Abstract
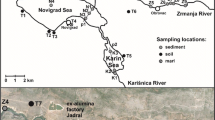
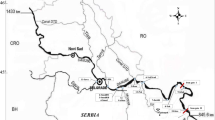
Bed sediments were collected monthly at the outlet of the Ibrahim River between May 2016 and July 2017. Their physical and chemical characteristics were studied to highlight the impact of seasonal variations and discharge on the sediments’ geochemical signatures. Granulometric analysis showed that samples collected after rain events contained abundant sand fractions (> 80%), while the clay fraction was more present at the beginning of the dry season, at low monthly average flows (1 m3/s). Ten major elements, 14 rare earth elements (REE), and 30 trace elements (TE) were analyzed. An excess of CaO reflected the contribution of the carbonate rocks of the Ibrahim karstic springs (30.35 ± 3.91%) but CaO concentration decreased during periods of high water. On another hand, no REE enrichment was detected, both in high and low flows. Most sediments collected at low flow had a pronounced REE depletion that occurred particularly for LREE composition (Nd, Pr, Ce, and La). A negative Ce anomaly (0.992) and a positive Eu anomaly (1.313) were revealed with an average La/Yb ratio of 0.570, reflecting a slight enrichment in HREE. Most studied TE were less concentrated than the averages mentioned in PAAS, UCC, and WSA references. However, a Ze enrichment was mainly due to the regional geochemical background, an As enrichment was associated with anthropogenic contribution, and a Zr enrichment was linked to discharges from pharmaceutical industries located at the river outlet. This study still needs to be complemented binding both spatial and temporal criteria for further fluvial sediments’ monitoring of the entire catchment area.


(Source: Lebanese National Council for Scientific Research – Lebanon CNRS)








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abboud, M. M. (2002). Ibrahim river a case study for investigating vegetation patterns and assessing riparian habitats - by Maya Malak Abboud.
Abboud, M., Makhzoumi, J., Clubbe, C., Zurayk, R., Jury, S., & Talhouk, S. N. (2012). Riparian habitat assessment tool for lebanese rivers (RiHAT): Case study ibrahim river. BioRisk, 7, 99.
Abdallah, C., & Faour, G. (2017). Landslide hazard mapping of Ibrahim River basin Lebanon. Natural Hazards, 85(1), 237–266.
Al Sayah, M. J., Abdallah, C., Khouri, M., Nedjai, R., & Darwich, T. (2021). A framework for climate change assessment in Mediterranean data-sparse watersheds using remote sensing and ARIMA modeling. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 143(1), 639–658.
Assaker, A. (2016). Hydrologie et biogéochimie du bassin versant du fleuve ibrahim: Un observatoire du fonctionnement de la zone critique au liban.
Avumadi, A., Gnandi, K., & Probst, J. (2019). Trace element distribution and enrichment in the stream sediments of the lake togo watersheds (south of togo) trace element distribution and enrichment in the stream sediments of the lake togo watersheds (south of togo). Advances in Ecological and Environmental Research, 4(4), 87–114.
Badassan, T. E. E., Avumadi, A. M. D., Ouro-Sama, K., Gnandi, K., Jean-Dupuy, S., & Probst, J. L. (2020). Geochemical composition of the Lomé lagoon sediments, Togo: Seasonal and spatial variations of major, trace and rare earth element concentrations. Water, 12(11), 3026.
Bayon, G., Toucanne, S., Skonieczny, C., André, L., Bermell, S., Cheron, S., & Barrat, J. A. (2015). Rare earth elements and neodymium isotopes in world river sediments revisited. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 170, 17–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.08.001
Benabdelkader, A., Taleb, A., Probst, J. L., Belaidi, N., & Probst, A. (2019). Origin, distribution, and behaviour of rare earth elements in river bed sediments from a carbonate semi-arid basin (Tafna River, Algeria). Applied Geochemistry, 106, 96–111.
