Abstract
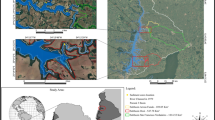
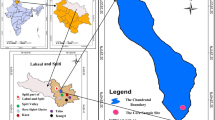
This work presents a piece of initial information about the estimation of the sedimentation rate for Lake Pykara. In this investigation, a chronological sequence of sediment core was set up dependent on 137Cs and 210Pbex analysis to study sediment accumulation rates in Lake Pykara. Caesium-137 (Cs) is an artificial radionuclide and is regularly utilized in building up the chronology of lake sediments in the Anthropocene period. The unsupported 210Pb profile shows a non-exponential decline of 210Pb activity with sediment depth. Sedimentation rates dependent on global atmospheric nuclear weapon maximum fallout of 137Cs (1963) bolster the utilization of the consistent rate of 210Pb supply (CRS) model in core sediments. The geochronology studies of the core were performed using the 137Cs method, to evaluate the model of time changes in the sediment. The 137Cs radioactivity was resolved directly by gamma spectrometry and fluctuated from 13.11 ± 1.3 Bq kg−1 for top layers to 1.21 ± 0.1 Bq kg−1 for the bottom of the core. Two trademark peaks of 137Cs radioactivity identified with the global fallouts after atomic weapons testing and the Chernobyl mishap were observed and used to affirm the 210Pb dating method. Radioactivity of 210Pbex ranged from 8.00 ± 1.0 to 1.40 ± 0.1 Bq kg−1. The mean sedimentation rate evaluated from both models was 0.71 ± 0.06 cm year−1, while the estimated age of Lake Pykara was 514.08 years (137Cs) and 521.43 years (210Pbex), respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
The author used ArcGIS 10.1, Origin 2019, SPSS (version 21) to carry out the analysis.
References
Alhajji, E. Ismail, I., Al-Masri, M., Salman, N., Al-haleem, A. B. D., Mohamed., & Doubal, A. (2014). Sedimentation rates in the Lake Qattinah using 210Pb and 137Cs as geochronometer. Geochronometria, 41. https://doi.org/10.2478/s13386-013-0142-5
Alvarez-Iglesias, P. (2006). El registrosed imentarioreciente de la Ensenada de San Simon (Rfa de Vigo, Noroestede Espana): interaccion entre procesos naturales y actividades antropogenicas. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Vigo (Vigo, Spain), unpublished, 356 pp.
Andersen, T. J., Mikkelsen, O. A., Annette, L. M., & Pejrup, M. (2000). Deposition and mixing depths on some European intertidal mudflats based on Pb and Cs activities. Continental Shelf Research, 20, 1569–1591.
Anusiya, D. K., Lekeshmanaswamy, M., Ramesh, J., & Vasuki, C. A. (2015). Studies on the heavy metals concentration in the Pykara Lake, Udhagamandalam, Nilgiris, Tamilnadu. International Journal of Pure and Applied Zoology, 3(4), 358–367.
Appleby, P. G., Shotyik, W., & Fankhauser, A. (1997). Lead-210 age dating of three-peat cores in the Jura Mountains. Switzerland. Water Air Soil Pollut., 100, 223–231.
Appleby, P. G. (2001). Chronostratigraphic techniques in recent sediments. In W. M. Last & J. P. Smol (eds), Tracking environmental change using lake sediments, Vol. 1: Basin analysis, Coring, and Chronological Techniques. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 171–203.
Avnimelech, Y., Ritvo, G., Meijer, L., & Kochba, M. (2001). Water content, organic carbon and dry bulk density in flooded sediments. Aquacultural Engineering, 25. 25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8609(01)00068-1
Baskaran, M. (2011). Po-210 and Pb-210 as atmospheric tracers and global atmospheric Pb-210 fallout: A review. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 102, 500–513.
Baskaran, M., Nix, J., Kuyper, C., & Karunakara, N. (2014). Problems with the dating of sediment cores using excess 210Pb in a freshwater system impacted by large-scale watershed changes. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 138, 355–363.
Bikit, I., Slivka, J., Conkic, L. J., Krmar, M., Veskovic, M., ZikicTodorovic, N., Varga, E., Curcic, S., & Mrdja, D. (2004). Radioactivity of the soil in Vojvodina (northern province of Serbia and Montenegro). Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 78 (1), 11–19.
