178(3):1745–1754. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.079707
Swarts K, Li H, Romero Navarro JA, An D (2014) Novel methods to optimize genotypic imputation for low-coverage, next-generation sequence data in crop plants. Plant Genome 7. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2014.05.0023
Tang Y, Liu X, Wang J, Li M et al (2016) GAPIT version 2: an enhanced integrated tool for genomic association and prediction. Plant Genome 9(2). https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2015.11.0120
Thakur RP (1989) Effects of temperature and light on virulence of exserohilum turcicum on corn. Phytopathology 79:631
Van Inghelandt D, Melchinger AE, Martinant JP, Stich B (2012) Genome-wide association mapping of flowering time and northern corn leaf blight (Setosphaeria turcica) resistance in a vast commercial maize germplasm set. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-12-56
Vanraden PM (2008) Efficient methods to compute genomic predictions. J Dairy Sci 91(11):4414–4423. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2007-0980
Vivek BS, Odongo O, Njuguna J, Imanywoha J, Bigirwa G et al (2010) Diallel analysis of grain yield and resistance to seven diseases of 12 African maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines. Euphytica 172(3):329–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-9993-5
Wang H, Xiao ZX, Wang FG, Xiao YN, Zhao JR et al (2012) Mapping of HtNB, a gene conferring non-lesion resistance before heading to Exserohilum turcicum (Pass) in a maize inbred line derived from the Indonesian variety Bramadi. Genet Mol Res 11(3):2523–2533. https://doi.org/10.4238/2012.July.10.7
Weems JD, Bradley CA, Sciences C (2018) Exserohilum Turcicum race population distribution in the North central United States. Plant Dis 102(2):292–299. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-01-17-0128-RE
Welz HG, Geiger HH (2000) Genes for resistance to northern corn leaf blight in diverse maize populations. Plant Breed 119(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1439-0523.2000.00462.x
Wisser RJ, Balint-Kurti PJ, Nelson RJ (2006) The genetic architecture of disease resistance in maize: a synthesis of published studies. Phytopathology 96(2):120–129. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-96-0120
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M et al (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38(2):203–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1702
Zhu C, Gore M, Buckler ES, Yu J (2008) Status and prospects of association mapping in plants. Plant Genome 1:5–20
Zila CT, Ogut F, Romay MC, Gardner CA, Buckler ES et al (2014) Genome-wide association study of Fusarium ear rot disease in the U.S.A. maize inbred line collection. BMC Plant Biol 14(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0372-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DAR: data curation, formal analysis, methodology, writing draft; EP: data curation, methodology and formal analysis; RJBP: funding acquisition, writing-review; CAS: funding acquisition, supervision, writing review; MVF: supervision and writing review; RCS: conceptualization, formal analysis, writing draft and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizzardi, D.A., Peterlini, E., Scapim, C.A. et al. Genome wide association study identifies SNPs associated with northern corn leaf blight caused by Exserohilum turcicum in tropical maize germplasm (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 218, 40 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-02986-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-02986-1