Abstract
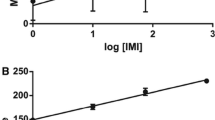
Malathion is a highly toxic organophosphate insecticide, being one of the most widely used in the world and is generally used for insect control in food production. Thus, ecotoxicological studies have been used to verify its toxic effects on aquatic organisms, such as Daphnia magna and biomarkers, as the comet assay. The comet assay is a microgel electrophoresis method for the detection and quantification of DNA strand breaks in individual cells. Cells were obtained from Daphnia magna after disaggregation of newborn organisms, exposed at concentrations of 0.23 μg L−1 and 0.47 μg L−1 for 48 h. Malathion has shown to cause damage to DNA of the exposed organisms. It was also observed the need of further studies to standardize the comet assay technique for Daphnia magna, once methodologies used present several differences.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altshuler, I., Demiri, B., Xu, S., Constantin, A., Yan, N., & Cristescu, M. (2011). An integrated multi-disciplinary approach for studying multiple stressors in freshwater ecosystems: Daphnia as a model organism. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 51, 623–633.
Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnica – ABNT 12.713. Aquatic ecotoxicology –acute toxicity – test with Daphnia spp (Cladocera, Crustacea), isbn 987–85–07-06243-1, 20–23, Rio de Janeiro, 2016.
Barata, C., Solayan, A., & Porte, C. (2004). Role of B-esterases in assessing toxicity of organophosphorus (chlorpyrifos, malathion) and carbamate (carbofuran) pesticides to Daphnia magna. Aquatic Toxicology, 66, 125–139.
Blasiak, J., Jaloszynski, P., Trzeciak, A., & Szyfter, K. (1999). In vitro studies on the genotoxicity of the organophosphorus insecticide malathion and its two analogues. Mutation Research, 445, 275–283.
Bownik, A. (2017). Daphnia swimming behaviour as a biomarker in toxicity assessment: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 601-602, 194–205.
Brianezi, G., Camargo, J., & Miot, H. (2009). Desenvolvimento e validação de técnica quantitativa de análise de imagem para avaliação do teste do Cometa corado pela prata. Jornal Brasileiro de Patologia e Medicina Laboratorial, 45(4), 325–334.
Cavalcanti, N., Aguiar, A., Lima, A., & Lima, S. (2016). Intoxicação por organofosforados: tratamento e metodologias analíticas empregadas na avaliação da reativação e inibição da acetilcolinesterase. Revista Virtual de Química, 8(3), 739–766.
Collins, A., Dobson, V. L., Dusinska, M., Kennedy, G., & Stetina, R. (1997). The comet assay: what can it really tell us? Mutation Research, 375, 183–193.
Damásio, J., Guilhermino, L., Soares, A., Riva, M. C., & Barata, C. (2007). Biochemical mechanisms of resistance in Daphnia magna exposed to the insecticide fenitrothion. Chemosphe, 70, 74–82.
De Deus, RM.; Bakonyi, S. (2012) O impacto da agricultura sobre o meio ambiente. Revista Eletrônica em Gestão, Educação e Tecnologia Ambiental. v.7, n° 7, 1306–1315.
Dearfield, K. L., Stack, F., Quest, J., Whiting, J., & Waters, M. (1993). A survey of EPA/OPP and open literature data on selected pesticide chemicals tested for mutagenicity. Mutation Research, 297, 197–233.
Depledge, M. H. (1998). The ecotoxicological significance of genotoxicity in marine invertebrates. Mutation Research, 23, 109–122.
Guilhermino, L., Lacerda, M. N., Nogueira, A., & Soares, A. (2000). In vitro and in vivo inhibition of Daphnia magna acetylcolinesterase by surfactant agents: possible implications for contamination biomonitoring. The Science of the Total Environment, 247, 137–141.
Heckmann, L., Sibly, R., Connon, R., Hooper, H., Hutchinson, T., Maund, S., Hill, C., Bouetard, A., & Callaghan, A. (2008). Systems biology meets stress ecology: linking molecular and organismal stress responses in Daphnia magna. Genome Biology, 9, 40.0–40.13.
Hongcui, L., Bingqiang, Y., & Shaonan, L. (2012). Altered quantities and in vivo activities of cholinesterase from Daphnia magna in sub-lethal exposure to organophosphorus insecticides. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 80, 118–125.
Jemec, A., Drobne, D., Tisler, T., Trebse, P., Ros, M., & Sepcic, K. (2007). The applicability of acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase in Daphnia magna toxicity test. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, Part C, 144, 303–309.
