Abstract
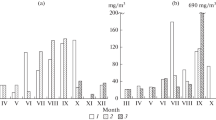
The dynamics of physico-chemical, nutrient, and chlorophyll-a variables were studied in the bloom and non-bloom locations along the off-Gujarat coastal waters to understand the variability in biogeochemistry using multivariate analytical tests. The dissolved oxygen was significantly lower in the bloom stations (3.89 ± 0.44 mgL−1) than in the non-bloom stations (5.50 ± 0.70 mg L−1), due to the biological degradation of organic matter in addition to anaerobic microbial respiration. Nutrients (PO4 and NO3) and Chl-a concentrations were recorded higher in the bloom locations at 0.83 ± 0.21 µmol L−1, 4.47 ± 0.69 µmol L−1, 4.14 ± 1.49 mg m−3, respectively. PO4 and NO3 have shown a significantly higher positive correlation of r = 0.73 and r = 0.69 with Chl-a for bloom data than the non-bloom data. The percentage variance contributed by PC1 and PC2 for both bloom and non-bloom locations were estimated at 52.33%. The variable PO4 explains the highest 24.19% variability in PC1, followed by Chl-a (19.89%). The PO4 triggers the bloom formation and also correlates to the higher concentrations of Chl-a in the bloom locations. The bloom concentration ranges from 9553 to 12,235 trichomes L−1. The bloom intensity has shown a significant positive correlation with Chl-a (r = 0.77), NO3 (r = 0.56), and PO4 (r = 0.30), but a negative correlation was noticed with DO (r = − 0.63) and pH (r = − 0.49). The study also initiates a way forward research investigation on ocean-color technologies to identify and monitor blooms and climate change–driven factors for bloom formation. The occurrence of bloom and its influence on fishery resources and other marine biotas will open many research windows in marine fisheries, oceanography, remote sensing, marine biology, and trophodynamics.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The supporting data is available with the corresponding author.
References
Ahmed, A., Gauns, M., Kurian, S., Bardhan, P., Pratihary, A., Naik, H., & Naqvi, S. W. A. (2017). Nitrogen fixation rates in the eastern Arabian Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 191, 74–83.
Ahn, Y. H., & Shanmugam, P. (2006). Detecting the red tide algal blooms from satellite ocean color observations in optically complex Northeast-Asia coastal waters. Remote Sensing of Environment, 103, 419–437.
Al Shehhi, M .R., Gherboudj, I., & Ghedira, H. (2014). An overview of historical harmful algae blooms outbreaks in the Arabian Seas. Marine Pollution bulletin, 86(1–2), 314–324. pmid: 25038981.
Al-Azri, A., Al-Hashmi, K., Goes, J., Gomes, H., Rushdi, A. I., Al-Habsi, H., et al. (2007). Seasonality of the bloom-forming heterotrophic dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans in the Gulf of Oman in relation to environmental conditions. International Journal of Oceans and Oceanography, 2(1), 51–60.
Allen, J. I., Anderson, D., Burford, M., Dyhrman, S., Flynn, K., Glibert, P. M., Granéli, E., Heil, C., Sellner, K., Smayda, T., & Zhou, M. (2006). Global ecology and oceanography of harmful algal blooms, harmful algal blooms in eutrophic systems (P. Glibert, Ed., GEOHAB report 4, p. 74). Paris/Baltimore: IOC and SCOR.
Anderson, D. M., Gilbert, P. M., & Burkholder, J. M. (2002). Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition and consequences. Estuaries, 25, 704–726.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). American Public Health Association.
Basu, S., Matondkar, S. G., & Furtado, I. (2011). Enumeration of bacteria from a Trichodesmium spp. bloom of the eastern Arabian Sea: Elucidation of their possible role in biogeochemistry. Journal of Applied Phycology, 23(2), 309–319.
Bracher, A., Vountas, M., Dinter, T., Burrows, J. P., Röttgers, R., & Peeken, I. (2009). Quantitative observation of cyanobacteria and diatoms from space using PhytoDOAS on SCIAMACHY data. Biogeosciences, 2009(6), 751–764.
Bracher, A., Bouman, H. A., Brewin, R. J. W., Bricaud, A., Brotas, V., Ciotti, A. M., Clementson, L., Devred, E., Di Cicco, A, Dutkiewicz, S., Hardman-Mountford, N. J., Hickman, A. E., Hieronymi, M., Hirata, T., Losa, S. N., Mouw, C. B., Organelli, E., Raitsos, D. E., Uitz, J., Vogt, M., & Wolanin, A. (2017). Obtaining phytoplankton diversity from ocean color: A scientific roadmap for future development. Frontiers in Marine Science, 4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00055.