Benabdelkader, A., Taleb, A., Probst, J. L., Belaidi, N., & Probst, A. (2018). Anthropogenic contribution and influencing factors on metal features in fluvial sediments from a semi-arid Mediterranean river basin (Tafna River, Algeria): A multi-indices approach. Science of the Total Environment, 626, 899–914.
Bounouira, H., Choukri, A., El Moursli, R. C., Chakiri, S., Said, F., Bounakhla, M., & Embarch, K. (2013). Geochemical behaviour of major and trace elements in dissolved and particulate phases of the bouregreg river (morocco). Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 295(2), 1067–1083.
Bowen, H. J. M. (1979). Environmental chemistry of the elements. Academic Press.
Canfield, T. J., Kemble, N. E., Brumbaugh, W. G., Dwyer, F. J., Ingersoll, C. G., & Fairchild, J. F. (1994). Use of benthic invertebrate community structure and the sediment quality triad to evaluate metal-contaminated sediment in the upper Clark Fork River, Montana. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 13(12), 1999–2012.
Chamas, L., Akl, G., Hamdan, O., Kaskas, A., Abu Salman, R., Nasr, W., & Karam, J. (2001). State of the environment report. (). Beirut: Ministry of Environnement.
Coryell, C. D., Chase, J. W., & Winchester, J. W. (1963). A procedure for geochemical interpretation of terrestrial rareâ€earth abundance patterns. Journal of Geophysical Research, 68(2), 559–566.
Darwish, T., Shaban, A., Portoghese, I., Vurro, M., Khadra, R., Saqallah, S., & Amacha, N. (2015). Inducing water productivity from snow cover for sustainable water management in ibrahim river basin, lebanon. British Journal of Applied Science & Technology, 519.
El Amil, R., & Oudwane, J. (2000). Les ressources en eau et en matières minérales du bassin versant du nahr ibrahim.
El Azzi, D. (2012). Transfert de polluants organiques et inorganiques dans les hydrosystèmes en période de crue: Interactions avec les matières en suspension et la matière organique. Retrieved from http://thesesups.ups-tlse.fr/1885/
El Mrissani, S., Haida, S., Probst, J. L., & Probst, A. (2021). Multi-indices assessment of origin and controlling factors of trace metals in river sediments from a semi-arid carbonated basin (the Sebou Basin, Morocco). Water, 13(22), 3203.
El Najjar, P., Kassouf, A., Probst, A., Probst, J., Ouaini, N., Daou, C., & El Azzi, D. (2019). High-frequency monitoring of surface water quality at the outlet of the ibrahim river (lebanon): A multivariate assessment. Ecological Indicators, 104, 13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.04.061
El Najjar, P., Pfaffl, M., Ouaini, N., Nour, A. A., & El Azzi, D. (2020). Water and sediment microbiota diversity in response to temporal variation at the outlet of the ibrahim river (lebanon). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(3), 1–11.
Fadel, A., Faour, G., Mhawej, M., Ghazal, M., & Jarlan, L. (2022). A combined remote sensing and modelling approach to simulate the impact of climate change on the river discharge in a Lebanese snow-covered basin. In Satellite Monitoring of Water Resources in the Middle East (pp. 379–391). Springer, Cham.
Fernandes, D. N., Elisabete, A., & Martins Bacchi, F. A. (1998). Lanthanides in the study of lithologic discontinuity in soils from the piracicaba river basin. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 275–277, 924–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8388(98)00486-1
Fitzpatrick, A., Fox, J., & Leung, K. (2001). Environmental baseline survey of the nahr ibrahim, lebanon.
Gerlach, R. W., Dobb, D. E., Raab, G. A., & Nocerino, J. M. (2002). Gy sampling theory in environmental studies. 1. assessing soil splitting protocols. Journal of Chemometrics: A Journal of the Chemometrics Society, 16(7), 321–328.
Ghsoub, M., Fakhri, M., Courp, T., Khalaf, G., Buscail, R., & Ludwig, W. (2020). River signature over coastal area (eastern mediterranean): Grain size and geochemical analyses of sediments. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101169
Goldstein, S. J., & Jacobsen, S. B. (1988). Nd and sr isotopic systematics of river water suspended material: Implications for crustal evolution. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 87(3), 249–265.
