Abstract
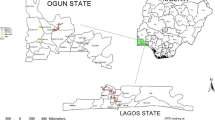
Knowledge of dietary intakes of essential elements in groundwater is important for proper assessment of the actual contribution of drinking water to daily nutrient requirements. This study assessed the daily intake of nutritional elements in drinking groundwater of Lagos and Ogun States of Nigeria. One hundred and seventy (170) water samples were collected and analyzed for thirteen (13) nutritional elements (K, Mg, Ca, Co, Fe, Cu, Zn, Mo, Se, Na, Mn, Cr, and I) by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP/MS). Chronic daily intake CDI of the nutritional elements was higher for children and infants than adults in all cases. Percentages of tolerable daily intake reference value (TIRV) obtained for Lagos State groundwater were Mg 0.425%, Ca 0.309%, Fe 14.0%, Cu 1.84%, Zn 6.25%, Mo 0.057%, and Mn 1.08%; for Ogun State groundwater, % TIRV were Mg 1.99%, Ca 0.586%, Fe 81.1%, Cu 2.12%, Zn 9.21%, Mo 1.16%, and Mn 0.023%. The order of dermal absorption by an adult in Lagos when the water is used for bathing daily was Cr > Mn > Fe > Zn > Cu while the order in Ogun was Fe > Mn > Zn > Cu > Cr. The research concluded that groundwater alone cannot provide enough essential elements for human dietary needs in the study area.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used is from the PhD work of the corresponding author while the co-authors are the minor and major supervisors. Some of the raw data is attached as supplementary materials.
References
Abdul, R. M., Mutnuri, L., Dattatreya, P. J., & Mohan, D. A. (2012). Assessment of drinking water quality using ICPMS and microbiological methods in the Bholakpur area, Hyderabad, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 1581–1592.
Aher, K. R. (2012). Geochemistry and assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes: A case study of Sukhana River sub basin, district Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. International Journal of Recent Trends Science Technology, 4, 45–49.
Al-Rimawi, F., Kanan, K., & Qutob, M. (2013). Analysis of different rare metals, rare earth elements, and other common metals in groundwater of South West Bank/Palestine by ICP/MS-data and health aspects. Journal of Environmental Protection, 4, 1157–1164.
Andersen, S., Petersen, S. B., & Laurberg, P. (2002). Iodine in drinking water in Denmark is bound in humic substances. European Journal of Endocrinology, 147, 663–670.
Asubiojo, O. I., Nkono, N. A., Ogunsua, A. O., Oluwole, A. F., Wardi, N. I., Akanle, O. A., & Spyrou, N. M. (1997). Trace elements in drinking and ground water samples in southern Nigeria. The Science of the Total Environment, 208, 1–8.
Ayedun, H., Gbadebo, A. M., Idowu, O. A., & Arowolo, T. A. (2015). Toxic elements in groundwater of Lagos and Ogun States, Southwest, Nigeria and their human health risk assessment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4319-7
Ayedun, H., Arowolo, T. A., Gbadebo, A. M., & Idowu, O. A. (2017). Evaluation of rare earth elements in groundwater of Lagos and Ogun States, Southwest, Nigeria. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39, 649–664.
Barton, H. (2010). Predicted intake of trace elements and minerals via household drinking water by 6-year-old children from Krakow, Poland. Part 5 Zinc. Food Additives and Contaminants, 27, 315–326.
Bashir, Y., Sneddon, J. F., Staunton, H. A., Hayewood, G. A., Simpson, I. A., McKenna, W. J., & Camm, A. J. (1993). Effects of long-term oral magnesium chloride replacement in congestive heart failure secondary to coronary heart disease. American Journal of Cardiology, 72, 1156–1162.
Bernard, E., & Ayeni, N. (2012). Physicochemical analysis of groundwater samples of Bichi local Government of Kano State of Nigeria. ARPN Journal of Science and Technology, 325–332.
Białecka – Dębek, A., & Pietruszka, B. (2019). The association between hydration status and cognitive function among free-living elderly volunteers. Aging Clinical Experimental ResEarch, 31(5), 695–703.
