Abstract
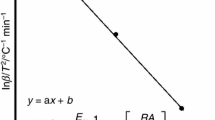
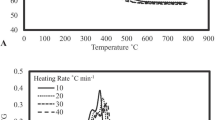
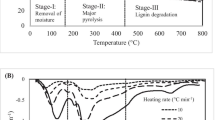
Pyrolysis is a very fast and effective thermochemical conversion scheme, hence suitable for the processing of elephant grass, a fast-growing and invasive grass, into bioenergy. This research investigates the pyrolysis characteristics and the thermal degradation of elephant grass using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Different characterization techniques were carried out to study the biomass and its bio-oil in order to ascertain their fuel properties. The two most widely used iso-conversional methods, Flynn–Wall–Ozawa (FWO) and Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose (KAS), were used to analyze the TGA data obtained over a range of temperatures at heating rates of 10, 15, and 25 °C/min in order to calculate the activation energy and other thermodynamic parameters. From the pyrolysis study, the highest bio-oil yield of 39 wt% was achieved at 500 °C. The obtained bio-oil has excellent fuel properties because of its higher heating value (HHV) of 20.9 MJ/kg, low ash and sulphur contents. The average activation energies (Ea) were 172.48 kJ/mol and 164.11 kJ/mol, respectively, for the FWO and KAS methods, while the average enthalpy changes (∆H) were 168.31 kJ/mol and 159.32 kJ/mol. These values of Ea and ∆H revealed that the overall reaction is favourable since their difference is less than 5 kJ/mol. FWO produces higher and more accurate results since it can capture the decomposition behaviour of the different biomass components for any conversion fraction, while KAS is based on the overall reaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw data were generated from laboratory experiments and different analyses. Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author (H.O Orugba) on request.
References
Ahmad, R., Ilays, H. N., Yin, W., Liu, X., Li, B., Sultan, M., Imran, M. A., Abbas, A., Javed, Z., & Raman, P. (2023). Agricultural residue management using forced draft gasifier cookstove. In A. Rakshit, A. Biswas, D. Sarkar, V. S. Meena, & R. Datta (Eds.), Handbook of energy management in agriculture. Springer.
Ahmad, R., Ilyas, H. N., Li, B., Sultan, M., Amjad, M., Aleem, M., Abbas, A., Imran, M. A., & Riaz, F. (2022). Current challenges and future prospect of biomass cooking and heating stoves in Asian Countries. Frontiers in Energy Research, 10, 880064. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenrg.2022.880064
Ahmed, A., Hidayat, S., Abu Bakar, M. S., Azad, A. K., Sukri, R. S., & Phusunti, N. (2018). Thermochemical characterisation of Acacia auriculiformis tree parts via proximate, ultimate, TGA, DTG, calorific value and FTIR spectroscopy analyses to evaluate their potential as a biofuel resource. Biofuels, 7269, 9–20.
Akhtar, N., Goyal, D., & Goyal, A. (2016). Physico-chemical characteristics of leaf litter biomass to delineate the chemistries involved in biofuel production. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 62, 239–246.
Alcaraz, V. J. V., Ávalos, R. M. L., López, S. L. B., Rutiaga, Q. J. G., Pintor, I. L. F., Márquez, M. F., & Aguado, Z. R. (2022). Analysis of pyrolysis kinetic parameters based on various mathematical models for more than twenty different biomasses: A review. Energies, 15, 6524. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15186524
Apaydın Varol, E., & Mutlu, Ü. (2023). TGA-FTIR analysis of biomass samples based on the thermal decomposition behavior of hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin. Energies, 16, 3674. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16093674
Aup-Ngoen, K., & Noipitak, M. (2020). Effect of carbon-rich biochar on mechanical properties of PLA-biochar composites. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy, 15, 100204.
Bardalai, M., & Mahanta, D. K. (2018). Characterization of pyrolysis oil derived from Teak Tree sawdust and Rice Husk. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 13(1), 242–253.
Braga, R. M., Melo, D. M. A., Sobrinho, E. V., Barros, J. M. F., Melo, M. A. F., Carvalho, A. F. M., Fontes, D. M. B., & Freitas, J. C. O. (2017). Catalytic upgrading of Elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum) pyrolysis vapor using WO3 supported on RHA and RHA-MCM-41. Catalysis Today, 279, 224–232.
