Abstract
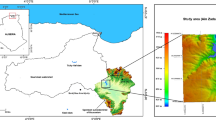
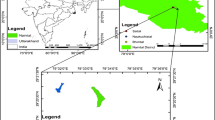
Istanbul is a megacity with a population of 15.5 million and is one of the fastest-growing cities in Europe. Due to the rapidly increasing population and urbanization, Istanbul’s daily water needs are constantly increasing. In this study, eight drinking water basins that supply water to Istanbul were comprehensively examined using remote sensing observations and techniques. Water surface area changes were determined monthly, and their relationships with meteorological parameters and climate change were investigated. Monthly water surface areas of natural lakes and dams were determined with the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) applied to Sentinel-2 satellite images. Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images were used in months when optical images were unavailable. The study was carried out using 3705 optical and 1167 SAR images on the Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform. Additionally, to determine which areas of water resources are shrinking, water frequency maps of the major drinking water resources were produced. Land use/land cover (LULC) changes that occurred over time were determined, and the effects of the increase in urbanization, especially on drinking water surface areas, were investigated. ESRI LULC data was used to determine LULC changes in watersheds, and the increase in urbanization areas from 2017 to 2022 ranged from 1 to 91.43%. While the basin with the least change was in Istranca, the highest increase in the artificial surface was determined to be in the Büyükçekmece basin with 1833.03 ha (2.89%). While there was a 1–12.35% decrease in the surface areas of seven water resources from 2016 to 2022, an increase of 2.65–93% was observed in three water resources (Büyükçekmece, Sazlıdere, and Elmalı), each in different categories depending on their size. In the overall analysis, total WSA decreased by 62.33 ha from 2016 to 2022, a percentage change of 0.70%. Besides the areal change analysis, the algae contents of the drinking water resources over the years were examined for the major water basins using the Normalized Difference Chlorophyll Index (NDCI) and revealed their relationship with meteorological factors and urbanization.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data not available due to legal restrictions.
References
Abera, W., Tamene, L., Abegaz, A., & Solomon, D. (2019). Understanding climate and land surface changes impact on water resources using Budyko framework and remote sensing data in Ethiopia. Journal of Arid Environments, 167, 56–64.
Abu-Bakar, H., Williams, L., & Hallett, S. H. (2021). Quantifying the impact of the COVID-19 lockdown on household water consumption patterns in England. NPJ Clean Water, 4(1), 13.
Amgoth, A., Rani, H. P., & Jayakumar, K. V. (2022). Extraction of water surface bodies for Pakhal Lake, India using GEE. In Innovative Trends in Hydrological and Environmental Systems (pp. 433–448) Springer, Singapore
Arnell, N. W., van Vuuren, D. P., & Isaac, M. (2011). The implications of climate policy for the impacts of climate change on global water resources. Global Environmental Change, 21(2), 592–603.
Ashrafuzzaman, M., Gomes, C., & Guerra, J. (2023). The changing climate is changing safe drinking water, impacting health: A case in the Southwestern Coastal Region of Bangladesh (SWCRB). Climate, 11(7), 146.
Attwa, M., El Bastawesy, M., Ragab, D., Othman, A., Assaggaf, H. M., & Abotalib, A. Z. (2021). Toward an integrated and sustainable water resources management in structurally-controlled watersheds in desert environments using geophysical and remote sensing methods. Sustainability, 13(7), 4004.
Balcik, F. B., & Goksel, C. (2012). Determination of magnitude and direction of land use/land cover cnges in Terkos water basin. Istanbul. Intl Archives of the Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 39, 275–9.
Bhaga, T. D., Dube, T., Shekede, M. D., & Shoko, C. (2020). Impacts of climate variability and drought on surface water resources in Sub-Saharan Africa using remote sensing: A review. Remote Sensing, 12(24), 4184.
Bijeesh, T. V., & Narasimhamurthy, K. N. (2020). Surface water detection and delineation using remote sensing images: A review of methods and algorithms. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 6, 1–23.
Bioresita, F., Puissant, A., Stumpf, A., & Malet, J. P. (2019). Fusion of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 image time series for permanent and temporary surface water mapping. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(23), 9026–9049.
Blickensdörfer, L., Schwieder, M., Pflugmacher, D., Nendel, C., Erasmi, S., & Hostert, P. (2022). Mapping of crop types and crop sequences with combined time series of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 data for Germany. Remote Sensing of Environment, 269, 112831.
Caballero, I., & Navarro, G. (2021). Monitoring cyanoHABs and water quality in Laguna Lake (Philippines) with Sentinel-2 satellites during the 2020 Pacific typhoon season. Science of the Total Environment, 788, 1166800.
