Abstract
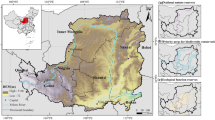
Based on the DEM (digital elevation model) data and land use data from 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015 and 2020, the spatiotemporal differentiation characteristics of habitat quality in Hubei Province were evaluated by the InVEST model (Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs) and GIS (Geographic Information System) spatial analysis method, and the topographic gradient effect on habitat quality was analyzed by regression analysis and terrain index. The spatial distribution of habitat quality in Hubei Province was quite different, and the overall level was high. High-quality habitats were mainly located in hilly regions and water areas, while low-level habitats are mainly distributed in agricultural areas and urban areas. From 2000 to 2020, the high-level habitats in Hubei Province tended to degenerate to low-level habitats, and the average habitat quality decreased slightly. The habitat quality in most areas of Hubei Province had no obvious change from 2000 to 2020, and the overall spatial features were "rising in the southeast and decreasing in the middle". With the elevation of the terrain grade, the number of county-level units with high-level habitat quality increased gradually, and the average habitat quality increased accordingly. From 2000 to 2020, the habitat quality of the first-class terrain improved, while the habitat quality of the other class terrain showed a downward trend. The results are helpful to discover the spatiotemporal change process of habitat quality in Hubei Province, and provide theoretical support for biodiversity conservation and land use planning in Hubei Province.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaniz, A. J., Carvajal, M. A., Fierro, A., Vergara-Rodríguez, V., Toledo, G., Ansaldo, D., Moreira-Arce, D., Rojas-Osorio, A., & Vergara, P. M. (2021). Remote-sensing estimates of forest structure and dynamics as indicators of habitat quality for magellanic woodpeckers. Ecological Indicators, 126, 107634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107634
Berta Aneseyee, A., Noszczyk, T., Soromessa, T., & Elias, E. (2020). The invest habitat quality model associated with land use/cover changes: a qualitative case study of the Winike watershed in the Omo-gibe basin, Southwest Ethiopia. Remote Sensing-Basel, 12(7), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12071103
Brown, G., & Brabyn, L. (2012). The extrapolation of social landscape values to a national level in new zealand using landscape character classification. Applied Geography, 35(1–2), 84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2012.06.002
Budnik, R. R., Conroy, J. D., Zweifel, R. D., Ludsin, S. A., & Marschall, E. A. (2021). Projecting future habitat quality of three midwestern reservoir fishes under warming conditions. Ecology of Freshwater Fish, 30(1), 31–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/eff.12561
Caixian, X., Jie, G., Yan, L., Lingling, Y., & Bingli, G. (2020). Spatial distribution characteristics of typical ecosystem services based on terrain gradients of bailongjiang watershed in gansu. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(13), 4291–4301.
Chang-Li, Z., Ji-Fei, Z., Yu-Luan, Z., & Chun-Yan, L. (2017). Topographic gradient effects of typical watershed ecosystem services in the eastern tibetan plateau—a case study of the upper reaches of minjiang river. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 26(10), 1687–1699.
Chuanzhun, S., Lin, Z., Chao, W., Jie, H., & Bingzhen, D. (2015). Biodiversity simulation of poyang lake wetlands by invest model under different scenarios. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 24(07), 1119–1125.
Chunfang, L., Chuan, W., & Licheng, L. (2018). Spatio-temporal variation on habitat quality and its mechanism within the transitional area of the three natural zones: A case study in yuzhong county. Geographical Research, 37(02), 419–432.
Codato, D., Pappalardo, S. E., & de Marchi, M. (2017). Participatory gis in mapping ecosystem services: Two case studies from high-biodiversity regions in Italy and Peru. GI Forum, 1, 78–96. https://doi.org/10.1553/giscience2017_02_s78
Dai, L., Li, S., Lewis, B. J., Wu, J., Yu, D., Zhou, W., Zhou, L., & Wu, S. (2019). The influence of land use change on the spatial–temporal variability of habitat quality between 1990 and 2010 in northeast china. Journal of Forestry Research, 30(6), 2227–2236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0771-x
Forestry, S., & Administration, G. (2019). China forest resources report (2014–2018). China Forestry Publishing House.