Chukwuneke, J. L., Orugba, H. O., Olisakwe, H. C., & Chikelu, P. O. (2021). Pyrolysis of pig-hair in a fixed bed reactor: Physico-chemical parameters of bio-oil. South African Journal of Chemical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2021.09.003
Chukwuneke, J. L., Sinebe, J. E., Orugba, H. O., Olisakwe, H. C., & Ajike, C. (2022). Production and physico-chemical characteristics of pyrolyzed bio-oil derived from cow hooves. Arab Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 29(1), 363–371. https://doi.org/10.1080/25765299.2022.2129633
Clemente-Castro, S., Palma, A., Ruiz-Montoya, M., Giráldez, I., & Díaz, M. J. (2022). Pyrolysis kinetic, thermodynamic and product analysis of different leguminous biomasses by Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose and pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 162, 105457.
Collazzo, G. C., Broetto, C. C., Perondi, D., Junges, J., Dettmer, A., DornellesFilho, A. A., Foletto, E. L., & Godinho, M. (2017). A detailed non-isothermal kinetic study of elephant grass pyrolysis from different models. Applied Thermal Engineering, 110, 1200–1211.
Danquah, J. A., Roberts, C. O., & Appiah, M. (2018). Elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum): A potential source of biomass for power generation in Ghana. Current Journal of Applied Science and Technology, 30(6), 1–12.
Fu, P., Yi, W., Bai, X., Li, Z., Hu, S., & Xiang, J. (2011). Effect of temperature on gas composition and char structural features of pyrolyzed agricultural residues. Bioresource Technology, 102(17), 8211–8219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.05
Gu, J., Chong, C. T., Mong, G. R., Ng, J.-H., & Chong, W. W. F. (2023). Determination of pyrolysis and kinetics characteristics of chicken manure using thermogravimetric analysis coupled with particle swarm optimization. Energie, 16, 1919.
Halder, P., & Azad, A. K. (2019). Recent trends and challenges of algal biofuel conversion technologies. In Advanced Biofuels: Applications, Technologies and Environmental Sustainability (pp. 169–179). Elsevier: Amsterdam, ISBN 9780081027912.
Hidayat, S., Abu Bakar, M. S., Yang, Y., Phusunti, N., & Bridgwater, A. V. (2018). Characterisation and Py-GC/MS analysis of Imperata Cylindrica as potential biomass for bio-oil production in Brunei Darussalam. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 134, 510–519.
Huang, C., Han, L., Yang, Z., & Liu, X. (2009). Ultimate analysis and heating value prediction of straw by near infrared spectroscopy. Waste Management, 29, 1793–1797.
Hussain, M., Ali, O., Raza, N., Zabiri, H., Ahmed, A., & Ali, I. (2023). Recent advances in dynamic modelling and control studies of biomass gasification for production of hydrogen rich syngas. RSC Advances, 13(34), 23796–23811. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ra01219k
Imam, T., & Capareda, S. (2012). Characterization of bio-oil, syn-gas and bio-char from switchgrass pyrolysis at various temperatures. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 93, 170–177.
Islam, M. S., Kwak, J. H., Nzediegwu, C., Wang, S., Palansuriya, K., Kwon, E. E., Naeth, M. A., El-Din, M. G., Ok, Y. S., & Chang, S. X. (2021). Biochar heavy metal removal in aqueous solution depends on feedstock type and pyrolysis purging gas. Environmental Pollution, 281, 117094.
Ivanovski, M., Petrovic, A., Ban, I., Goricanec, D., & Urbancl, D. (2021). Determination of the kinetics and thermodynamic parameters of lignocellulosic biomass subjected to the torrefaction process. Materials, 14, 7877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247877
Kabeyi, M. J. B., & Olanrewaju, O. A. (2022). Sustainable energy transition for renewable and low carbon grid electricity generation and supply. Frontiers in Energy Research, 9, 1–45.
Kenney, K. L., Smith, W. A., Gresham, G. L., & Westover, T. L. (2013). Understanding biomass feedstock variability. Biofuels, 4, 111–127.
Kongkaew, N., Pruksakit, W., & Patumsawad, S. (2015). Thermogravimetric kinetic analysis of the pyrolysis of rice straw. In 2015 International Conference on Alternative Energy in Developing Countries and Emerging Economies, Energy Procedia (vol. 79, pp. 663–670).
Kwak, J. H., Islam, M. S., Wang, S., Messele, S. A., Naeth, M. A., El-Din, M. G., & Chang, S. X. (2019). Biochar properties and lead(II) adsorption capacity depend on feedstock type, pyrolysis temperature, and steam activation. Chemosphere, 231, 393–404.
Li, G., Hu, R., Wang, N., Yang, T., Xu, F., Li, J., Wu, J., Huang, Z., Pan, M., & Lyu, T. (2022). Cultivation of microalgae in adjusted wastewaterto enhance biofuel production and reduce environmental impact: Pyrolysis performances and life cycle assessment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 355, 131768.