Breitburg, D., Levin, L. A., Oschlies, A., Grégoire, M., Chavez, F. P., Conley, D. J., & Zhang, J. (2018). Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science, 359(6371).
Capone, D. G., Subramaniam, A., Montoya, J. P., Voss, M., Humborg, C., Johansen, A. M., & Carpenter, E. J. (1998). An extensive bloom of the N2-fixing cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum in the central Arabian Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 172, 281–292.
Capone, D. G., Zehr, J. P., Paerl, H. W., Bergman, B., & Carpenter, E. J. (1997). Trichodesmium, a globally significant marine bacteria. Science, 276, 1221–1229.
Chang, J., Chiang, K. P., & Gong, G. C. (2000). Seasonal variation and cross-shelf distribution of the nitrogen-fixing cyanobacterium, Trichodesmium, in the southern East China Sea. Continental Shelf Research, 20, 479–492.
Chaturvedi, N., Chakravarty, M. & Narain, A. (1986). “Techniques in algal bloom mapping using LANDSAT MSS data”. In Scientific Note IRS-UP/SAC/MAF/SN/01/86.
Chauhan, P., Nagur, C. R. C., Mohan, M., Nayak, S. R., & Navalgund, R. R. (2001). Surface chlorophyll distribution in Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal using IRS-P4 ocean color monitor satellite data. Current Science, 80, 127–129.
D’Silva, M. S., Anil, A. C., Naik, R. K., & D’Costa, P. M. (2012). Algal blooms: A perspective from the coasts of India. Natural Hazards, 63, 1225–1253.
De Sousa, S. N., Dileepkumar, M., Sardessai, S., Sarma, V. V. S. S., & Shirodkar, P. V. (1996). Seasonal variability in oxygen and nutrients in the central and eastern Arabian Sea. Current Science, 71, 847–851.
Desa, E., Suresh, T., Matondkar, S. G. P., Desa, E., Goes, J., Mascarenhas, A., Parab, S. G., Shaikh, N., & Fernandes, C. E. G. (2005). Detection of Trichodesmium bloom patches along the eastern Arabian Sea coast by IRS-P4/OCM ocean color sensor and by in situ measurements. Ind. J. Mar. Sci., 34, 374–386.
Devassy, V. P., Bhatrarhiri, P. M. A., & Qasim, S. Z. (1978). Trichodesmium phenomenon. Indian Journal of Marine Science, 73, 168–186.
Dias, A., Kurian, S., & Thayapurath, S. (2020). Optical characteristics of colored dissolved organic matter during blooms of Trichodesmium in the coastal waters off Goa. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(8), 1–18.
Diaz, R. J., & Rosenberg, R. (2008). Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science, 321(5891), 926–929.
Gomes do Rosario, H., Goes, J. I., Matondkar, S. P., Parab, S. G., Al-Azri, A. R. & Thoppil, P. G. (2008). Blooms of Noctiluca miliaris in the Arabian Sea—An in situ and satellite study. Deep Sea Research Part i: Oceanographic Research Papers, 55(6), 751–765.
Dupouy C., Petit, M., & Dandonneau, Y. (1988). Satellite detected cyanobacteria bloom in the southwestern tropical Pacific implication for oceanic nitrogen fixation. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 9(3), 389–396.
Dwivedi R., Rafeeq M., Smitha B. R., Padmakumar K. B., Thomas L. C., Sanjeevan V. N., et al. (2015). Species identification of mixed algal bloom in the northern Arabian Sea using remote sensing techniques. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(2), 51. pmid:25638059.
Dwivedi, R. M., Chauhan, R., Solanki, H. U., Raman, M., Matondkar, S. G. P., Madhu, V., & Meenakumari, B. (2012). Study of ecological consequence of the bloom (Noctiluca miliaris) in off shore waters of the northern Arabian Sea. Indian Journal of Geo Marine Sciences, 41(4), 304–313.
Dwivedi, R. M., Raman, M., Parab, S., Matondkar, S. G. P., & Nayak, S. (2006). Influence of northeasterly trade winds on intensity of winter bloom in the northern Arabian Sea. Current Science, 90(10), 1397–1406.