Blake, G. R., & Hartge, K. H. (1986). Bulk density. In: Klute, A., Ed., Methods of soil analysis, part 1—Physical and Mineralogical methods, 2nd Edition, Agronomy Monograph 9, American Society of Agronomy—Soil Science Society of America, Madison, 363–382.
Boyd, C. E. (1995). Bottom soils, sediment, and pond aquaculture. Chapman & Hall, New York.
Butler, D. (2011). Radioactivity spreads in Japan: fallout is localized, but could persist for years in some regions. Nature, 471(7340), 555–556.
Cheng, Z., Wang, X. H., Rojas, I. J., Liu, Y. (2019). Reconstruction of sedimentation changes under anthropogenic influence in a medium-scale estuary based on a decadal chronological framework Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 106295https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.106295
Chino, M., Nakayama, H., Nagai, H., Terada, H., Katata, G., & Yamazawa, H. (2011). Preliminary estimation of release amounts of 131I and 137Cs accidentally discharged from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the atmosphere. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology (tokyo), 48(7), 1129–1134.
Corcoran, M. (2018). Accumulation rates, focusing factors, and chronologies from depth profiles of 210Pb and 137Cs in sediments of the Laurentian Great Lakes, Journal of Great Lakes Research. (2018), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jglr.2018.05.013.
Garcia-Tenorio, R. (1988). El metodo de fechadopor210Pb y su application a sedimentos. Review of Geofis., 44, 225–234.
Gharibreza, M., Raj, J. K., & Yusoff, I. (2013). Sedimentation rates in Bera Lake (Peninsular Malaysia) using 210Pb and 137Cs radioisotopes. Geosciences Journal, 17, 211–220 (2013).https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-013-0013-3.
Guo, J., Costa, O. S., Wang, Y., Lin, W., Wang, S., Zhang, B., & Zhang, L. (2020). Accumulation rates and chronologies from depth profiles of 210Pbex and 137Cs in sediments of northern Beibu Gulf, South China sea. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 213, 106136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2019.106136
Jeter, H. W. (2000). Determining the ages of the recent sediments using measurements of trace radioactivity. Terra Et Aqua, 78, 21–28.
Kirchner, G. (2011). 210Pb as a tool for establishing sediment chronologies: Examples of potentials and limitations of conventional dating models. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 102, 490–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.11.010
Klaminder, J., Appleby, P., Crook, P., & Renberg, I. (2012). Post-deposition diffusion of 137Cs in lake sediment: implications for radiocaesium dating. Sedimentology, 59, 2259–2267.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.2012.01343.x
Krmar, M., Wattanavatee, K., Radnovic, D., Slivka, J., Bhongsuwan, T., Frontasyeva, M. V., & Pavlov, S. S. (2013). Airborne radionuclides in mosses collected at different latitudes. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 117, 45–48.
Kumar, B., Rai, ShivePrakash, Nachiappan, Rm., Kumar, U., Singh, S., & Diwedi, V. (2007). Sedimentation rate in North Indian lakes estimated using Cs-137 and Pb-210 dating techniques. Current Science, 92, 1416–1420.
Kumar, A., Rout, S., & Karpe, R. (2015). Inventory, fluxes, and residence times from the depth profiles of naturally 210Pb in marine sediments of Mumbai Harbor Bay. Environmental Earth Science, 73, 4019–4031 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3687-6
Longmore, M. E. (1982). The cesium-137 dating technique and associated applications in Australia C A review. In W. Ambrose & P. Duerden (Eds.), Archaeometry: An Australasian perspective (pp. 310–321). Australian National Univ. Press.
Nielsen, S. P. (1995). A box model for North-East Atlantic coastal waters compared with radioactive tracers. Journal of Marine Systems, 6, 545–560.
Ojala, A. E. K., Luoto, T. P., & Virtasalo, J. J. (2017). Establishing a high-resolution surface sediment chronology with multiple dating methods - testing Cs-137 determination with Nurmijarviclastic-biogenic varves. Quaternary Geochronology, 37, 32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quageo.2016.10.005
Perkins, R. W., & Thomas, C. W. (1980). Worldwide fallout. In Transuranic elements in the environment.
Robbins, J. A., & Edgington, D. N. (1975). Determination of recent sedimentation rates in Lake Michigan using Pb-2l0 and Cs-137. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 39, 285–304.