Foster, E., Love, J., Rader, R., Reid, N., & Drielsma, M. J. (2017). Integrating a generic focal species, metapopulation capacity, and connectivity to identify opportunities to link fragmented habitat. Landscape Ecology, 32(9), 1837–1847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-017-0547-2
Gao, J. (2019). How china will protect one-quarter of its land. Nature, 569(7757), 457. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-01563-2
gradient in wujiang river basin. Ecological Science, 35(05): 154–159.
Güntner, A., Seibert, J., & Uhlenbrook, S. (2004). Modeling spatial patterns of saturated areas: An evaluation of different terrain indices. Water Resources Research. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003WR002864
Han, R., Feng, C., Xu, N., & Guo, L. (2020). Spatial heterogeneous relationship between ecosystem services and human disturbances: A case study in chuandong, China. Science of the Total Environment, 721, 137818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137818
Han, R., Jingjing, Z., Wenbo, Z., Liyuan, W., Lijuan, Z., & Lianqi, Z. (2018). Impact of land use change on habitat in the qihe river basin of taihang mountains. Progress in Geography, 37(12), 1693–1704.
He, J., Huang, J., & Li, C. (2017). The evaluation for the impact of land use change on habitat quality: A joint contribution of cellular automata scenario simulation and habitat quality assessment model. Ecological Modelling, 366, 58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.10.001
Hongjuan, G., Huiqing, H., Hongyan, Y., & Moran, H. (2016). Distribution characteristic of important ecosystem services in terrain gradient in Wujiang river Basin. Ecological Science, 35(05), 154–159.
Hongliang, Z. (2001). The prospect of gis application in wildlife habltat studies. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 03, 52–55.
Hua, L., Ying, C., Mengqiu, Y., Leiting, G., & Shuqing, A. (2012). Assessment of river habitat quality in yixing district of taihu lake basin. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31(05), 1288–1295.
Jianqiang, Y., Yonggui, Z., Wenpeng, S., Juan, Z., Longjun, Z., & Xianxiang, L. (2014). The eco-environmental evaluation based on habitat quality and ecological response of laizhou bay. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(01), 105–114.
Jiansheng, W., Jiaying, M., Qian, L., & Jiacheng, L. (2017). Urban growth boundary based on the evaluation of habitat quality:Taking the yangtze river delta as an example. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 37(01), 28–36.
Kang, H., Wenyuan, D., Wanli, H., Hui, O., & Hangxiao, H. (2019). Impacts of land use change evaluation on habitat quality based on ca-markov and invest models—taking fuzhou new district of fujian province as an example. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 39(06), 155–162.
Lee, D., & Jeon, S. W. (2020). Estimating changes in habitat quality through land-use predictions: Case study of roe deer (capreolus pygargus tianschanicus) in Jeju Island. Sustainability-Basel, 12(23), 10123. https://doi.org/10.3390/su122310123
Lewis, N. S., Fox, E. W., & Dewitt, T. H. (2019). Estimating the distribution of harvested estuarine bivalves with natural-history-based habitat suitability models. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 219, 453–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.02.009
Li, D., Sun, W., Xia, F., Yang, Y., & Xie, Y. (2021). Can habitat quality index measured using the invest model explain variations in bird diversity in an urban area? Sustainability-Basel, 13(10), 5747. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13105747
Li, F., Wang, L., Chen, Z., Clarke, K. C., Li, M., & Jiang, P. (2018). Extending the sleuth model to integrate habitat quality into urban growth simulation. Journal of Environmental Management, 217, 486–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.109
Li, M., Zhou, Y., Xiao, P., Tian, Y., Huang, H., & Xiao, L. (2021). Evolution of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effect in northwest hubei province from 2000 to 2020 based on the invest model. Land, 10(8), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10080857
Li, S., He, Y., Xu, H., Zhu, C., Dong, B., Lin, Y., Si, B., Deng, J., & Wang, K. (2021). Impacts of urban expansion forms on ecosystem services in urban agglomerations: a case study of Shanghai-Hangzhou bay urban agglomeration. Remote Sensing-Basel, 13(10), 1908. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13101908
Minxia, L. (2009). Biodiversity characters and eco-environment quality evaluation on nature reserve of xihu in dunhuang. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 23(03), 171–175.