Bingham, S. A., Williams, R., Cole, T. J., Price, C. P., & Cummings, J. H. (1988). Reference values for analytes of 24 h urine collections known to be complete. Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, 25, 610–619.
Briend, A., Hoque, B. A., & Aziz, K. M. A. (1990). Iron in tube well water and linear growth in rural Bangladesh. Archive of Disorder Children, 65, 224–237.
Camaschella, C. (2015). Iron-deficiency anemia. N English Journal of MedIcine, 372(19), 1832–1843. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1401038
Cannas, D., Loi, E., Serra, M., Firinu, D., Valera, P., & Zavattari, P. (2020). Relevance of essential trace elements in nutrition and drinking water for human health and autoimmune disease risk. Nutrients, 12, 2074–2096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072074
Cao, C., Xiao, Z., Wu, Y., & Ge, C. (2020). Diet and skin aging—from the perspective of food nutrition. Nutrients, 12(3), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030870
Chandra, R. K. (1984). Excessive intake of zinc impairs immune responses. Journal of American Medical AssocIation, 252, 1443–1446.
Costello, R. B., & Moser-Veillon, P. B. (1992). A review of magnesium intake in the elderly. A Cause of Concern. Magnesium Research, 5, 61–67.
Davis, C. D., Wolf, T. L., & Greger, J. L. (1992). Varying levels of manganese and iron affect absorption and gut endogenous losses of manganese by rats. Journal of Nutrition, 122, 1300–1308.
Deveau, M. (2008). Contribution of drinking water to dietary requirements of essential metals. University of Ottawa, Canada.
Deveau, M. (2010). Contribution of drinking water to dietary requirements of essential metals. Journal Toxicology & Environmental Health A, 73, 235–241.
Donohue, J. M., Abernathy, C. O., Lassovszky, P., & Hallberg, G. (2005). The contribution of drinking water to total daily dietary intakes of selected trace mineral nutrients in the United States. In Nutrients in drinking water, ed. World Health Organization, pp. 75–91. Geneva: WHO Press.
European Food Safety Authority EFSA. (2014). Scientific opinion on dietary reference values for zinc. European Food Safety Authority Journal, 12, 3844.
FAO/WHO. (1988). Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization. Requirements of vitamin A, iron, folate and vitamin B12. Report of a joint FAO/WHO Expert consultation Rome. FAO Food and Nutrition Series No. 23.
FAO/WHO. (2008). Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization. Human vitamin and mineral requirements. Report of a joint FAO/WHO Expert consultation Bangkok, Thailand.
FAO/WHO. (2010). Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization. Expert Committee on Food Additives. Summary and conclusion. 72nd Meeting Rome.
Fasunwon, O., Olufela, J., Akinyemi, O., Fasunwon, B., & Akintokun, O. (2008). Contaminants valuation as water quality indicator in Ago-Iwoye, South western Nigeria. African Journal of Physical Review, 2, 110–116.
Fine, K. D., Santa Ana, C. A., & Fordtran, J. U. S. (1991). Diagnosis of magnesium-induced diarrhea. England Journal of Medicine, 324, 1012–1017.
Flohe, L. (1988). Gluthathione peroxidase. Basic Life SciEnces, 49, 663–668.
FNB - Food and Nutrition Board. (1989). Commission on Life Sciences, National Research Council. Recommended dietary allowances. 10th Edition. Washington D.C.: National Academy Press.
Forster, S. (2001). The interdependence of groundwater and urbanization in rapidly developing Cities. Urban Water, 3, 185–192.
Fuge, R. (2005). Soils and iodine deficiency. In O. Selinus, B. J. Alloway, J.A. Centeno, R. B Finkelman, R., Fuge, U., Lindh (Eds) Essentials of medical geology. Impacts of the natural environment on public health (417 - 433) Amsterdam, Boston Elsevier. Academic Press.
Gibson, R. S., & De Wolfe, M. S. (1980). The dietary trace metal uptake of some Canadian full-term and low birth weight infants during the first twelve months of infancy. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 41, 206–215.