Casal, G., Monteys, X., Hedley, J., Harris, P., Cahalane, C., & McCarthy, T. (2019). Assessment of empirical algorithms for bathymetry extraction using Sentinel-2 data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(8), 2855–2879.
Chen, T., Song, C., Ke, L., Wang, J., Liu, K., & Wu, Q. (2021). Estimating seasonal water budgets in global lakes by using multi-source remote sensing measurements. Journal of Hydrology, 593, 125781.
Chen, Q., Liu, W., & Huang, C. (2022). Long-term 10 m resolution water dynamics of Qinghai lake and the driving factors. Water 14(4), 671.
Copernicus (n.d.) https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home. Accessed on April 8, 2023
Coskun, H. G. (2009). Remote sensing and GIS techniques for temporal evaluation of environmental impacts on major drinking water dam and Basin of Metropolis Istanbul. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 18, 261–269.
Coskun, H. G., Gulergun, O., & Yilmaz, L. (2006). Monitoring of protected bands of Terkos drinking water reservoir of metropolitan Istanbul near the Black Sea coast using satellite data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 8(1), 49–60.
Dang, A. T., Kumar, L., Reid, M., & Nguyen, H. (2021). Remote sensing approach for monitoring coastal wetland in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam: Change trends and their driving forces. Remote Sensing, 13(17), 3359.
Deng, X., Song, C., Liu, K., Ke, L., Zhang, W., Ma, R., & Wu, Q. (2020). Remote sensing estimation of catchment-scale reservoir water impoundment in the upper Yellow River and implications for river discharge alteration. Journal of Hydrology, 585, 124791.
Dervisoglu, A. (2021). Analysis of the temporal changes of inland Ramsar Sites in Turkey using Google Earth Engine. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(8), 521.
Dervisoglu, A. (2022). Investigation of long and short-term water surface area changes in coastal Ramsar Sites in Turkey with Google Earth Engine. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(1), 46.
Ebelediye 2024 https://www.ebelediye.info/haberler/iski-2023-yili-su-tuketim-rakamlarini-paylasti#:~:text=2022'de%201.103.672.,t%C3%BCketilen%20g%C3%BCn%20%20olarak%20%20tarihe%20ge%C3%A7ti. (Accessed on January 20, 2024)
ESRI, Living Atlas. https://livingatlas.arcgis.com/landcover/. Accessed on February 14, 2023
European Environment Agency. (2021). Water resources across Europe: Confronting water stress: An updated assessment. Publications Office.
Firatli, E., Dervisoglu, A., Yagmur, N., Musaoglu, N., & Tanik, A. (2022). Spatio-temporal assessment of natural lakes in Turkey. Earth Science Informatics, 15(2), 951–964.
General Directorate of Meteorology. https://www.mgm.gov.tr/FILES/iklim/yillikiklim/2020-iklim-raporu.pdf. Accessed on May, 2023
Goksel, C. (1998). Monitoring of a water basin area in Istanbul using remote sensing data. Water Science and Technology, 38(11), 209–216.
Goksel. C., Kaya. S., & Musaoglu. N. 2021 Using satellite data for land use cnge detection: a case study for Terkos water basin. Istanbul. In Observing our environment from space (pp. 299–302) CRC Press
Google Earth Engine. Available online: https://earthengine.google.com/. Accessed on June 20, 2023
Gorelick, N., Hancher, M., Dixon, M., Ilyushchenko, S., Thau, D., & Moore, R. (2017). Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sensing of Environment, 202, 18–27.
Gosling, S. N., & Arnell, N. W. (2016). A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Climatic Change, 134, 371–385.
Goyens, C., Lavigne, H., Dille, A., & Vervaeren, H. (2022). Using hyperspectral remote sensing to monitor water quality in drinking water reservoirs. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5607.
Griffith, A. W., & Gobler, C. J. (2020). Harmful algal blooms: A climate change co-stressor in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Harmful Algae, 91, 101590.
Gu, Q., Li, J., Deng, J., Lin, Y., Ma, L., Wu, C., & Hong, Y. (2015). Eco-environmental vulnerability assessment for large drinking water resource: A case study of Qiandao Lake Area, China. Frontiers of Earth Science, 9, 578–589.
Ho, J. C., & Michalak, A. M. (2020). Exploring temperature and precipitation impacts on harmful algal blooms across continental US lakes. Limnology and Oceanography, 65(5), 992–1009.
Ho, J. C., Michalak, A. M., & Pahlevan, N. (2019). Widespread global increase in intense lake phytoplankton blooms since the 1980s. Nature, 574(7780), 667–670.