Muyi, H., Wenze, Y., Shaoru, F., & Jiahui, Z. (2020). Spatial-temporal evolution of habitat quality and analysis of landscape patterns in dabie mountain area of west anhui province based on invest model. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(09), 2895–2906.
NATURAL CAPITAL PROJECT, (2021) Invest 3.2.0 user's guide_chinese version_20171008. https://naturalcapitalproject.stanford.edu/software/invest (accessed 2021.10.1.
Paudyal, K., Baral, H., & Keenan, R. J. (2018). Assessing social values of ecosystem services in the Phewa Lake Watershed, Nepal. Forest Policy and Economics, 90, 67–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forpol.2018.01.011
Petway, J. R., Lin, Y., & Wunderlich, R. F. (2020). A place-based approach to agricultural nonmaterial intangible cultural ecosystem service values. Sustainability (basel, Switzerland), 12(2), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12020699
Polasky, S., Nelson, E., Pennington, D., & Johnson, K. A. (2011). The impact of land-use change on ecosystem services, biodiversity and returns to landowners: A case study in the state of minnesota. Environmental and Resource Economics, 48(2), 219–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-010-9407-0
Qiang, W., Xingzhong, Y., Hong, L., Xu, P., Zhijian, W., & Yaoguang, Z. (2014). Stream habitat assessment of dong river, china, using river habitat survey method. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(06), 1548–1558.
Qiang, W., Xu, P., Xiuming, L., Zhijian, W., Xingzhong, Y., & Yaoguang, Z. (2019). Assessment method for the influence of hydroelectric dams on the physical habitat quality and longitudinal connectivity of rivers: A case study of the wubu and zaodu rivers. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(15), 5508–5516.
Rosas, Y. M., Peri, P. L., Huertas Herrera, A., Pastore, H., & Martínez Pastur, G. (2017). Modeling of potential habitat suitability of hippocamelus bisulcus: Effectiveness of a protected areas network in Southern Patagonia. Ecological Processes. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-017-0096-2
Sallustio, L., De Toni, A., Strollo, A., Di Febbraro, M., Gissi, E., Casella, L., Geneletti, D., Munafò, M., Vizzarri, M., & Marchetti, M. (2017). Assessing habitat quality in relation to the spatial distribution of protected areas in Italy. Journal of Environmental Management, 201, 129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.06.031
Shanthala, D. B. S., Murthy, M. S. R., Bijan, D., & Jha, C. S. (2016). Identification of potential habitat patches for connectivity using weighted linear combination (wlc) and integral index of connectivity (iic) at east Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 44(3), 385–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-015-0508-7
Sun, F., Xiang, J., Tao, Y., Tong, C., & Che, Y. (2019). Mapping the social values for ecosystem services in urban green spaces: Integrating a visitor-employed photography method into solves. Urban Forestry Urban Greening, 38, 105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ufug.2018.11.012
Sun, X., Jiang, Z., Liu, F., & Zhang, D. (2019). Monitoring spatio-temporal dynamics of habitat quality in nansihu lake basin, eastern china, from 1980 to 2015. Ecological Indicators, 102, 716–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.03.041
Sun, X., Yu, Y., Wang, J., & Liu, W. (2021). Analysis of the spatiotemporal variation in habitat quality based on the invest model- a case study of Shangri-la city, northwest Yunnan, China. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1961/1/012016
Swinton, S. M., Lupi, F., Robertson, G. P., & Hamilton, S. K. (2007). Ecosystem services and agriculture: Cultivating agricultural ecosystems for diverse benefits. Ecological Economics, 64(2), 245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2007.09.020
Tang, F., Fu, M., Wang, L., Song, W., Yu, J., & Wu, Y. (2021). Dynamic evolution and scenario simulation of habitat quality under the impact of land-use change in the huaihe river economic belt, china. PLoS ONE, 16(4), e249566. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0249566