Goldhaber, S. B. (2003). Trace element risk assessment: Essentiality Vs. Toxicity. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 38, 232–242.
Gurzau, E. S., Neagu, N., & Gurzau, A. E. (2003). Essential metals-case study on iron. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 56, 190–200.
Hairong, H., Jian, F. Z., Na, Z., Songming, D., Shufang, L., & Guansheng, M. (2021). The influence of fluid intake behavior on cognition and mood among college students in Baoding, China. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. https://doi.org/10.1159/000515020
Hambidge, H. (2000). Human zinc deficiency. Journal of Nutrition, 130, 1344–1349.
Ifegwu, C., & Anyakora, C. (2012). Screen for eight heavy metals from groundwater samples from a highly industrialized area in Lagos. African Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 3, 1–16.
IOM - Institute of Medicine. (2001). Dietary reference intakes: Vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron, chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, silicon, vanadium, and zinc. National Academy Press.
Jéquier, E., & Constant, F. (2010). Water as an essential nutrient: The physiological basis of hydration. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 64, 115.
Jianfen, Z., Na, Z., Shuxin, L., Yan, W., Shuzhuo, L., Shufang, L. Songming, D., Hairong, H., Yifan, X., Hao, C., Xiaohui, G., Lixin, M., & Guansheng, M. (2019). The amounts and contributions of total drinking fluids and water from food to total water intake of young adults in Baoding, China. European Journal of Nutrition. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1814-y
Jodi, J. D. S. (2016). Negative, null and beneficial effects of drinking water on energy intake, energy expenditure, fat oxidation and weight change in randomized trials: A qualitative review. Nutrients, 8, 1–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8010019
Jordana, S., & Batista, E. (2004). Groundwater quality and health. Geologica Acta, 2, 175–188.
Khattak, M. R. A., Puno, H. K., Saif, M. S., & Memon, K. S. (2005). Surface and groundwater contamination in NWFP and Sindh Provinces (Pakistan) with respect to trace elements. International Journal of Agriculture and BiolOgy, 7, 214–217.
Krishna, A. K., & Govil, P. K. (2004). Heavy metal distribution and contamination of soil around Pali Industrial area, Rajasthan, India. Environmental GeolOgy, 47, 38–44.
Laurberg, P., Cerquira, C., Ovesen, L., Rasmussen, L. B., Perrild, H., & Andersen, S. (2010). Iodine intake as a determinant of thyroid disorders in populations best practice and research. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 24, 13–27.
Lee, J. Y., Choi, J. C., Yi, M. J., Kim, J. W., Cheon, J. Y., Choi, Y. K., Choi, M. J., & Lee, K. K. (2005). Potential groundwater contamination with toxic metals in and around an abandoned Zn mine, Korea. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 165, 167–185.
Liang, F., Yang, S. G., & Sun, C. (2011). Primary health risk analysis of metals in surface water of Taihu lake. China. b. Environmental Contaminants and Toxicology, 87, 404.
Lu, S. Y., Zhang, H. M., Sojinu, S. O., Liu, G. H., Zhang, J. Q., & Ni, H. G. (2015). Trace elements contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from Shenzhen, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 4210–4220.
Marcussen, H., Jensen, B. H., Petersen, A., & Holm, P. E. (2013). Dietary exposure to essential and potentially toxic elements for the population of Hanoi, Vietnem. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical NutrItion, 22, 300–311.
May, J. M., Cobb, C. E., Mendirata, S., Hill, K. E., & Burk, R. F. (1998). Reduction of the Ascobyl free radical to ascorbate by thioredoxin reductase. Journal of Biological ChemIstry, 273, 23039–23045.
Mix, J., Elon, L., Vi, T., Mac, V., Flocks, J., Economos, E., & Tovar-Aguilar, A. J. (2018). Hydration status, kidney function, and kidney injury in Florida agricultural workers. Journal of Occupational and Environmental MedIcine, 60, e253–e260. https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0000000000001261
Mohamed, H., Haris, P. I., & Brima, E. I. (2019). Estimated dietary intake of essential elements from four selected staple foods in Najran City, Saudi Arabia. BMC Chemistry, 13, 73–83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-019-0588-5
Muhammad, S., Shah, M. T., & Khan, S. (2011). Health risk assessment of heavy metals and their source apportionment in drinking water of Kohistan region, northern Pakistan. Microchemical Journal, 98, 334–339.
