Abstract
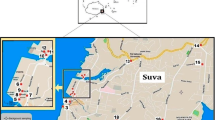
Metal-containing dust is a potential severe environmental and human health threat. Metals present in dust may originate from car exhausts, tear and wear of tires, and vehicular emissions, which are less manageable. Metal-containing dust from roads can contaminate the soils, and crops alongside motorway. This study aimed to investigate the Pb Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn concentrations in dust, soil, and vegetation collected from the M4 motorway Faisalabad. The results indicated that average metal concentrations in dust from all sites varies (Pb) 44.01 mg kg−1, (Cd) 1.22 mg kg−1, (Cu) 49.5 mg kg−1, (Ni) 28.3 mg kg−1, and (Zn) 113.7 mg kg−1. The pollution assessment indices CF and PLI of Industrial city and Painsra had comparatively maximum levels of environmental pollution. Moreover, the geo-accumulation index (Igeo) of metals was high at Chak 115 and Painsra, while Igeo at ten sites was in the following descending order: Cd > Pb > Cu > Ni > Zn. Furthermore, it was identified that the maximum ecological risk index (Eir) was in declining order, i.e., Cd > Pb > Cu > Ni > Zn, at all sites. The potential ecological risk was categorized as high risk in all respective sites. The particulate matter fractions PM2.5 and PM10 represented the maximum risk at the Industrial city site, which was unhealthy, although the Painsra site had poor air quality. The total suspended particulate was classified as hazardous at FDA city and Painsra. In contrast, food crops (maize, sugar cane, and sesame) and soil along the M4 motorway have similar Pb, Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn contamination patterns like dust. However, two crops, maize and sugarcane, along the M4 motorway were found to be more polluted. The level of metals contamination through dust disposition was consistently higher adjacent to roads, possibly indicating depraved impacts on food crops.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Adamiec, E., Jarosz-Krzemińska, E., & Wieszała, R. (2016). Heavy metals from non-exhaust vehicle emissions in urban and motorway road dusts. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188(6), 1–11.
Ahmad, K., Muhammad, S., Ali, W., Jadoon, I. A. K., & Rasool, A. (2020). Occurrence, source identification and potential risk evaluation of heavy metals in sediments of the Hunza River and its tributaries. Gilgit-Baltistan. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 18, 100700.
Akbar, K. F., Hale, W. H. G., Headley, A. D., & Athar, M. (2006). Heavy metal contamination of roadside soils of Northern England. Soil Water Res, 1(4), 158–163.
Al-Khashman, O. A. (2007). Determination of metal accumulation in deposited street dusts in Amman. Jordan. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29(1), 1–10.
Alloway, B. J. (Ed.) (2013). Sources of heavy metals and metalloids in soils. In Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. Springer, pp. 11–50.
Amato, F., Cassee, F. R., van der Gon, H. A. C. D., Gehrig, R., Gustafsson, M., Hafner, W., et al. (2014). Urban air quality: The challenge of traffic non-exhaust emissions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 275, 31–36.
Apeagyei, E., Bank, M. S., & Spengler, J. D. (2011). Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban-rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmospheric Environment, 45(13), 2310–2323.
Arslan, H. (2001). Heavy metals in street dust in Bursa, Turkey. Journal of Trace and Microprobe Techniques, 19(3), 439–445.
Butte, W., & Heinzow, B. (2002). Pollutants in house dust as indicators of indoor contamination. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 175, 1–46.
Centre, C. N. E. M. (1990). Background values of soil elements in China. China Environmental Science, 1(9), 9.
Chang, S.-H., Wang, K.-S., Chang, H.-F., Ni, W.-W., Wu, B.-J., Wong, R.-H., & Lee, H.-S. (2009). Comparison of source identification of metals in road-dust and soil. Soil and Sediment Contamination, 18(5), 669–683.
Charlesworth, S., Everett, M., McCarthy, R., Ordonez, A., & De Miguel, E. (2003). A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands. UK. Environment International, 29(5), 563–573.