Liu, Z., & Balasubramanian, R. (2013). A comparison of thermal behaviors of raw biomass, pyrolytic biochar and their blends with lignite. Bioresource Technology, 146, 371–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07
Luo, Y., Li, Z., Xu, H., Xu, X., Qiu, H., Cao, X., & Zhao, L. (2022). Development of phosphorus composite biochar for simultaneous enhanced carbon sink and heavy metal immobilization in soil. Science of the Total Environment, 8, 154845.
Maiti, S., Purakayastha, S., & Ghosh, B. (2007). Thermal characterization of mustard straw and stalk in nitrogen at different heating rates. Fuel, 86(10–11), 1513–1518.
McKendry, P. (2002). Energy production from biomass (part 1): Overview of biomass. Bioresource Technology, 83, 37–46.
Mehmood, M. A., Ye, G., Luo, H., Liu, C., Malik, S., Afzal, I., Xu, J., & Ahmad, M. S. (2017). Pyrolysis and kinetic analyses of Camel grass (Cymbopogon schoenanthus) for bioenergy. Bioresource Technology, 228, 18–24.
Mian, I., Li, X., Jian, Y., Dacres, O. D., Zhang, M., Liu, J., Ma, F., & Rahman, N. (2019). Kinetic study of biomass pellet pyrolysis by using distributed activation energy model and Coats Redfern methods and their comparison. Bioresource Technology, 294, 122099.
Mishra, G., & Bhaskar, T. (2014). Non isothermal model free kinetics for pyrolysis of rice straw. Bioresource Technology, 169, 614–621.
Mohammed, I. Y., Abkr, Y. A., Kazi, F. K., Yusuf, S., Alshareef, I., & Chin, S. A. (2015). Pyrolysis of Napier grass in a fixed bed reactor: Effect of operating conditions on product yields and characteristics. BioResources, 10(4), 2681–2690.
Mopoung, S., Moonsri, P., Palas, W., & Khumpai, S. (2015). Characterization and properties of activated carbon prepared from tamarind seeds by KOH activation for Fe(III) adsorption from aqueous solution. The Scientific World Journal. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/415961
Naik, S., Goud, V. V., Rout, P. K., Jacobson, K., & Dalai, A. K. (2010). Characterization of Canadian biomass for alternative renewable biofuel. Renewable Energy, 35, 1624–1631.
Nhuchhen, D. R., & Basu, P. (2014). Experimental investigation of mildly pressurized torrefaction in air and nitrogen. Energy & Fuels, 28(5), 3110–3121.
Ohimain, E. I., Kendabie, P., & Nwachukwu, R. E. S. (2022). Bioenergy potentials of elephant grass, Pennisetum purpureum Schumach. Annual Research and Reviews in Biology, 4, 2215–2227.
Oladokun, O., Ahmad, A., Abdullah, T. A. T., Nyakuma, B. B., Bello, A. A., & Al-Shatri, A. H. (2016). Multicomponent devolatilization kinetics and thermal conversion of Imperata cylindrical. Applied Thermal Engineering, 105, 931–940.
Orugba, H. O., Chukwuneke, J. L., Olisakwe, H. C., & Digitemie, I. E. (2021a). Multi-parametric optimization of the catalytic pyrolysis of pig hair into bio-oil. Clean Energy, 5(3), 527–535.
Orugba, H. O., Ogbeide, S. E., & Osagie, C. (2019a). Emission trading scheme and the effect of carbon fee on petroleum refineries. Asian Journal of Applied Sciences, 7(5), 537–545.
Orugba, H. O., Ogbeide, S. E., & Osagie, C. (2019b). Risk level assessment of the Desalter and Preflash column of a Nigerian Crude distillation unit. Journal of Material Science and Chemical Engineering, 10(2), 432–456.
Orugba, H. O., Oghenejoboh, K. M., Oghenejoboh, U. M., & Ohimor, O. E. (2021b). Production of biodiesel from a novel combination of Raphia Africana kernel oil and turtle shell (Centrochelys Sulcata) heterogenous catalyst. Journal of Human, Earth, and Future, 2(3), 258–268.
Panwar, N. L., Kaushik, S. C., & Kothari, S. (2011). Role of renewable energy sources in environmental protection: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15, 1513–1524.
Prine, G. M., Rockwood, D. L., & Stricker, J. A. (2000). Many short rotation trees and herbaceous plants available as energy crops in humid lower south. In Proceedings of Bioenergy 2000, Northeast Regional Bioenergy Program. Buffalo
Promdee, K., & Vitidsant, T. (2013). Preparation of biofuel by pyrolysis of plant matter in a continuous reactor. Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry, 49, 126–129.