Naveedullah, M. Z. H., Chunna, Y., Hui, S., Dechao, D., Chaofeng, S., Liping, L., & Yingxu, C. (2014). Concentration and human health risk assessment of selected heavy metals in surface water of the Siling reservoir watershed in Zhejiang province China. Polish Journal of Environmental StudIes, 23, 801–811.
Neal, C., Neal, M., Wickham, H., Hill, L., & Harman, S. (2007). Dissolved iodine in rainfall, cloud, stream and groundwater in the Plynlion area of mid-Wales. Hydrology and Earth System SciEnces, 11, 283–293.
Okagbue, C. O. (1998). Hydrology and chemical characteristics of surface and groundwater resources of the Okigwi area and environs, Imo State, Nigeria. In: Groundwater and Mineral Resources of Nigeria, ed: Ofoegbu CO, Vieweg & Son, Braunschweig, 3 -16.
Oluyemi, E. A., Makinde, W. O., & Oladipo, A. A. (2009). Potential groundwater contamination with toxic metals around refuse dumps in some parts of Lagos metropolis, Nigeria. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 91, 933–940.
OSPDP - Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Dietetic Products. (2005). Nutrition and allergies on a request from the commission related to the tolerable upper intake level of sodium. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Journal, 209, 1–26.
Palma, L., Marques, L. T., Bujan, J., & Rodrigues, L. M. (2015). Dietary water affects human skin hydration and biomechanics. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 8, 413.
Prasad, A. S. (1976). Deficiency of zinc in man and its toxicity. In A. S. Prasad & D. Oberleas (Eds.), Trace elements in human health and disease (Vol. 1, pp. 1–20). Academic press. New York.
Rabin, O., Hegedus, L., Bourre, J. M., & Smith, Q. R. (1993). Rapid brain uptake of manganese and zinc in humans. Journal of Neurochemistry, 61, 509–517.
Rajagopalan, K. V. (1998). Molybdenum: An essential trace element in human nutrition. Annual Review of Nutrition, 8, 401–427.
Raji, M. I. O., Ibrahim, Y. K. E., & Ehinmidu, J. O. (2010). Physico-chemical characteristics and heavy metal levels in drinking water sources in Sokoto metropolis in northwest Nigeria. Journal of Applied Environmental Management, 14, 81–85.
Rasheed, M. A., Radha, B. A., Rao, P. L. S., Chennaiah, J. B., & Dayal, A. M. (2012). Evaluation of potable groundwater quality in some villages of Adilabad in Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Environmental Biology, 33, 689–693.
Rehman, T., & Zahid, M. (2015). Comparative distribution of selected essential metals in drinking water by atomic absorption spectrophotometric method. Pakistan Journal of Chemistry, 5, 1–5.
Rosborg, I., Nihlgård, B., & Gerhardsson, L. (2005). Concentrations of inorganic elements in bottled waters on the Swedish market. Environmental Geochemistry & Health, 27, 17–227.
Sanna, A., Firinu, D., Zavattari, P., & Valera, P. (2018). Zinc status and autoimmunity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients, 10, 68–79. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10010068
Schwartz, B. F., Schenkman, N. S., & Bruce, J. E. (2002). Calcium nephro-lithiasis; effect of water hardness on urinary electrolytes. Urology, 60, 23–27.
Subramaniam, G., & Girish, M. (2015). Iron deficiency anemia in children. Indian Journal of PediatrIcs, 82, 558–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-014-1643-9
Uddin, M. R., Mayeen, U. K., Jainal, A., Nahida, A., Islam, S., Molla, J., Sultana, R., Shahnaz, S., Mehedi, H., Hamid, O., Basem, H. E., Sayyed, M. I., & Sulieman, A. (2021). Quality assessment of bottled and unbottled drinking water in Bangladesh. Water, 13, 2026–2032. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13152026
Umezawa, Y., Hosono, T., Onodera, S., Siringa, F., Buanpeng, S., Belinom, R., Yoshimizu, C., Tayasu, I., Nagata, T., & Taniguchi, M. (2009). Erratum to “Sources of nitrate and ammonium contamination in groundwater under developing Asian megacities.” Science of the Total Environment, 4078, 3219–3231.