Terrado, M., Sabater, S., Chaplin-Kramer, B., Mandle, L., Ziv, G., & Acuna, V. (2016). Model development for the assessment of terrestrial and aquatic habitat quality in conservation planning. The Science of the Total Environment, 540, 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.064
Thomas, E., Jansen, M., Chiriboga-Arroyo, F., Wadt, L., Corvera-Gomringer, R., Atkinson, R. J., Bonser, S. P., Velasquez-Ramirez, M. G., & Ladd, B. (2021a). Habitat quality differentiation and consequences for ecosystem service provision of an amazonian hyperdominant tree species. Frontiers in Plant Science, 12, 621064. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.621064
Ting, Z., Wanxu, C., Jiangfeng, L., & Jiale, L. (2021). Spatial relationship between human activities and habitat quality in shennongjia forest region from 1995 to 2015. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 15, 1–12.
Wenxian, Y., Shihua, L., Shuangyun, P., Yingxin, L., Shoulou, Z., & Lidan, Q. (2021). Identification of important biodiversity areas by invest model considering topographic relief: A case study of Yunnan Province, China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. https://doi.org/10.13287/j.1001-9332.202112.004
Wu, L., Sun, C., & Fan, F. (2021). Estimating the characteristic spatiotemporal variation in habitat quality using the invest model—a case study from guangdong–hong kong–macao greater bay area. Remote Sensing-Basel, 13(5), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13051008
Wu, P., Dai, P., Wang, M., Feng, S., Olhnuud, A., Xu, H., Li, X., & Liu, Y. (2021). Improving habitat quality at the local and landscape scales increases wild bee assemblages and associated pollination services in apple orchards in china. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2021.621469
Wu, Y., Shan, L., Guo, Z., & Peng, Y. (2017). Cultivated land protection policies in china facing 2030: Dynamic balance system versus basic farmland zoning. Habitat International, 69, 126–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2017.09.002
Xiao, P., Zhao, C., Zhou, Y., Feng, H., Li, X., & Jiang, J. (2021). Study on land consolidation zoning in hubei province based on the coupling of neural network and cluster analysis. Land, 10(7), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10070756
Xiaoyan, Z., Yiyi, H., Xin, H., & Miaomiao, Z. (2021). Topographic gradient effects of habitat quality and its response to land use change in hubei section of the three gorges reservoir. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 37(11), 259–267. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.11.029
Xiaoyang, S., Wenming, S., Huawei, W., Peng, H., & Gang, L. (2016). Dynamic monitoring of tibetan antelope habitat suitability in the hoh xil nature reserve using remote sensing images. Resources Science, 38(08), 1434–1442.
Xueru, Z., Jie, Z., & Mengmei, L. I. (2020). Analysis on spatial and temporal changes of regional habitat quality based on the spatial pattern reconstruction of land use. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(1), 160–178. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlxb202001012
Yan, S., Wang, X., Cai, Y., Li, C., Yan, R., Cui, G., & Yang, Z. (2018). An integrated investigation of spatiotemporal habitat quality dynamics and driving forces in the upper basin of miyun reservoir, north china. Sustainability-Basel, 10(12), 4625. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124625
Yang, S., Zhao, W., Liu, Y., Wang, S., Wang, J., & Zhai, R. (2018). Influence of land use change on the ecosystem service trade-offs in the ecological restoration area: Dynamics and scenarios in the Yanhe Watershed, China. The Science of the Total Environment, 644, 556–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.348
Yang, Z., Wang, S., Guo, M., Tian, J., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Spatiotemporal differentiation of territorial space development intensity and its habitat quality response in northeast China. Land, 10(6), 573. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10060573
Yanli, H., Kelong, C., & Deyong, Y. (2019). Evaluation on the impact of land use change on habitat quality in qinghai lake basin. Ecology and Environment Sciences, 28(10), 2035–2044.
