Abstract
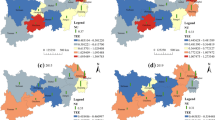
The understanding of the coupling relationship between tourism industry, urbanization, and ecological environment is important due to the complex interaction in environmental effects induced by tourism industry and urbanization. In this paper, a comprehensive evaluation index system of tourism industry, urbanization, and ecological environment is established, and the coupling degrees and coordination degrees of the three subsystems of Shandong province in China from 2001 to 2017 are calculated. After identifying the temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of coupling of the subsystems, this paper summarizes the driving factors of tourism industry, urbanization, and ecological environment. The results shown are as follows: (1) The level of comprehensive development of Shandong's tourism industry and urbanization subsystems has steadily increased, while its ecological environment subsystem has shown fluctuating development trends between 2001 and 2017. (2) The coupling coordination degree of tourism industry, urbanization, and ecological environment has increased from a low level of coordination to a very high level of coordination. A spatial difference in coupling coordination between cities is more unbalanced. The coupling coordination of “dual-core” cities (Qingdao and Jinan) is better than that of other cities. (3) The main factors influencing spatial differentiation are regional economic strength, industrial structure, market scale, technological innovation ability, government regulation, and control factors. Different factors have obvious temporal heterogeneity. The significance of this research not only helps increase the focus on ecological tourism and new urbanization, but also optimize the quality and path of tourism industry and new urbanization development, promote an environmentally friendly society, and achieve high-quality economic development and sustainable development in Shandong Province.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becken, S., & Patterson, M. (2006). Measuring national carbon dioxide emissions from tourism as a key step towards achieving sustainable tourism. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 14, 323–338.
Bhattacharjee, B. J.. (2012). Rural tourism: A preventive weapon of sinking urbanization and rural economic development. Annamalai International Journal of Business Studies, 1, 62–71.
Cong, X. L., Huang, Y., & Liu, J. S. H. (2019). Spatiotemporal evolution of coupling coordination degree between ecotourism and tourism environment in Jilin Province. Scientia Geography Sinica, 3, 496–505.
Du, X., Fang, C. L., & Ma, H. T. (2021). Coupling coordination and spatio-temporal evolution of tourism economy and urbanization in coastal provinces: A Case Study of Shandong Province. Economic Survey, 1, 15–26.
Fang, C. H. L., Zhou, C. H. H., Gu, C. H. L., Chen, L. D., & Li, S. H. C. H. (2016). Theoretical framework and technical path for the analysis of the interactive coupling effect of urbanization and ecological environment in megalopolis. Acta Geographica Sinica, 4, 531–550.
Gao, Y., Deng, Z., & Morrison, A. M. (2019). Can urban lake recreational pressure be measured? The impacts of urbanization on Wuhan’s Lakes. Applied Spatial Analysis & Policy, 6, 255–273.
Geneletti, D., & Dawa, D. (2009). Environmental impact assessment of mountain tourism in developing regions: A study in Ladakh, Indian Himalaya. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 29, 229–242.
Gossling, S. (2001). The consequences of tourism for sustainable water use on a tropical island: Zanzibar, Tanzania. Journal of Environmental Management, 61, 179–191.
Gossling, S., Hansson, C. B., Horstmeier, O., & Saggel, S. (2002). Ecological footprint analysis as a tool to assess tourism sustainability. Ecological Economics, 43, 199–211.
Grossman, G.M., & Krueger, A.B. (1995). Economic growth and the environment. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 2, 353–378.
Han, W. Y., Ch, X. P., Pang, J. X., Wang, N. F., & Yu, Y. H. (2018). Research on the coupling and coordinated development of urbanization ecological environment tourism industry: A case study of nine provinces (districts and cities) along the Silk Road Economic Belt. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 6, 762–769.
Hannigan, J. A. (1995). Tourism urbanization. Current Sociology, 1, 192–200.
Liu, D. G., & Qu, X. S. H. (2016). Calculation of coordinated development degree of tourism economy and ecological environment in China and analysis of regional differences. Journal of Guangdong University Finance & Economics, 6, 89–96.
Liu, L., & Zh, H. (2019). Calculation of coupling coordination degree between new urbanization and ecological environment. Statistics & Decision, 14, 137–141.