Govindaraju, K., & Mevelle, G. (1987). Fully automated dissolution and separation methods for inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry rock analysis. application to the determination of rare earth elements. plenary lecture. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2(6), 615–621.
Henderson, P. (2013). Rare earth element geochemistry Elsevier.
Herodotus, H. (1954). Trans. aubrey de sélincourt.
Hissler, C., & Probst, J. (2006). Impact of mercury atmospheric deposition on soils and streams in a mountainous catchment (vosges, france) polluted by chlor-alkali industrial activity: The important trapping role of the organic matter. Science of the Total Environment, 361(1–3), 163–178.
Hreiche, A., Najem, W., & Bocquillon, C. (2007). Hydrological impact simulations of climate change on Lebanese coastal rivers/Simulations des impacts hydrologiques du changement climatique sur les fleuves côtiers Libanais. Hydrological Sciences Journal/journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques, 52(6), 1119–1133.
Jain, C. K. (2004). Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of river yamuna, india. Water Research, 38(3), 569–578.
Korfali, S. I., & Davies, B. D. (2004a). The relationships of metals in river sediments (nahr-ibrahim, lebanon) and adjacent floodplain soils. Agricultural Engineering International: CIGR Journal.
Korfali, S. I., & Davies, B. E. (2005). Seasonal variations of trace metal chemical forms in bed sediments of a karstic river in lebanon: Implications for self-purification. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 27(5–6), 385–395.
Korfali, S. I., & Davies, B. E. (2003). A comparison of metals in sediments and water in the river Nahr-Ibrahim, Lebanon: 1996 and 1999. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 25(1), 41–50.
Korfali, S. I., & Davies, B. E. (2004b). Speciation of metals in sediment and water in a river underlain by limestone: Role of carbonate species for purification capacity of rivers. Advances in Environmental Research, 8, 599–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1093-0191(03)00033-9
Leleyter, L., Probst, J., Depetris, P., Haida, S., Mortatti, J., Rouault, R., & Samuel, J. (1999). REE distribution pattern in river sediments: Partitioning into residual and labile fractions. Comptes Rendus De L’académie Des Sciences-Series IIA-Earth and Planetary Science, 329(1), 45–52.
Li, C., Shi, X., Kao, S., Liu, Y., Lyu, H., Zou, J., & Qiao, S. (2013). Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of taiwan. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 69, 39–47.
Li, Y., Song, Y., Fitzsimmons, K. E., Chen, X., Wang, Q., Sun, H., & Zhang, Z. (2018). New evidence for the provenance and formation of loess deposits in the ili river basin, arid central asia. Aeolian Research, 35, 1–8.
Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Colin, C., Siringan, F. P., & Wu, Q. (2009). Chemical weathering in Luzon, Philippines from clay mineralogy and major-element geochemistry of river sediments. Applied Geochemistry, 24(11), 2195–2205.
Lortholarie, M., Zalouk-Vergnoux, A., Couderc, M., Kamari, A., François, Y., Herrenknecht, C., & Poirier, L. (2020). Rare earth element bioaccumulation in the yellow and silver european eel (anguilla anguilla): A case study in the loire estuary (france). Science of the Total Environment, 719, 134938.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingersoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39(1), 20–31.
McLennan, S. M. (1989). Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Geochemistry and Mineralogy of Rare Earth Elements, Reviews in Mineralogy., 21, 169–200.
Mohiuddin, K. M., Otomo, K., Ogawa, Y., & Shikazono, N. (2012). Seasonal and spatial distribution of trace elements in the water and sediments of the tsurumi river in japan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184(1), 265–279.
Mudroch, A., & Azcue, J. M. (1995). Manual of aquatic sediment sampling CRC Press.
Mudroch, A., & Bourbonniere, R. A. (1994). Sediment preservation, processing, and storage. Handbook of Techniques for Aquatic Sediments Sampling, 131–169.
Najjar, P. E. (2019). Transfert de matières dissoutes et particulaires dans le fleuve ibrahim (liban): Fluctuations temporelles haute résolution et rôle des crues.