Yu, W., Bitian, F., Yongpeng, L., Kai, Y., & Yue, C. (2016). Assessment of the social values of ecosystem services based on solves model: A case study of wusong paotaiwan wetland forest park, shanghai, china. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 27(06), 1767–1774.
Yu, Z., Pengtao, Z., Feng, T., Li, Z., & Xu, Z. (2018). The effect of land use change on habitat quality in changli county based on invest model. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 39(07), 121–128.
Yuan, L., Yong, Z., & Yuetian, D. (2019). Study on the spatio-temporal patterns of habitat quality and its terrain gradient effects of the middle of the yangtze river economic belt based on invest model. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28(10), 2429–2440.
Zhang, C., & Fang, S. (2021). Identifying and zoning key areas of ecological restoration for territory in resource-based cities: A case study of huangshi city, china. Sustainability-Basel, 13(7), 3931. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13073931
Zhang, H., Sun, T., Xue, S., Yang, W., & Shao, D. (2018). Habitat-mediated, density-dependent dispersal strategies affecting spatial dynamics of populations in an anthropogenically-modified landscape. Science of the Total Environment, 625, 1510–1517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.065
Zhang, T., Gao, Y., Li, C., Xie, Z., Chang, Y., & Zhang, B. (2020). How human activity has changed the regional habitat quality in an eco-economic zone: Evidence from poyang lake eco-economic zone, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17), 6253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176253
Zhang, X., Song, W., Lang, Y., Feng, X., Yuan, Q., & Wang, J. (2020). Land use changes in the coastal zone of china’s hebei province and the corresponding impacts on habitat quality. Land Use Policy, 99, 104957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104957
Zhifang, L., Lina, T., Quanyi, Q., Lishan, X., Tong, X., & Li, Y. (2017). Temporal and spatial changes in habitat quality based on land-use change in fujian province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(13), 4538–4548.
Zhiqiang, W., Zhichao, C., & Chengyuan, H. (2009). Breeding habitat suitability evaluation of red-crown crane in zhalong national nature reserve by the method of habitat suitability index. Wetland Science, 7(03), 197–201.
Zhiyun, O., Jianguo, L., Han, X., Yincun, T., & Heming, Z. (2001). An assessment of giant panda habitat in wolong nature reserve. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 11, 1869–1874.
Zhu, C., Zhang, X., Zhou, M., He, S., Gan, M., Yang, L., & Wang, K. (2020). Impacts of urbanization and landscape pattern on habitat quality using OLS and GWR models in Hangzhou, China. Ecological Indicators, 117, 106654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106654
Acknowledgements
The author is very grateful to Mengyao Lu, Li Wang, and Muhtar·AMAT for their great contributions to this paper. We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions, which improved the quality greatly of this paper.
Funding
This work was financial supported by two projects: Special Foundation for National Science and Technology Basic Research Program of China (2021FY100505) and Study on temporal and spatial response mechanism of cultivated land quality change and grain productivity in Lianghu Plain in the past 40 years (42171061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yong Zhou and Pengnan Xiao contributed to conceptualization; Pengnan Xiao, mengyao Li contributed to methodology; Jie Xu and Pengnan Xiao contributed to software; Pengnan Xiao contributed to writing—original draft preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The manuscript was not submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration.
Consent for publication
The submitted works are original and have not been published elsewhere in any form or language. The study was not divided into several parts to increase the number of submissions and submitted to various journals or one journal over time. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Human or animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, P., Zhou, Y., Li, M. et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of habitat quality and its topographic gradient effects of Hubei Province based on the InVEST model. Environ Dev Sustain 25, 6419–6448 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02310-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02310-w