Hossain, M. S., & Saha, U. (2024). Study on shoreline migration and island dynamics over the last five decades in the Muriganga River using multi-temporal satellite images. Environ Monitoring and Assessment, 196, 199.
Hu, Q., Li, C., Wang, Z., Liu, Y., & Liu, W. (2022). Continuous monitoring of the surface water area in the Yellow River basin during 1986–2019 using available Landsat imagery and the Google Earth Engine. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(5), 305.
IBB, Open Data Portal. https://data.ibb.gov.tr/dataset/ilce-bazinda-su-tuketim-miktari. Accessed on May 24, 2023
Ioannou, I., Gilerson, A., Ondrusek, M., Foster, R., El-Habashi, A., Bastani, K., & Ahmed, S. (2014). Algorithms for the remote estimation of chlorophyll-a in the Chesapeake Bay. In Ocean Sensing and Monitoring VI, 9111, 257–266. SPIE.
IPCC Climate Change 2021: Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., et al., Eds.; The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022
Irannezhad, M., Ahmadi, B., Liu, J., Chen, D., & Matthews, J. H. (2022). Global water security: A shining star in the dark sky of achieving the sustainable development goals. Sustainable Horizons, 1, 100005.
ISKI. (2022). Activity report of 2022. Istanbul water and sewerage administration. https://www.iski.gov.tr/web/assets/SayfalarDocs/faaliyetraporlari/faaliyetraporu/pdf/2022%20Faaliyet%20Raporu.pdf
Istanbul Climate Change Action Plan (ICCAP). (2021). Available online: https://cevre.ibb.istanbul/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/ist_iklim_degisikligi_eylem_plani.pdf. Accessed on May 24, 2023
Karakuyu, M., Karaburun, A., & Fatih, K. A. R. A. (2012). Kentleşmenin Büyükçekmece Gölü Havzasindaki Arazi Kullanim Değişimleri Üzerindeki Etkisinin Zamansal Analizi. Marmara Coğrafya Dergisi, 26, 42–54. (in Turkish).
Karpuzcu, M. E., Fakioglu, M., & Ozturk, I. (2021). Analysis of eutrophication potential in main drinking water basins of Istanbul. Clean-Soil, Air, Water, 49(4), 2000222.
Kaya, Ş, Şeker, D. Z., & Tanik, A. (2014). Temporal impact of urbanization on the protection zones of two drinking water reservoirs in Istanbul. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 23(12), 2984–2989.
Keith, D., Rover, J., Green, J., Zalewsky, B., Charpentier, M., Thursby, G., & Bishop, J. (2018). Monitoring algal blooms in drinking water reservoirs using the Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39(9), 2818–2846.
Kislik, C., Dronova, I., Grantham, T. E., & Kelly, M. (2022). Mapping algal bloom dynamics in small reservoirs using Sentinel-2 imagery in Google Earth Engine. Ecological Indicators, 140, 109041.
Kucukmehmetoglu, M., & Geymen, A. (2008). Measuring the spatial impacts of urbanization on the surface water resource basins in Istanbul via remote sensing. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 142(1), 153–169.
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Shi, K., Zhu, G., Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., & Guo, Y. (2017). Monitoring spatiotemporal variations in nutrients in a large drinking water reservoir and their relationships with hydrological and meteorological conditions based on Landsat 8 imagery. Science of the Total Environment, 599, 1705–1717.
Li, M., Hong, L., Guo, J., & Zhu, A. (2022). Automated extraction of lake water bodies in complex geographical environments by fusing Sentinel-1/2 Data. Water, 14(1), 30.
Lins, R. C., Martinez, J. M., Motta Marques, D. D., Cirilo, J. A., & Fragoso, C. R., Jr. (2017). Assessment of chlorophyll-a remote sensing algorithms in a productive tropical estuarine-lagoon system. Remote Sensing, 9(6), 516.
Liu, X., Shi, Z., Huang, G., Bo, Y., & Chen, G. (2020). Time series remote sensing data-based identification of the dominant factor for inland lake surface area change: Anthropogenic activities or natural events? Remote Sensing, 12(4), 612.
McFeeters, S. K. (1996). The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(7), 1425–1432.
McGrane, S. J. (2016). Impacts of urbanisation on hydrological and water quality dynamics, and urban water management: A review. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 61, 2295–2311.
Mentese. H. & Eymen. A. (2021). Investigation of temporal change of land use in Elmali basin using remote sensing and geographic information systems. Isprs Annals of Photogrammetry. Remote Sensing & Spatial Information Sciences
Miao, S., Liu, C., Qian, B., & Miao, Q. (2020). Remote sensing-based water quality assessment for urban rivers: A study in linyi development area. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 34586–34595.