Ghatkar, J. G., Singh, R. K., & Shanmugam, P. (2019). Classification of algal bloom species from remote sensing data using an extreme gradient boosted decision tree model. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(24), 9412–9438.
Gilbert, D., Rabalais, N. N., Diaz, R. J., & Zhang, J. (2010). Evidence for greater oxygen decline rates in the coastal ocean than in the open ocean. Biogeosciences, 7(7), 2283–2296.
Glibert, P. M., Anderson, D. M., Gentien, P., Granéli, E., & Sellner, K. G. (2005). The global, complex phenomena of harmful algal blooms. Oceanography, 18(2), 130–141.
Gokul, E. A., Raitsos, D. E., Gittings, J. A., Alkawri A., & Hoteit, I. (2019). Remotely sensing harmful algal blooms in the Red Sea. PLoS ONE, 14(4), e0215463. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal. pone.0215463
Gokul, E. A., & Shanmugam, P. (2016). An optical system for detecting and describing major algal blooms in coastal and oceanic waters around India. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 121(6), 4097–4127.
Gopinathan, C. P., Rajagopalan, M., Kaladharan, P., & Prema, D. (2007). Training manual on phytoplankton identification/taxonomy.
Grasshoff, K., Ehrhardt, M., & Kremling, K. (1983). Seawater analysis.
Hallegraeff, G. M. (1993). A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia, 32(2), 79–99.
Harrison, P. J., Piontkovski, S., & Al-Hashmi, K. (2017). Understanding how physical-biological coupling influences harmful algal blooms, low oxygen and fish kills in the Sea of Oman and the western Arabian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114(1), 25–34.
Hegde, S., Anil, A. C., Patil, J. S., Mitbavkar, S., Krishnamurthy, V., & Gopalakrishna, V. V. (2008). Influence of environmental settings on the prevalence of Trichodesmium spp. in the Bay of Bengal. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 356, 93–101. https://github.com/valentint/pcaPP
Hu, C., Cannizzaro, J., Carder, K. L., Muller-Karger, F. E., & Hardy, R. (2010). Remote detection of Trichodesmium blooms in optically complex coastal waters: Examples with MODIS full-spectral data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114(9), 2048–2058.
IOCCG. (2000). Remote sensing of ocean colour in coastal, and other optically-complex waters. In S. Sathyendranath (Ed.), reports of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group, No. 3, IOCCG, Dartmouth, Canada (140pp.).
Jyothibabu, R., Madhu, N. V., Murukesh, N., Haridas, P., Nair, K. K. C., & Venugopal, P. (2003). Intense blooms of Trichodesmium erythraeum (Cyanophyta) in the open waters along east coast of India. Indian J Mar Sci, 32, 165–167.
Jyothibabu, R., Karnan, C., Jagadeesan, L., Arunpandi, N., Pandiarajan, R. S., Muraleedharan, K. R., & Balachandran, K. K. (2017). Trichodesmium blooms and warm-core ocean surface features in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 121(1–2), 201–215.
Kannan, R., & Vasantha, K. (1992). Hydrobiologia, 1992(247), 77–86.
Kim, S., Chung, S., Park, H., Cho, Y., & Lee, H. (2019). Analysis of environmental factors associated with cyanobacterial dominance after river weir installation. Water, 11(6), 1163.
King, T., Claassen, L., Borchert, J. & Trainer, V. (2018). “Soundtoxins: A puget sound harmful algae monitoring partnership,” in Proceedings of the Salish Sea ecosystem conference, (Seattle, WA).
Koya, K. P. S., & Kaladharan, P. (1997). Trichodesmium bloom and mortality of Canthigaster margaritatus in the Lakshadweep Sea. Marine Fisheries Information Service Technical and Extension Series, 147, 14.
Krishnan, A. A., Krishnakumar, P. K., & Rajagopalan, M. (2007). Trichodesmium erythraeum (EHR) bloom along the southwest coast of India (Arabian Sea) and its impact on trace metal concentrations in seawater. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 71, 641–646.
Kudela, R. M., Seeyave, S., & Cochlan, W. P. (2010). The role of nutrients in regulation and promotion of harmful algal blooms in upwelling systems. Progress in Oceanography, 85(1–2), 122–135.
Kumar, M., Padmavati, G., & Pradeep, H. (2015). Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 37(2), 49–57.