Chen, Q. Y., Tyrer, M., Hills, C. D., Yang, X. M., & Carey, P. (2009). Immobilisation of heavy metal in cement-based solidification/stabilisation: A review. Waste Management, 29(1), 390–403.
Chen, X., Xia, X., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, P. (2010). Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing. China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181(1–3), 640–646.
de Miguel, E., Llamas, J. F., Chacón, E., Berg, T., Larssen, S., Røyset, O., & Vadset, M. (1997). Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: Unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmospheric Environment, 31(17), 2733–2740.
Deepalakshmi, A. P., Ramakrishnaiah, H., Ramachandra, Y. L., & Kumar, N. N. (2014). Leaves of higher plants as indicators of heavy metal pollution along the urban roadways. Int J Sci Technol, 3(6), 340–346.
Duong, T. T. T., & Lee, B.-K. (2011). Determining contamination level of heavy metals in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(3), 554–562.
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Wong, C., Aydin, A., Song, Z., You, M., & Li, X. D. (2006). Heavy metal contamination and distribution in the urban environment of Guangzhou, SE China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 28, 375–391.
Faiz, Y., Tufail, M., Javed, M. T., & Chaudhry, M. M. (2009). Road dust pollution of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn along Islamabad expressway. Pakistan. Microchemical Journal, 92(2), 186–192.
Gunawardana, C., Goonetilleke, A., Egodawatta, P., Dawes, L., & Kokot, S. (2012). Source characterisation of road dust based on chemical and mineralogical composition. Chemosphere, 87(2), 163–170.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Hjortenkrans, D. S. T., Bergbäck, B. G., & Häggerud, A. V. (2008). Transversal immission patterns and leachability of heavy metals in road side soils. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 10(6), 739–746.
Hseu, Z.-Y., Chen, Z.-S., Tsai, C.-C., Tsui, C.-C., Cheng, S.-F., Liu, C.-L., & Lin, H.-T. (2002). Digestion methods for total heavy metals in sediments and soils. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 141(1), 189–205.
Ikenaka, Y., Nakayama, S. M. M., Muzandu, K., Choongo, K., Teraoka, H., Mizuno, N., & Ishizuka, M. (2010). Heavy metal contamination of soil and sediment in Zambia. African Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(11), 729–739.
Jan, F. A., Saleem, S., Faisal, S., Hussain, I., Rauf, A., & Ullah, N. (2021). Road dust as a useful tool for the assessment of pollution characteristics and health risks due to heavy metals: A case study from District Charsadda, Pakistan. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14, 1–13.
Jian-Hua, M. A., Chun-Jie, C. H. U., Jian, L. I., & Bo, S. (2009). Heavy metal pollution in soils on railroad side of Zhengzhou-Putian section of Longxi-Haizhou railroad. China. Pedosphere, 19(1), 121–128.
Jiries, A. (2003). Vehicular contamination of dust in Amman. Jordan. Environmentalist, 23(3), 205–210.
Kabadayi, F., & Cesur, H. (2010). Determination of Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni Co, Cd, and Mn in road dusts of Samsun City. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 168, 241–253.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2000). Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press.
Kabir, M. H., Kormoker, T., Shammi, R. S., Tusher, T. R., Islam, M. S., Khan, R., et al. (2022). A comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in road dusts along a hectic national highway of Bangladesh: Spatial distribution, sources of contamination, ecological and human health risks. Toxin Reviews, 41(3), 860–879.
Khoder, M. I., Al Ghamdi, M. A., & Shiboob, M. H. (2012). Heavy metal distribution in street dust of urban and industrial areas in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. JKAU: Met. Env & Arid Land Agric. Sc, 23, 55–75.
Kong, S., Lu, B., Ji, Y., Zhao, X., Chen, L., Li, Z., et al. (2011). Levels, risk assessment and sources of PM10 fraction heavy metals in four types dust from a coal-based city. Microchemical Journal, 98(2), 280–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2011.02.012
Kumari, M., Kumar, A., & Bhattacharya, T. (2023). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in street dust: concentrations, bio accessibility, and human health risks in coal mine and thermal power plant complex. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45(10), 7339–7362.