Liu, N., Liu, C., Xia, Y., & Da, B. (2018). Examining the coordination between urbanization and eco-environment using coupling and spatial analyses: A case study in China. Ecological Indicators, 93, 1163–1175.
Luo, J. M., Qiu, H. Q., Goh, G., & Wang, D. (2016). An analysis of tourism development in China from urbanization perspective. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 1, 24–44.
Lv, Y. J., Kong, L. C. H., & Li, Y. (2019). Measurement of coupling coordination degree between urbanization and ecological environment in China. Urban Problems, 12, 13–22.
Martínez, M. (2011). The impact of urbanization on CO2 emissions: Evidence from developing countries. Ecological Economics, 70, 1344–1353.
Mullins, P. (1991). Tourism urbanization. International Journal of Urban and Reginal Research, 3, 326–342.
Nielsen, S. P., Sesartic, A., & Stucki, M. (2010). The green house gas intensity of the tourism sector: The case of Switzerland. Environment of Science & Policy, 13, 131–140.
OECD. (2002). Indicator to Measure Decoupling of Environmental Pressure from Economic Growth. OECD.
Patterson, T. M., Niccolucci, V., & Marchettini, N. (2008). Adaptive environmental management of tourism in the Province of Siena, Italy using the ecological footprint. Journal of Environmental Management, 86, 407–418.
Pickering, C. M., & Hill, W. (2007). Impacts of recreation and tourism on plant biodiversity and vegetation in protected areas in Australia. Journal of Environmental Management, 85, 791–800.
Shi, M. H., Zhang, Y., & Ye, Q. Q. (2021). Study on the coupling, coordination and temporal and spatial differentiation of high-quality urbanization and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin. Social Science in Ningxia, 10(7), 216–222.
Simpson, M. C., Gossling, S., & Scott, D. (2008). Climate change adaptation and mitigation in the tourism sector: Frameworks, tools and practices. UNEP, University of Oxford, UNWTO, WMO.
Tian, L., & Zhang, Z. B. (2018). Evolutionary characteristics and influencing factors of green growth in China’s Tourism Industry. Journal of Shandong Normal University (social Sciences), 1, 116–125.
Truly, D. (2002). International retirement migration and tourism along the lake Chapala Riviera: Developing a matrix of retirement migration behavior. Tourism Geography, 3, 899–918.
Wang, W. J., & Tian, Y. J. (2020). Coupling analysis of new urbanization quality and ecological environment carrying capacity in Henan Province. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 4, 21–26.
Wang, W. F., Lu, Y. G., & Wang, Q. (2019). Study on the coupling and coordinated development of regional tourism industry and urbanization construction—A case study of 14 prefecture-level cities in Guangxi. Journal Northwest Normal University(Natural Science), 6, 92–101.
Yi, T. T., & Li, X. X. (2020). Study on the characteristics and evolution mode of coupling efficiency between tourism and urbanization. Tourism Research, 1, 19–33.
Yu, F. L., Huang, Z. H. F., Cao, F. D., Wu, L. M., & Tao, Y. G. (2014). The impact of China’s urbanization process on the development of tourism economy. Journal of Natural Resources, 8, 1297–1309.
Yuan, Y., Jin, M., Ren, J., Hu, M., & Ren, P. (2014). The dynamic coordinated development of a regional environment-tourism-economy system: A case study from western Hunan province, China. Sustainability, 8, 5231–5251.
Zhang, H., Gu, C. L., Gu, L. W., & Zhang, Y. (2011). The evaluation of tourism destination competitiveness by TOPSIS & information entropy: A case in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Tourism Management, 32, 443–451.
Zhao, L., Pan, T., Fang, C., & Lin, S. (2020). Tourism and new urbanization—from the perspective of system coupling and coordination. Tourism Tribune, 1, 14–31.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the editor of the journal and the reviewers for their valuable comments on the research. The research was supported by Project of Shandong Provience (NO.2022BLYJ18). We thank TopEdit (www.topeditsci.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, L., Sun, F., Zhang, Z. et al. Coupling coordination and driving mechanism of tourism industry, urbanization, and ecological environment: a case study of Shandong, China. Environ Dev Sustain (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03815-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03815-8