Madhu, N. V., Reny, P. D., Paul, M., Ullas, N., & Resmi, P. (2011). Occurrence of red tide caused by Karenia mikimotoi (toxic dinoflagellate) in the southwest coast of India. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 40(6), 821–825.
Martin, G. D., Jyothibabu, R., Madhu, N. V., Balachandran, K. K., Nair, M., Muraleedharan, K. R., & Revichandran, C. (2013). Impact of eutrophication on the occurrence of Trichodesmium in the Cochin backwaters, the largest estuary along the west coast of India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(2), 1237–1253.
McCabe, R. M., Hickey, B. M., Kudela, R. M., Lefebvre, K. A., Adams, N. G., Bill, B. D., & Trainer, V. L. (2016). An unprecedented coastwide toxic algal bloom linked to anomalous ocean conditions. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(19), 10–366.
McKinna, L. I. (2015). Three decades of ocean-color remote-sensing Trichodesmium spp. in the world’s oceans: A review. Progress in Oceanography, 131, 177–199.
Minu, P., Shaju, S. S., Souda, V. P., Usha, B., Ashraf, P. M., & Meenakumari, B. (2015). Hyperspectral variability of phytoplankton blooms in coastal waters off Kochi, south-eastern Arabian Sea. Fishery technology, 52(4), 218–222. Retrieved from https://epubs.icar.org.in/index.php/FT/article/view/52989
Mohanty, A. K., Satpathy, K. K., Sahu, G., Hussain, K. J., Prasad, M. K. V. & Sarkar, S. K. (2010). Bloom of Trichodesmium erythraeum (Ehr.) and its impact on water quality and plankton community structure in the coastal waters of southeast coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Science, 39(3), 323–333.
Naqvi, S. W. A., George, M. D., Narvekar, P. V., Jayakumar, D. A., Shailaja, M. S., Sardesai, S., Sarma, V. V. S. S., Shenoy, D. M., Naik, H., Maheswaran, P. A., Krishnakumari, K., Rajesh, G., Sudhir, A. K., & Binu, M. S. (1998). Severe fish mortality associated with ‘red tide’ observed in the sea off Cochin. Current Science, 75, 543–544.
Nayak, B. B., & Karunasagar, I. (2000). Bacteriological and physico-chemical factors associated with Noctiluca milicans bloom along Mangalore, southwest coast of Indian. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 29, 139–143.
Padmakumar, K. B., Menon, N. R., & Sanjeevan, V. N. (2012). Is occurrence of harmful algal blooms in the exclusive economic zone of India on the rise? International Journal of Oceanography, 2012, 1–7.
Padmakumar, K. B., Smitha, B. R., Thomas, L. C., Fanimol, C. L., SreeRenjima, G., Menon, N. R., & Sanjeevan, V. N. (2010). Blooms of Trichodesmium erythraeum in the south eastern Arabian Sea during the onset of 2009 summer monsoon. Ocean Science Journal, 45(3), 151–157.
Parab, S. G., & Matondkar, S. G. P. (2012). Primary productivity and nitrogen fixation by Trichodesmium spp. in the Arabian Sea. Journal of Marine Systems, 105, 82–95.
Parab, S. G., Matondkar, S. P., Raman, M. I. N. I., & Dwivedi, R. M. (2012). Distribution and ecology of the Trichodesmium spp. in the Arabian Sea: Ship and satellite studies.
Pettersson, L. H., & Pozdnyakov, D. (2013). Potential of remote sensing for identification, delineation, and monitoring of harmful algal blooms. In Monitoring of harmful algal blooms. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg., 2013, 49–111.
Prabhu Matondkar, S. G., Bhat, S. R., Dwivedi, R. M., & Nayak, S. R. (2004). Indian satellite IRS-P4 (OCEANSAT). Monitoring algal blooms in the Arabian Sea. Harmful Algae News, 26, 4–5.
Qasim, S. Z. (1970). Some characteristics of a Trichodesmium bloom in the Laccadives. Deep Sea Res, 17, 655–660.
Raghavan, B. R., Deepthi, T., Ashwini, S., Shylini, S. K., Kumarswami, M., Kumar, S. R. I. N. I. V. A. S., & Lotliker, A. A. (2010). Spring inter monsoon algal blooms in the eastern Arabian sea: Shallow marine encounter off Karwar and Kumbla coast using a hyperspectral radiometer. International Journal of Earth Sciences and Engineering, 3(6), 827–832.
