Abstract
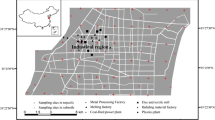
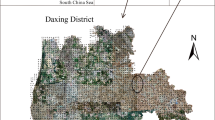
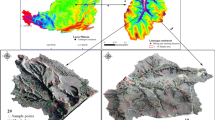
Source identification and quality monitoring of soil nutrients and beneficial elements (NBEs) are crucial for agricultural production and environmental protection. In this study, grid sampling (223 topsoil samples and 223 subsoil samples) was carried out in the Tongzhou District of Beijing. The concentration level of representative NBEs (N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Se, V, Ge, Mn, Zn) and some typical soil properties representing indicators (total organic carbon, TFe2O3, Al2O3/SiO2, and pH) in soils and their spatial distribution were analyzed. The major sources contributing to these NBEs were assessed by principal component analysis (PCA), redundancy analysis (RDA), and positive matrix factorization (PMF) analysis. The results suggested that the soil parent material contributed 40.09–69.84% to Zn, V, Ge, Mn, F, and K in soils; the local external source contributed 54.89–75.04% to N, Se, and TOC; and the hydrous system contributed 40.67–77.31% to Ca and Mg. The enrichment degree of each NBE was calculated using the standardized concentration ratio method. These indices exhibited the influence and mixing process of different sources on the target NBEs in topsoils. The individual concentrations of the target NBEs and the combined concentrations of N, P, and K were used to evaluate the soil quality. Our study estimated the relative contributions from dominant sources to NBEs in soils from a typical suburban area, providing a basis for agricultural activities and environmental protection.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request from the authors. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, G-L Yuan, upon reasonable request.
References
Alimu, A., Xiaohan, C. O. N. G., Xiaoying, X. I. A., Li, X. I., & Weixia, W. A. N. G. (2022). Characteristics of soil nutrient under different land use patterns. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 59(4), 925. https://doi.org/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.04.017
Allison, L. (1965). Organic carbon. Methods of soil analysis: Part 2 chemical and microbiological properties, 9, 1367–1378. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.c39
Armiento, G., Barsanti, M., Caprioli, R., et al. (2022). Heavy metal background levels and pollution temporal trend assessment within the marine sediments facing a brownfield area (Gulf of Pozzuoli, Southern Italy). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194, 814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10480-3
Boahen, F., Száková, J., Kališová, A., Najmanová, J., & Tlustoš, P. (2022). The assessment of the soil–plant-animal transport of the risk elements at the locations affected by brown coal mining. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22254-y
Brown, P. H., Zhao, F. J., & Dobermann, A. What is a plant nutrient? Changing definitions to advance science and innovation in plant nutrition. Plant Soil, 476, 11–23 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-021-05171-w
Cai, K., & Song, Z. (2020). Cycling and total risks of multiple as fractions in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei area on the agricultural plain. China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 190, 110097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110097
Cai, L. M., Jiang, H. H., & Luo, J. (2019a). Metals in soils from a typical rapidly developing county, Southern China: Levels, distribution, and source apportionment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(19), 19282–19293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05329-1
Cai, L. M., Wang, Q. S., Wen, H. H., Luo, J., & Wang, S. (2019b). Heavy metals in agricultural soils from a typical township in Guangdong Province, China: Occurrences and spatial distribution. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 168, 184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.092
Cassman, K. G., Kerby, T. A., Roberts, B. A., Bryant, D. C., & Brouder, S. M. (1989). Differential response of two cotton cultivars to fertilizer and soil potassium. Agronomy Journal, 81(6), 870–876. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1989.00021962008100060006x
da Silva, V. D., de Mello Gabriel, G. V., Botero, W. G., Fernandes, A. P., & do Carmo, J. B., & de Oliveira, L. C. (2022). Leafy vegetables marketed as organic and conventional: Assessment of essential and non-essential elements’ content. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(10), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10439-4
Djodjic, F., Börling, K., & Bergström, L. (2004). Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33(2), 678–684. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2004.6780