Reza, M. S., Afroze, S., Kuterbekov, K., Kabyshev, A., Bekmyrza, K. Z., Haque, M. N., Islam, S. N., Hossain, M. A., Hassan, M., Roy, H., et al. (2023b). Advanced applications of carbonaceous materials in sustainable water treatment, energy storage, and CO2 capture: A comprehensive review. Sustainability, 15, 8815.
Reza, M. S., Afroze, S., Kuterbekov, K., Kabyshev, A., Bekmyrza, K. Z., Taweekun, J., Ja’afar, F., Bakar, M. S. A., Azad, A. K., Roy, H., & Islam, M. S. (2023a). Ex situ catalytic pyrolysis of invasive Pennisetum purpureum grass with activated carbon for upgrading bio-oil. Sustainability, 15, 7628.
Reza, M. S., Azad, A. K., Bakar, M. S. A., Karim, M. R., Sharifpur, M., & Taweekun, J. (2022). Evaluation of thermochemical characteristics and pyrolysis of fish processing waste for renewable energy feedstock. Sustainability, 14, 1203.
Reza, M. S., Taweekun, J., Afroze, S., Siddique, S. A., Islam, M. S., Wang, C., & Azad, A. K. (2023c). Investigation of thermochemical properties and pyrolysis of barley waste as a source for renewable energy. Sustainability, 15, 1643.
Sadiku, N. A., Oluyege, A. O., & Sadiku, I. B. (2016). Analysis of the calorific and fuel value index of bamboo as a source of renewable biomass feedstock for enegry generation in Nigeria. Lignocellulose, 5, 34–49.
Singh, B. P., Singh, H. P., & Obeng, E. (2013). Elephant grass. In B. P. Singh (Ed.), Biofuel crops: Production, physiology and genetics (pp. 271–291). CABI.
Singh, S. B., & De, M. (2020). thermally exfoliated graphene oxide for hydrogen storage. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 239, 122102.
Sirinwaranon, P., Atong, D., & Sricharoenchaikul, V. (2019). Thermal degradation and kinetic study of Cassava Rhizome for torrefaction application. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (vol 401, p 012007). https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/401/1/012007
Slopiecka, K., Bartocci, P., & Fantozzi, F. (2012). Thermogravimetric analysis and kinetic study of poplar wood pyrolysis. Applied Energy, 97, 491–497.
Strezov, V., Evans, T. J., & Hayman, C. (2008). Thermal conversion of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schum) to bio-gas, bio-oil and charcoal. Bioresource Technology, 99, 8394–8399.
Treedet, W., Suntivarakorn, R., & Mufandi, I. (2020). Bio-oil production from Napier grass using a pyrolysis process: Comparison of energy conversion and production cost between bio-oil and other biofuels. International Energy Journal, 20, 155–168.
Wang, C., Huang, R., Sun, R., Yang, J., & Sillanpää, M. (2021). A review on persulfates activation by functional biochar for organic contaminants removal: Synthesis, characterizations, radical determination, and mechanism. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9, 106267.
Wang, D., Poss, J. A., Donovan, T. J., Shannon, M. C., & Lesch, S. M. (2002). Biophysical properties and biomass production of elephant grass under saline conditions. Journal of Arid Environments, 52(4), 447–456.
Wang, F., Shi, D., Han, J., Zhang, G., Jiang, X., Yang, M., Wu, Z., Fu, C., Li, Z., Xian, M., & Zhang, H. (2020). Comparative study on pretreatment processes for different utilization purposes of switchgrass. ACS Omega, 5(35), 21999–22007.
Wang, W.-C., & Lee, A.-C. (2018). Thermochemical processing of miscanthus through fluidized-bed fast pyrolysis: A parametric study. Chemical Engineering and Technology, 41, 1737–1745.
Yang, H., Yan, R., Chen, H., Lee, D. H., & Zheng, C. (2007). Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel, 86, 1781–1788.
Zaman, C. Z., Pal, K., Yehye, W. A., Sagadevan, S., Shah, S. T., Adebisi, G. A., Marliana, E., Rafique, R. F., & Johan, R. (2017). Bin pyrolysis: A sustainable way to generate energy from waste. In Pyrolysis (1–35). In Tech. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.69036
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ikpeseni, S.C., Orugba, H.O., Efetobor, U.J. et al. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of the thermal degradation of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum): a comparative analysis using the Flynn–Wall–Ozawa and the Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose methods. Environ Dev Sustain (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04322-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04322-6