Raghavan B. R., Raman, M., Chauhan, P., Kumar, B. S., Shylini, S. K., Mahendra, R. S., & Nayak S. R. (2006). “Summer chlorophyll-a distribution in eastern Arabian Sea off Karnataka-Goa coast from satellite and in-situ observations”, Proc. SPIE 6406. Remote Sensing of the Marine Environment, 64060W. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.694232
Ramamurthy, V. D., & Krishnamurthy, S. (1968). Current Science, 1968(37), 21–22.
Roy, R., Pratihary, A., Narvenkar, G., Mochemadkar, S., Gauns, M., & Naqvi, S. W. A. (2011). The relationship between volatile halocarbons and phytoplankton pigments during a Trichodesmium bloom in the coastal eastern Arabian Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 95(1), 110–118.
Sahu, B. K., Baliarsingh, S. K., Lotliker, A. A., Parida, C., Srichandan, S., & Sahu, K. C. (2017). Winter thermal inversion and Trichodesmium dominance in north-western Bay of Bengal. Ocean Science Journal, 52(2), 301–306.
Sahu, G., Mohanty, K. A., Sarangi, K. R., Bramha, N. S., & Satpathy, K. K. (2016). Current Science, 110(6), 979–981.
Sahu, K., B., Begum, M., Kumarasamy, P., Vinithkumar, V. N., & Kirubagaran, R. (2014). Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 43(9).
Santhanam, P., Balaji, P. B., Nandakumar, R., Jothiraj, K., Dineshkumar, S., Ananth, S., Premkumar, C., Shenbagadevi, A., & Jayalakshmi, T. (2013). Occurrence of Trichodesmium erythraeum Ehrenberg bloom in the Muthupettai mangrove lagoon, southeast coast of India. Seaweed Research Utilization, 35(1&2), 178–186.
Sarangi, R. K. (2012). Observation of algal bloom in the northwest Arabian Sea using multisensor remote sensing satellite data. Marine Geodesy, 35(2), 158–174.
Sarangi, R. K., Chauhan, P., Nayak, S. R., & Shreedhar, U. (2005). Cover: Remote sensing of Trichodesmium blooms in the coastal waters off Gujarat, India using IRS-P4 OCM. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26(9), 1777–1780.
Sarangi, R. K., Chauhan, P., & Nayak, S. R. (2004). Detection and monitoring of Trichodesmium blooms in the coastal waters off Saurastra coast, India using IRS-P4 OCM data. Current Science, 86, 1636–1641.
Sarkar S. K. (2018). Algal blooms: Potential drivers, occurrences and impact. In: Marine algal bloom: Characteristics, causes and climate change impacts. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8261-0_2
Satpathy, K. K., & Nair, K. V. K. (1996). Occurrence of phytoplankton bloom and its effect on coastal water quality. Indian J Mar Sci, 25, 145–147.
Shanmugam, P. (2011). A new bio-optical algorithm for the remote sensing of algal blooms in complex ocean waters. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C4).
Simon, A., & Shanmugam, P. (2012). An algorithm for classification of algal blooms using MODIS-Aqua data in oceanic waters around India. Advances in Remote Sensing, 1(2).
Smetacek, V. (1998). Diatoms and the silicate factor. Nature, 391, 224–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/34528
Smitha, B. R., Sanjeevan, V. N., Padmakumar, K. B., Hussain, M. S., Salini, T. C., & Lix, J. K. (2022). Role of mesoscale eddies in the sustenance of high biological productivity in north eastern Arabian Sea during the winter-spring transition period. Science of the Total Environment, 809, 151173.
Spatharis, S., Skliris, N., Meziti, A., & Kormas, K. A. (2012). First record of a Trichodesmium erythraeum bloom in the Mediterranean Sea. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 69(8), 1444–1455.
Strickland, J. D. H., & Parsons, T. R. (1972). A practical handbook of seawater analysis.
Stone, H. B., Banas, N. S., MacCready, P., Trainer, V. L., Ayres, D. L., & Hunter, M. V. (2022). Assessing a model of Pacific northwest harmful algal bloom transport as a decision-support tool. Harmful Algae, 119, 102334.
Subramaniam, A., Brown, C. W., Hood, R. R., Carpenter, E. J., & Capone, D. G. (2001). Detecting Trichodesmium blooms in SeaWiFS imagery. Deep sea research part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 49(1–3), 107–121.