Leghari, S. K., Zaid, M. A., Sarangzai, A. M., Faheem, M., & Shawani, G. R. (2014). Effect of road side dust pollution on the growth and total chlorophyll contents in Vitis vinifera L.(grape). African Journal of Biotechnology, 13(11).
Liang, S.-Y., Cui, J.-L., Bi, X.-Y., Luo, X.-S., & Li, X.-D. (2019). Deciphering source contributions of trace metal contamination in urban soil, road dust, and foliar dust of Guangzhou, southern China. Science of the Total Environment, 695, 133596.
Lone, A. H., Lal, E. P., Thakur, S., Ganie, S. A., Wani, M. S., Khare, A., et al. (2013). Accumulation of heavy metals on soil and vegetable crops grown on sewage and tube well water irrigation. Scientific Research and Essays, 8(44), 2187–2193.
Lu, X., Pan, H., & Wang, Y. (2017). Pollution evaluation and source analysis of heavy metal in roadway dust from a resource-typed industrial city in Northwest China. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(3), 587–595.
Mafuyai, G. M., Kamoh, N. M., Kangpe, N. S., Ayuba, S. M., & Eneji, I. S. (2015). Heavy metals contamination in roadside dust along major traffic roads in Jos metropolitan area, Nigeria.
Meza-Figueroa, D., De la O-Villanueva, M., & De la Parra, M. L. (2007). Heavy metal distribution in dust from elementary schools in Hermosillo, Sonora. México. Atmospheric Environment, 41(2), 276–288.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2, 108–118.
Norouzi, S., Khademi, H., Cano, A. F., & Acosta, J. A. (2015). Using plane tree leaves for biomonitoring of dust borne heavy metals: A case study from Isfahan, Central Iran. Ecological Indicators, 57, 64–73.
Olukanni, D. O., & Adebiyi, S. A. (2012). Assessment of vehicular pollution of road side soils in Ota Metropolis, Ogun State, Nigeria. International Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 12(4), 40–46.
Padoan, E., Ajmone-Marsan, F., Querol, X., & Amato, F. (2018). An empirical model to predict road dust emissions based on pavement and traffic characteristics. Environmental Pollution, 237, 713–720.
Pal, R., Gupta, A., & Tripathi, A. (2014). Assessment of heavy metals in suspended particulate matter in Moradabad. India. Journal of Environmental Biology, 35(2), 357.
Qadeer, A., Saqib, Z. A., Ajmal, Z., Xing, C., Khalil, S. K., Usman, M., et al. (2020). Concentrations, pollution indices and health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust from two urbanized cities of Pakistan: Comparing two sampling methods for heavy metals concentration. Sustainable Cities and Society, 53, 101959.
Rahman, M. S., Khan, M. D. H., Jolly, Y. N., Kabir, J., Akter, S., & Salam, A. (2019). Assessing risk to human health for heavy metal contamination through street dust in the Southeast Asian Megacity: Dhaka, Bangladesh. Science of the Total Environment, 660, 1610–1622.
Rasmussen, P. E., Subramanian, K. S., & Jessiman, B. J. (2001). A multi-element profile of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soils in the city of Ottawa Canada. Science of the Total Environment, 267(1–3), 125–140.
Raza Ahmad, H., Mehmood, K., Sardar, M. F., Maqsood, M. A., Ur Rehman, M. Z., Zhu, C., & Li, H. (2020). Integrated risk assessment of potentially toxic elements and particle pollution in urban road dust of megacity of Pakistan. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 26(7), 1810–1831.
Roy, A., & Bhattacharya, T. (2022). Ecological and human health risks from pseudo-total and bio-accessible metals in street dusts. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(2), 101.
Roy, S., Gupta, S. K., Prakash, J., Habib, G., Baudh, K., & Nasr, M. (2019). Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in road dust in the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 30413–30425.
Roy, A., Bhattacharya, T., & Kumari, M. (2020). Air pollution tolerance, metal accumulation and dust capturing capacity of common tropical trees in commercial and industrial sites. Science of the Total Environment, 722, 137622.