Duan, X. C., Yu, H. H., Ye, T. R., Huang, Y., Li, J., Yuan, G. L., & Albanese, S. (2020). Geostatistical mapping and quantitative source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in top-and sub-soils: A case of suburban area in Beijing. China. Ecological Indicators, 112, 106085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106085
Fei, X., Lou, Z., Xiao, R., Ren, Z., & Lv, X. (2020). Contamination assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil through the synthesis of PMF and GeogDetector models. Science of the Total Environment, 747, 141293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141293
Fei, X., Xiao, R., Christakos, G., Langousis, A., Ren, Z., Tian, Y., & Lv, X. (2019). Comprehensive assessment and source apportionment of heavy metals in Shanghai agricultural soils with different fertility levels. Ecological Indicators, 106, 105508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105508
Gabarrón, M., Faz, A., & Acosta, J. A. (2018). Use of multivariable and redundancy analysis to assess the behavior of metals and arsenic in urban soil and road dust affected by metallic mining as a base for risk assessment. Journal of Environmental Management, 206, 192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.10.034
Gao, L., Wang, Z., Shan, J., Chen, J., Tang, C., & Yi, M. (2017). Aquatic environmental changes and anthropogenic activities reflected by the sedimentary records of the Shima River, Southern China. Environmental Pollution, 224, 70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.056
Jiang, T., Yang, Z., Huang, Z., Shi, J., & Cai, L. (2010). Tendency and mechanism analysis of total hardness in shallow groundwater in the suburb of Beijing. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 37, 33–37.
Jin, Y., O’Connor, D., Ok, Y. S., Tsang, D. C., Liu, A., & Hou, D. (2019). Assessment of sources of heavy metals in soil and dust at children’s playgrounds in Beijing using GIS and multivariate statistical analysis. Environment International, 124, 320–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.024
Kumpiene, J., Antelo, J., Brännvall, E., Carabante, I., Ek, K., Komárek, M, et al. (2019). In situ chemical stabilization of trace element-contaminated soil – field demonstrations and barriers to transition from laboratory to the field – A review. Applied Geochemistry, 100, 335–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.12.003
Lalitha, M., & Dhakshinamoorthy, M. (2014). Forms of soil potassium-a review. Agricultural reviews, 35(1). https://doi.org/10.5958/j.0976-0741.35.1.008
Lazo, P., Stafilov, T., Qarri, F., Allajbeu, S., Bekteshi, L., Frontasyeva, M., & Harmens, H. (2019). Spatial distribution and temporal trend of airborne trace metal deposition in Albania studied by moss biomonitoring. Ecological Indicators, 101, 1007–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.11.053
Li, N., Arshad, M., Zhao, D., Sefton, M., & Triantafilis, J. (2019). Determining optimal digital soil mapping components for exchangeable calcium and magnesium across a sugarcane field. CATENA, 181, 104054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.04.034
Limwikran, T., Kheoruenromne, I., Suddhiprakarn, A., Prakongkep, N., & Gilkes, R. J. (2019). Most plant nutrient elements are retained by biochar in soil. Soil Systems, 3(4), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems3040075
Lin, Y., Han, P., Huang, Y., Yuan, G.L., Guo, J.X., & Li, J., (2017). Source identification of potentially hazardous elements and their relationships with soil properties in agricultural soil of the Pinggu district of Beijing, China: multivariate statistical analysis and redundancy analysis. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 173, 110-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.12.006
Liu, R., Wang, M., Chen, W., & Peng, C. (2016). Spatial pattern of heavy metals accumulation risk in urban soils of Beijing and its influencing factors. Environmental Pollution, 210, 174–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.11.044
Liu, X., Wang, B., & Zheng, B. (2014). Geochemical process of fluorine in soil. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 33(3), 277–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0688-9
Ma, Z., Chen, K., Li, Z., Bi, J., & Huang, L. (2016). Heavy metals in soils and road dusts in the mining areas of Western Suzhou, China: A preliminary identification of contaminated sites. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 16(1), 204–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1208-1
Seyedmohammadi, J., & Navidi, M. N. (2022). Applying fuzzy inference system and analytic network process based on GIS to determine land suitability potential for agricultural. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194, 712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10327-x
Sharpley, A. N. (1989). Relationship between soil potassium forms and mineralogy. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 53(4), 1023–1028. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1989.03615995005300040006x