Subramaniam, A., Carpenter, E. J., & Falkowski, P. G. (1999). Bio‐optical properties of the marine diazotrophic cyanobacteria Trichodesmium spp. II. A reflectance model for remote sensing. Limnology and Oceanography, 44(3), 618–627.
Tang, D. L., Kuwamura, H., & Luis, A. J. (2002). Short term variability of phytoplankton blooms associated with a cold eddy in the northwest Arabian Sea. Remote Sensing of Environment, 81, 82–89.
Temkar, G. S., Abdul Azeez, P., Sikotaria, K. M., Brahmane, V. T., Metar, S. Y., Gangan, S. S., Mathew, K. L., & Desai, A. Y. (2015). Correlation of phytoplankton density with certain hydrological parameters along the coastal waters of Veraval, Gujarat. Journal of Marine Biological Association of India. https://doi.org/10.6024/jmbai.2015.57.2.01870-0x
Tholkapiyan, M., Shanmugam, P., & Suresh, T. (2014). Monitoring of ocean surface algal blooms in coastal and oceanic waters around India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186(7), 4129–4137.
Thomas, L. C., Padmakumar, K. B., Smitha, B. R., Devi, C. A., Nandan, S. B., & Sanjeevan, V. N. (2013). Spatio-temporal variation of microphytoplankton in the upwelling system of the south-eastern Arabian Sea during the summer monsoon of 2009. Oceanologia, 55(1), 185–204.
Trainer, V. L., Cochlan, W. P., Erickson, A., Bill, B. D., Cox, F. H., Borchert, J. A., et al. (2007). Recent domoic acid closures of shellfish harvest areas in Washington State inland waterways. Harmful Algae, 6, 449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2006.12.001
Trivedi, R. K., & Goel, P. K. (1986). Chemical and biological methods for water pollution studies. Publication, Karad.
Vase, V. K., Dash, G., Sreenath, K. R., Shailendra, R., Mohammed, K. K., Divu, D., Dash, S., Pradhan, R. K., Sukhdhane, K. S., & Jayasankar, J. (2018). Spatio-temporal variability of physico-chemical variables, chlorophyll a, and primary productivity in the northern Arabian Sea along India coast (2018). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 148.
Venables, W. N., & Ripley, B. D. (2002). Modern applied statistics with s. Springer-Verlag.
Westberry, T. K., & Siegel, D. A. (2006). Global Biogeochmical Cycle, 2006(20), 4016.
Yu, S., Gong, F., He, X., Bai, Y., Zhu, Q., Wang, D., & Chen, P. (2016). Satellite views of the massive algal bloom in the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman during 2008–2009. In Remote sensing of the ocean, sea ice, coastal waters, and large water regions 2016 (Vol. 9999, p. 99990Z). International Society for Optics and Photonics.
Zhan, P., Subramanian, A.C., Yao, F., & Hoteit, I. (2014). Eddies in the Red Sea: A statistical and dynamical study. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 119(6), 3909–3925.
Zingone, A., & Enevoldsen, H. O. (2000). The diversity of harmful algal blooms: A challenge for science and management. Ocean and Coastal Management, 43, 725–748.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Director, ICAR-CMFRI, former Scientist In-Charge and Scientists, Veraval Regional Station, and Head, Fishery Resources Assessment Division, ICAR-CMFRI, Kochi, for the encouragement and support during the study period. The authors are thankful for the support and encouragement provided by Director, ISRO-SAC, Ahmadabad, to carry out the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VKV: conceptualization, data curation and analysis, and writing the manuscript. MR: data curation, project administration, and supervision. AS: investigation and review and editing. SR: data curation, writing original draft, and literature retrieval. RK: formal analysis, review and editing. SKR: investigation, project administration, and methodology. GRD: investigation and project administration. JJ: methodology, supervision, and review and editing. PR: supervision, review, and editing. RK: investigation, resources, and review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
In no case, human participants whose consent to participate was needed to be involved.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was taken from the competent authority and all co-authors.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
“All authors have read, understood, and complied as applicable with the statement on ‘Ethical responsibilities of Authors’ as found in the instructions for authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.”
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vase, V.K., Raman, M., Sahay, A. et al. Dynamics of environmental variables during the incidence of algal bloom in the coastal waters of Gujarat along the northeastern Arabian Sea. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1238 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11827-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11827-0