Kapczinski, F., Santin A., Andreazza, A., Frey, N., Erdtmann, B., Cereser, M., Salvador, M., Rombaldi, F., Costa, C.S. (2004) Avaliação de Danos Oxidativos ao DNA de Pacientes Portadores de Transtorno do Humor Bipolar em Comparação com Controles Comunitários, Revista psiquiatria clínica, São Paulo.
Kumar, R., Nagpure, N., Kushwaha, B., Srivastava, S., & Lakra, W. (2010). Investigation of the genotoxicity of malathion to freshwater teleost fish Channa punctatus (Bloch) using the micronucleus test and comet assay. Environmental Contamination and Toxicology., 58, 123–130.
Lan, P., & Gray, J. (2003). Predicting effects of toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 42(3), 169–173.
Lee, R., & Steinert, S. (2001). Use of the single cell gel electrophoresis/comet assay for detecting DNA damage in aquatic (marine and freshwater) animals. Mutation Research, 544, 43–64.
Lee, S., Kim, S., & Choi, J. (2009). Genotoxicity and ecotoxicity assays using the freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna and the larva of the aquatic midge Chironomus riparius to screen the ecological risks of nanoparticle exposure. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 28, 86–91.
Mangas-Ramirez, E., Sarma, S., & Nandini, S. (2004). Combined effects of algal (Chlorella vulgaris) density and ammonia concentration on the population dynamics of Ceriodaphnia dubia and Moina macropoca (Cladocera). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 51, 216–222.
Nagato, E., Simpson, A., & Simpson, M. (2016). Metabolomics reveals energetic impairments in Daphnia magna exposed to diazinon, malathion and bisphenol-A. Aquatic Toxicology, 170, 175–186.
Park, S., & Choi, J. (2007). Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and ecotoxicity assay using human cell and environmental species for the screening of the risk from pollutant exposure. Environmental International, 33, 817–822.
Parrella, A., Lavorgna, M., Criscuolo, E., Russo, C., & Isidori, M. (2015). Eco-genotoxicity of six anticancer drugs using comet assay in daphnids. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 286, 573–580.
Phan, B., Miranda, A., Allinson, G., & Nugegoda, D. (2017). Evaluating the non-lethal effects of organophosphorous and carbamate insecticides on the yabby (Cherax destructor) using cholinesterase (AChE, BChE), Glutathione S-Transferase and ATPase as biomarkers. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 143, 283–288.
Printes, L., & Callaghan, A. (2004). A comparative study on the relationship between acetylcholinesterase activity and acute toxicity in Daphnia magna exposed to anticholinesterase insecticides. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23, 1241–1247.
Saler, S., Saglan, N. (2005) Acute toxicity of Malathion on Daphnia magna Straus,1820. Journal of Biological Sciences v.5, 297–299.
Secretaria de estado da saúde do Paraná (2019) Vigilância da saúde de populações expostas a agrotóxicos no paraná. Curitiba.
Singh, N., Maccoy, M., Tice, R., & Schneider, E. (1988). A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Experimental Cell Research, 175, 184–191.
Srivastava, A., & Singh, D. (2020). Assessment of malathion toxicity on cytophysiological activity. DNA damage and antioxidant enzymes in root of Allium cepa model. Scientific Reports., 10(886), 1–10.
Stein, R. J., Lopes, S. I. G., & Fett, J. P. (2014). Iron toxicity in field-cultivated rice: contrasting tolerance mechanisms in distinct cultivars. Theoretical and Experimental. Plant Physiology, 26, 135–146.
Trac, N., Andersen, O., & Palmqvist, A. (2016). Deciphering mechanisms of malathion toxicity under pulse exposure of the freshwater cladoceran Daphnia magna. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 35, 394–403.
U.S Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2009) Registration Eligibility Decision (RED) for Malathion Revised. U.S, Office of Prevention, Pesticides and Toxic Substances. Washington, DC.
Van Der Oost, R., Beyer, J., & Vermeulen, N. (2003). Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Envirnmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 13(57–149), 2003.
Wild, D. (1975). Mutagenicity studies on organophosphorus insecticides. Mutation Research, 32, 133–115.
Zepeda-Arce, R., Trinidad, A., Diaz, I., Ochoa, I., Garcia, A., Moreno, J., Vivanco, B., Heredia, M., Villegas, G., & Hernandez, Y. (2017). Oxidative stress and genetic damage among workers exposed primarily to organophosphate and pyrethroid pesticides. Environmental Toxicology, 32, 1754–1764.
Zucker, E. (1986) Hazard evaluation division standard evaluation precedure ecological risk assessment. EPA, The United States.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knapik, L.F.O., Ramsdorf, W. Ecotoxicity of malathion pesticide and its genotoxic effects over the biomarker comet assay in Daphnia magna. Environ Monit Assess 192, 264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8235-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8235-0