Mishra, S., & Mishra, D. R. (2012). Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 117, 394–406.
Mishra, D. R., Schaeffer, B. A., & Keith, D. (2014). Performance evaluation of normalized difference chlorophyll index in northern Gulf of Mexico estuaries using the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean. Giscience & Remote Sensing, 51(2), 175–198.
Mohammadi, A. A., Zarei, A., Majidi, S., Ghaderpoury, A., Hashempour, Y., Saghi, M. H., & Ghaderpoori, M. (2019). Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic health risk assessment of heavy metals in drinking water of Khorramabad Iran. MethodsX, 6, 1642–1651.
Moore, C., Barnard, A., Fietzek, P., Lewis, M. R., Sosik, H. M., White, S., & Zielinski, O. (2009). Optical tools for ocean monitoring and research. Ocean Science, 5(4), 661–684.
Mpandeli, S., Nhamo, L., Moeletsi, M., Masupha, T., Magidi, J., Tshikolomo, K., & Mabhaudhi, T. (2019). Assessing climate change and adaptive capacity at local scale using observed and remotely sensed data. Weather and Climate Extremes, 26, 100240.
Musaoglu, N., Tanik, A., & Kocabas, V. (2005). Identification of land-cover changes through image processing and associated impacts on water reservoir conditions. Environmental Management, 35(2), 220–230.
Musaoglu, N., Gurel, M., Ulugtekin, N., Tanik, A., & Seker, D. Z. (2006). Use of remotely sensed data for analysis of land-use change in a highly urbanized district of mega city, Istanbul. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 41(9), 2057–2069.
Mushtaq, F., Nee Lala, M.G. (2016). Remote estimation of water quality parameters of Himalayan lake (Kashmir) using Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Geocarto International. 1–12
Nath, B., Ni-Meister, W., & Choudhury, R. (2021). Impact of urbanization on land use and land cover change in Guwahati city, India and its implication on declining groundwater level. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 12, 100500.
Oliveira, E. N., Fernandes, A. M., Kampel, M., Cordeiro, R. C., Brandini, N., Vinzon, S. B., & Paranhos, R. (2016). Assessment of remotely sensed chlorophyll-a concentration in Guanabara Bay Brazil. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 10(2), 026003–026003.
Oularé, S., Sokeng, V. C. J., Kouamé, K. F., Komenan, C. A. K., Danumah, J. H., Mertens, B., & Pillot, B. (2022). Contribution of Sentinel-3A radar altimetry data to the study of the water level variations in Lake Buyo (West of Côte d’Ivoire). Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5602.
Quang, D. N., Linh, N. K., Tam, H. S., & Viet, N. T. (2021). Remote sensing applications for reservoir water level monitoring, sustainable water surface management, and environmental risks in Quang Nam province Vietnam. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 12(7), 3045–3063.
Rizvi, S., Rustum, R., Deepak, M., Wright, G. B., & Arthur, S. (2021). Identifying and analyzing residential water demand profile; including the impact of COVID-19 and month of Ramadan, for selected developments in Dubai United Arab Emirates. Water Supply, 21(3), 1144–1156.
Ross, M. R., Topp, S. N., Appling, A. P., Yang, X., Kuhn, C., Butman, D., & Pavelsky, T. M. (2019). AquaSat: A data set to enable remote sensing of water quality for inland waters. Water Resources Research, 55(11), 10012–10025.
Sagan, V., Peterson, K. T., Maimaitijiang, M., Sidike, P., Sloan, J., Greeling, B. A., & Adams, C. (2020). Monitoring inland water quality using remote sensing: Potential and limitations of spectral indices, bio-optical simulations, machine learning, and cloud computing. Earth-Science Reviews, 205, 103187.
Schmitt, M. (2020). Potential of large-scale inland water body mapping from sentinel-1/2 data on the example of bavaria’s lakes and rivers. PFG-Journal of Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Science, 88(3–4), 271–289.
Shrestha, A., Kazama, S., & Takizawa, S. (2021). Influence of service levels and COVID-19 on water supply inequalities of community-managed service providers in Nepal. Water, 13(10), 1349.
Tang, H., Lu, S., Ali Baig, M. H., Li, M., Fang, C., & Wang, Y. (2022). Large-scale surface water mapping based on landsat and sentinel-1 images. Water, 14(9), 1454.
Tanik. A., Musaoglu. N., Kaya. S. & Seker. D. Z. (2016). Integration of RS and GIS as modern technological tools in environmental management studies: Case studies from Istanbul. In Conference: Conference: The 37th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing.