Valera, P., Zavattari, P., Sanna, A., Pretti, S., Marcello, A., Mannu, C., Targhetta, C., Bruno, G., & Songini, M. (2015). Zinc and other metals deficiencies and risk of type 1 diabetes: An ecological study in the high risk Sardinia Island. PLoS ONE, 10, e0141262.
Westgard, C. M., Luis, A. O-F., Liz, F. C. & Alexandra, M. R. (2021). Dietary intake, intestinal infection, and safe drinking water among children with anemia in Peru: a cross-sectional analysis. BMC (BioMed Central) Nutrition, 7, 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-021-00417-3
WHO - World Health Organisation. (1996). Trace elements in human nutrition and human health. World Health Organization.
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2003a). Chromium in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/04, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2003b). Iron in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/08, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2003c). Zinc in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/17, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2003d). Sodium in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/15, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2003e). Iodine in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/46, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2004). Copper in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/88, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO. (2005). Nutrients in drinking water (p. 186). Geneva: World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/nutrientsindw/en/index.html
WHO - World Health Organisation. (2006). Chemical aspects. In Guidelines for drinking water quality (3rd Ed. incorporating the 1st Addendum), volume 1 recommendations.145–196. Geneva.
WHO - World Health Organisation. (2008). Guidelines for drinking water quality (3rd Ed. incorporating the 1st and 2nd Addenda) volume 1 recommendation. Geneva. http://www.who.int/water_sanitationhealth/dwq/gdwq3rev/en/. Accessed on 19th August 2009.
WHO. (2009a). Calcium and Magnesium in drinking water: Public health concern. Geneva. Cotruvo, J. & Bartram, J. Eds. printed in Spain.
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2009b). Potassium in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/HSE/09.1/7, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - World Health Organisation. (2011a). Guidelines for drinking water quality (GDWQ). Genva.
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2011b). Molybdenum in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/11/Rev1, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - (World Health Organization). (2011c). Selenium in drinking water — background document for development of WHO ―guidelines for drinking-water quality WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/13/Rev1, World Health Organization (Geneva).
WHO - World Health Organisation. (2012). Sodium intake for adult and children. Geneva. www.who.int/nutrition/publications/guidelines/sodium_intakes_printversionpdf. Accessed on October 23, 2018.
Wolter, R., & Erhebung, B. (2003). cited. In: Großklaus R, Vorkommen, Bedeutung undestimmung von Natrium und Chlorid. In A. Grohmann, U. Hässelbarth, & W. Schwerdtfeger (Eds.), Die Trinkwasserverordnung (4th ed., pp. 547–555). Erich Schmidt Verlag.
Wood, R. J. (2000). Calcium and phosphorus. In M. H. Stipanuck (Ed.), Biochemical and Physiological Aspects of Human Nutrition (pp. 643–670). WB Saunders Company.
Yang, G. Q., & Zhou, R. H. (1994). Further observations on the human maximum safe dietary selenium intake in a seleniferous area of China. Journal of Trace Elements & Electrolytes-in-Health and Disease, 8, 159–165.
Zatta, P., Drago, D., Bolognin, S., & Sensi, S. L. (2009). Alzheimer’s disease, metal ions and metal homeostatic therapy. Trends Pharmacological Sciences, 30, 346–355.
Zietz, B. P., Dieter, H. H., & Lakomed, M. (2003). Epidemiological investigation on chronic copper toxicity to children exposed via the public drinking water supply. Science of the Total EnvironMent, 302, 127–144.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the staff of Activation Laboratories Canada for ICP/MS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ayedun, H., Gbadebo, A., Idowu, O. et al. Contribution of groundwater to dietary requirements of essential metals in Lagos and Ogun States, Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1295 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11893-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11893-4