Sayyed, G., & Sayadi, M. H. (2011). Variations in the heavy metal accumulations within the surface soils from the Chitgar industrial area of Tehran. Proceedings of the International Academy of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 1(1), 36–46.
Shabbaj, I. I., Alghamdi, M. A., Shamy, M., Hassan, S. K., Alsharif, M. M., & Khoder, M. I. (2018). Risk assessment and implication of human exposure to road dust heavy metals in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(1), 36.
Shah, M. H., Shaheen, N., & Nazir, R. (2012). Assessment of the trace elements level in urban atmospheric particulate matter and source apportionment in Islamabad Pakistan. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 3(1), 39–45.
Shah, K., An, N., Ma, W., Ara, G., Ali, K., & Kamanova, S. (2020). Chronic cement dust load induce novel damages in foliage and buds of Malus domestica. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1–12.
Shehzad, M. T., Sabir, M., Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Zia, M. A., & Naidu, R. (2022). Arsenic concentrations in soil, water, and rice grains of rice-growing areas of Punjab, Pakistan: Multivariate statistical analysis. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(5), 346.
Shi, G., Chen, Z., Xu, S., Zhang, J., Wang, L., Bi, C., & Teng, J. (2008). Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai. China. Environmental Pollution, 156(2), 251–260.
Soltani, N., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Tavakol, T., Lahijanzadeh, A. R., Jaafarzadeh, N., & Kermani, M. (2015). Ecological and human health hazards of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in road dust of Isfahan metropolis Iran. Science of the Total Environment, 505, 712–723.
Swaileh, K. M., Hussein, R. M., & Abu-Elhaj, S. (2004). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in roadside surface soil and vegetation from the West Bank. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 47, 23–30.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1995). The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2), 241–265.
Thorpe, A., & Harrison, R. M. (2008). Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 400(1–3), 270–282.
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen, 33(1), 566–575.
Trujillo-González, J. M., Torres-Mora, M. A., Keesstra, S., Brevik, E. C., & Jiménez-Ballesta, R. (2016). Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Science of the Total Environment, 553, 636–642.
U.S. EPA. (2010). National Center for Environmental Research PM Centers. Available at http://www.epa.gov/ncer/science/pm/centers.html. Accessed 2 Dec 2009.
Wahab, M. I. A., Abd Razak, W. M. A., Sahani, M., & Khan, M. F. (2020). Characteristics and health effect of heavy metals on non-exhaust road dusts in Kuala Lumpur. Science of the Total Environment, 703, 135535.
Wei, X., Gao, B., Wang, P., Zhou, H., & Lu, J. (2015). Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112, 186–192.
WHO. (1996). Permissible limits of heavy metals in soil and plants. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Yuen, J. Q., Olin, P. H., Lim, H. S., Benner, S. G., Sutherland, R. A., & Ziegler, A. D. (2012). Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in road deposited sediments in residential and light industrial neighborhoods of Singapore. Journal of Environmental Management, 101, 151–163.
Zhao, L., Hu, G., Yan, Y., Yu, R., Cui, J., Wang, X., & Yan, Y. (2019). Source apportionment of heavy metals in urban road dust in a continental city of eastern China: Using Pb and Sr isotopes combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Atmospheric Environment, 201, 201–211.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support from University of Agriculture, Faisalabad. We acknowledge editors and reviewers for refining the language of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muhammad Hassan Bashir contributed to planning the experiment, executed the experiment, and completed the analytical work; Hamaad Raza Ahmad supervised the planning of experiment and proof reading of the final draft and submission; Ghulam Murtaza contributed to planning and executing the experiment, co-supervised the research, and proofread the draft; Muhammad Farrakh Nawaz helped in planning and final proof reading of the draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
All the authors are willing and have no conflict in publishing the article in this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bashir, M.H., Ahmad, H.R., Murtaza, G. et al. Spatial distribution of heavy metals, source identification, risk assessment and particulate matter in the M4 motorway. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1541 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12120-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12120-w