Singhal, R. K., Fahad, S., Kumar, P., et al. (2022). Beneficial elements: New players in improving nutrient use efficiency and abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Growth Regulation. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-022-00843-8
Slessarev, E. W., Lin, Y., Bingham, N. L., Johnson, J. E., Dai, Y., Schimel, J. P., & Chadwick, O. A. (2016). Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale. Nature, 540(7634), 567–569. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20139
Tan, Q., & Wang, G. (2016). Decoupling of nutrient element cycles in soil and plants across an altitude gradient. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34875
Thomas, G. W. (1996). Soil pH and soil acidity. Methods of soil analysis: part 3 chemical methods, 5, 475–490. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.3.c16
Van Groenigen, J. W., Huygens, D., Boeckx, P., Kuyper, T. W., Lubbers, I. M., Rütting, T., & Groffman, P. M. (2015). The soil N cycle: New insights and key challenges. The Soil, 1(1), 235–256. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-1-235-2015
Vatansever, R., Ozyigit, I. I., & Filiz, E. (2017). Essential and beneficial trace elements in plants, and their transport in roots: A review. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 181(1), 464–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2224-3
Wang, A. T., Wang, Q., Li, J., Yuan, G. L., Albanese, S., & Petrik, A. (2019). Geo-statistical and multivariate analyses of potentially toxic elements’ distribution in the soil of Hainan Island (China): A comparison between the topsoil and subsoil at a regional scale. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 197, 48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.11.008
Wang, A., Lin, K., Ma, C., Gao, Q., Zhu, Q., Ji, X., & Li, D. (2018). A brief study on pH, exchangeable Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ in farmlands under tobacco-rice rotation in Xuancheng City of South Anhui. Agricultural Sciences, 9(04), 480. https://doi.org/10.4236/as.2018.94033
Wang, J., Zhu, S., Xu, J., et al. (2022). Spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of metal(loid)s in cultivated land from Xianjia Town in Fujian. Southeast China. Environ Monit Assess, 194, 763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10448-3
Worsfold, P. J., Gimbert, L. J., Mankasingh, U., Omaka, O. N., Hanrahan, G., Gardolinski, P. C., & McKelvie, I. D. (2005). Sampling, sample treatment and quality assurance issues for the determination of phosphorus species in natural waters and soils. Talanta, 66(2), 273–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2004.09.006
Wuddivira, M. N., & Camps-Roach, G. (2007). Effects of organic matter and calcium on soil structural stability. European Journal of Soil Science, 58(3), 722–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2006.00861.x
Xiao, L., Guan, D., Chen, Y., et al. (2019). Distribution and availability of heavy metals in soils near electroplating factories. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 22596–22610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04706-0
Yuan, G. L., Sun, T. H., Han, P., Li, J., & Lang, X. X. (2014). Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: Typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 136, 40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.10.002
Zhang, H. Z., Li, H., Wang, Z., & Zhou, L. D. (2011). Accumulation characteristics of copper and cadmium in greenhouse vegetable soils in Tongzhou District of Beijing. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 10, 289–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2011.09.047
Zhang, X., Wei, S., Sun, Q., Wadood, S. A., & Guo, B. (2018). Source identification and spatial distribution of arsenic and heavy metals in agricultural soil around Hunan industrial estate by positive matrix factorization model, principle components analysis and geo statistical analysis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 159, 354–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.072
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41872100) and Beijing Municipal Finance Project, Geochemical monitoring of soil quality (11000022T000000439575) and Investigation of ecological geology of Western Beijing (11000022T000000491145).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qin-Rui Zhang: investigation, resources, formal analysis, writing—original draft; Sheng-Qiang Zhang: software, data curation, writing—original draft; Yong Huang: investigation, resources; Huan Li: investigation; Yan-Hui Jia: software; data curation; Jun Li: writing—original draft; Guo-Li Yuan: supervision, conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, QR., Zhang, SQ., Huang, Y. et al. Spatial distribution and quantitative source identification of nutrients and beneficial elements in the soil of a typical suburban area, Beijing. Environ Monit Assess 195, 218 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10849-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10849-4