Papazian, H. S. (1981). A hydrological study of the nahr ibrahim basin in the vicinity of the paper mill project of indevco in Lebanon. Lebanon.
Piper, D. Z., & Bau, M. (2013). Normalized rare earth elements in water, sediments, and wine: Identifying sources and environmental redox conditions. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 4(10), 69–83.
Riou, C. (1999). Géochimie des terres rares et des éléments traces associés dans les nappes et l'eau des sols hydromorphes. application au traçage hydrologique.
Saab, H., Nassif, N., El Samrani, A., Daoud, R., Medawar, S., & Ouaïni, N. (2007). Suivi de la qualité bactériologique des eaux de surface (rivière nahr ibrahim, liban). Revue Des Sciences De L’eau/journal of Water Science, 20(4), 341–352.
Schumacher, B. A., Shines, K. C., Burton, J. V., & Papp, M. L. (1990). Comparison of three methods for soil homogenization. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 54(4), 1187–1190.
Shepard, F. P. (1954). Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 24(3), 151–158.
Silva, S. A., Franklin, R. L., Silva, W. L., & Favaro, D. I. (2015). Metal trace and rare earth element assessment in a sedimentary profile from promissao reservoir, são paulo state, brazil, by INAA.
Singh, P., & Rajamani, V. (2001). Geochemistry of the floodplain sediments of the kaveri river, southern india. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 71(1), 50–60.
SLIM, K., Saad, Z., Kazpard, V., Ouaini, N., Elsamarani, A., & Lartiges, B. S. (2005). Trace element carriers in river sediments (ibrahim river-lebanon): Investigation on natural and anthropogenic inputs. International Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering (Print), 1–16.
Sow, M. A., Payre-Suc, V., Julien, F., Camara, M., Baque, D., Probst, A., & Probst, J. L. (2018). Geochemical composition of fluvial sediments in the milo river basin (guinea): Is there any impact of artisanal mining and of a big african city, kankan? Journal of African Earth Sciences, 145, 102–114.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39(6), 611–627.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: Its composition and evolution.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 72(2), 175–192.
Viers, J., Dupré, B., & Gaillardet, J. (2009). Chemical composition of suspended sediments in world rivers: New insights from a new database. Science of the Total Environment, 407(2), 853–868.
Vital, H., & Stattegger, K. (2000). Major and trace elements of stream sediments from the lowermost amazon river. Chemical Geology, 168(1–2), 151–168.
Walling, D. E., & Moorehead, P. W. (1989). The particle size characteristics of fluvial suspended sediment: An overview. Sediment/water interactions (pp. 125–149) Springer.
Williams, M. (2012). River sediments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 370(1966), 2093–2122.
Wright, J., Schrader, H., & Holser, W. T. (1987). Paleoredox variations in ancient oceans recorded by rare earth elements in fossil apatite. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 51(3), 631–644.
Yang, S. Y., Jung, H. S., Choi, M. S., & Li, C. X. (2002). The rare earth element compositions of the changjiang (yangtze) and huanghe (yellow) river sediments. Earth and Planetary Science Letters. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00715-X
Zhang, C., Wang, L., Zhang, S., & Li, X. (1998). Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the mainstream of the yangtze river, china. Applied Geochemistry, 13(4), 451–462.
Acknowledgements
We give special thanks to the Lebanese-French Environmental Observatory O-LIFE (CNRS-L, CNRS-F, Lebanese, and French Universities), the Chamber of Commerce of Tripoli, and the CNRS Rocks and Minerals Analysis Service (SARM) part of the Center for Petrographic and Geochemical Research (CRPG) in Nancy, France, for their technical assistance as well as their scientific support.
Funding
This project was partly jointly funded by the National Council for Scientific Research in Lebanon CNRS-L and the Holy Spirit University of Kaslik (USEK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Najjar, P.E., Chidiac, S., Probst, JL. et al. Geochemical signature of the bed sediments at the outlet of the Ibrahim River (Lebanon): temporal variation. Environ Monit Assess 195, 509 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11103-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11103-1