Tian, H., Li, W., Wu, M., Huang, N., Li, G., Li, X., & Niu, Z. (2017). Dynamic monitoring of the largest freshwater lake in China using a new water index derived from high spatiotemporal resolution Sentinel-1A data. Remote Sensing, 9(6), 521.
Torbick, N., Hession, S., Hagen, S., Wiangwang, N., Becker, B., & Qi, J. (2013). Mapping inland lake water quality across the Lower Peninsula of Michigan using Landsat TM imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 34(21), 7607–7624.
Tsai, Y. L. S., Klein, I., Dietz, A., & Oppelt, N. (2020). Monitoring large-scale inland water dynamics by fusing Sentinel-1 SAR and Sentinel-3 altimetry data and by analyzing causal effects of snowmelt. Remote Sensing, 12(23), 3896.
TUIK https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Search/Search?text=t%C3%BCrkiye%20ve%20istanbul%20n%C3%BCfusu&dil=1. Accessed on January 20, 2024
Visualcapitalist https://www.visualcapitalist.com/ranked-the-worlds-largest-cities-by-population/. Accessed on January 20, 2024
Wagh, P., Sojan, J. M., Babu, S. J., Valsala, R., Bhatia, S., & Srivastav, R. (2021). Indicative lake water quality assessment using remote sensing images-effect of COVID-19 lockdown. Water, 13(1), 73.
Wang, C., Jiang, W., Deng, Y., Ling, Z., & Deng, Y. (2021). Long time series water extent analysis for SDG 6.6. 1 based on the GEE platform: A case study of Dongting Lake. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 15, 490–503.
Wang, X., Xiao, X., Qin, Y., Dong, J., Wu, J., & Li, B. (2022). Improved maps of surface water bodies, large dams, reservoirs, and lakes in China. Earth System Science Data, 14(8), 3757–3771.
Watanabe, F. S. Y., Alcantara, E., Rodrigues, T. W. P., Imai, N. N., Barbosa, C. C. F., & Rotta, L. H. D. S. (2015). Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration and the trophic state of the Barra Bonita hydroelectric reservoir using OLI/Landsat-8 images. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(9), 10391–10417.
Watanabe, F., Alcantara, E., Rodrigues, T., Rotta, L., Bernardo, N., & Imai, N. (2017). Remote sensing of the chlorophyll-a based on OLI/Landsat-8 and MSI/Sentinel-2A (Barra Bonita reservoir, Brazil). Anais Da Academia Brasileira De Ciências, 90, 1987–2000.
Whitehead, P. G., Wilby, R. L., Battarbee, R. W., Kernan, M., & Wade, A. J. (2009). A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 54(1), 101–123.
World Health Organization (WHO) (2004). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (Vol. 1). World Health Organization.
Xia, H., Zhao, J., Qin, Y., Yang, J., Cui, Y., Song, H., & Meng, Q. (2019). Changes in water surface area during 1989–2017 in the Huai River Basin using Landsat data and Google earth engine. Remote Sensing, 11(15), 1824.
Yagmur, N., Bilgilioglu, B. B., Dervisoglu, A., Musaoglu, N., & Tanik, A. (2021). Long and short-term assessment of surface area changes in saline and freshwater lakes via remote sensing. Water and Environment Journal, 35(1), 107–122.
Yilmaz, N. (2018). Assesment of seasonal variation of phytoplankton and related water quality parameters of Sazlidere Dam Lake (Istanbul, Turkey). Water Treat, 131, 107–113.
Zegait, R., Bouznad, I. E., Remini, B., Bengusmia, D., Ajia, F., Guastaldi, E., ... & Petrone, D. (2023). Comprehensive model for sustainable water resource management in Southern Algeria: integrating remote sensing and WEAP model. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 1–16
Zhou, Y., Zhang, Y., Shi, K., Liu, X., & Niu, C. (2015). Dynamics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter influenced by hydrological conditions in a large, shallow, and eutrophic lake in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 12992–13003.
Acknowledgements
We thank the ISKI General Directorate for sharing Istanbul’s monthly water consumption amounts and dam occupancy rate data. We thank the General Directorate of Meteorology for sharing Istanbul meteorological station data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Adalet Dervisoglu and Nur Yagmur wrote the main manuscript text, and Fulya Basak Sariyilmaz prepared figures 2,12. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declarations
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dervisoglu, A., Yagmur, N. & Sariyilmaz, F.B. A comprehensive research on open surface drinking water resources in Istanbul using remote sensing technologies. Environ Monit Assess 196, 377 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12496-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12496-3