Sanchez-Cabeza, J. A., Masque, P., & Ani-Ragolta, I. (1998). 210Pb and 210Po analysis in sediments and soils by microwave acid digestion. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 227, 19–22.
Sanders, C. J., Santos, I. R., Silva-Filho, E. V., & Patchineelam, S. R. (2006). Mercury flux to estuarine sediments, derived from Pb-210 and Cs-137 geochronologies (Guaratuba Bay, Brazil). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 52, (9), 1085–1089.
Sanders, C. J., Smoak, J. M., Cable, P. H., Patchineelam, S. R., & Sanders, L. M. (2011). Lead-210 and Beryllium-7 fallout rates on the southeastern coast of Brazil. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity. 102 (12), 1122–1125.
Sarı, E., Catgatay, M. N., Acar, D., & Belivermis¸, M., Kılıc, O., Arslan, T.N., Tutay, A., Kurt, M.A., & Sezer, N. (2018). Geochronology and sources of heavy metal pollution in sediments of Istanbul Strait (Bosporus) outlet area, SW Black Sea. Turkey Chemosphere, 205, 387–395.
Shah, C., Banerji, U. S., Chandana, K. R., & Bhushan, R. (2020). 210Pb dating of recent sediments from the continental shelf of western India: factors influencing sedimentation rates. Environment Monitoring Assessment. (2020) Jun 29; 192(7):468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08415-x. PMID: 32601774.
Simon, H., Kelemen, S., & Begy, R. (2017). Anthropic influences on the sedimentation rates of lakes situated in different geographic areas. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity. https://bit.ly/31AyWyK
Singhal, R. K., Venkatesh, M., Wagh, D. N., Basu, H., Chavan, T., Pimple, M. V., & Reddy, A. V. R. (2012). Determination of chronological heavy metal deposition and pollution intensity in the bottom sediments of Mumbai Harbour Bay, India using 137Cs as a tracer.Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry 292(2): 863–869.
Smol, J. P. (2008). Pollution of Lakes and Rivers: A Paleoenvironmental Perspective–2nd ed. UK: Blackwell.
Tee, L. T., Ahmad, Z., & Mohamed, C. A. R. (2003). Estimation of sedimentation rates using 210Pb and 210Po at the coastal water of Sabah. Malaysia Journal of Radioanal and Nuclear Chemistry, 256, 115–120.
Urban, N. R., & Schurr, K. T. (1990). Mobility and diagenesis of Pb and 210Pb in peat. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 54, 3329–3346.
Wang, T., Tan, L., Xu, H., Zang, J., Li, D., Lan, J., Han, Y., & Li, L. (2019). The selection of a primary marker for the Anthropocene. Science Bulletin, 64, 1643–1645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.09.019
Waters, C. N., Zalasiewicz, J., Summerhayes, C., Barnosky, A. D., Poirier, C., Galuszka, A., Cearreta, A., Edgeworth, M., Ellis, E. C., Ellis, M., Jeandel, C., Leinfelder, R., McNeill, J.R., Richter, D. D., Steffen, W., Syvitski, J., Vidas, D., Wagreich, M., Williams, M., An, Z. S., Grinevald, J., Odada, E., Oreskes, N., & Wolfe, A. P. (2016). The Anthropocene is functionally and stratigraphically distinct from the Holocene. Science, 351, 137.https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad
Xueshi, S., Dejiang, F., Huijie, L., Ming, L., Yuan, T., Xilin, Z., & Zuosheng, Y. (2020). Variation in sedimentary 210Pb over the last 60 years in the Yangtze River Estuary: New insight to the sedimentary processes, Marine Geology, Volume 427, 106240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106240
Acknowledgements
The authors are greatly indebted to R.K. Singhal, Head, Analytical Spectroscopy Section, Department of Analytical Chemistry Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Center (BARC), Mumbai, India, for his support to uphold at different phases of this work. The authors are additionally grateful to the Principal Chief conservator of Forests, Chennai, and the District Forest Officer, Nilgiri Forest division, Udhagamandalam for allowing us to gather sediment samples at Lake Pykara. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, K.K., Vasudevan, S. Reconstruction of sedimentation rates based on the chronological framework of Lake Pykara, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 193, 428 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09200-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09200-0