Abstract
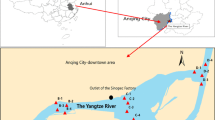
Sediment samples in this study were taken from five typical sites near the outlet of Shekou industrial district of Shenzhen City, China. The concentrations of seven elements including Cr, Cu, Cd, Pb, Hg, Zn, and As were determined respectively by atomic absorption spectrometry or atomic fluorescence spectrometry. The pollution degrees of the seven elements were assessed with the contamination factor and potential ecological risk index respectively, and their different sources were identified using multivariate statistical methods. The calculated contamination factors of these elements indicated that the sediments were at least moderately polluted by all the surveyed elements except As. The values of potential ecological risk indexes obtained decreased as the following order: Cd > Hg > Cu > As > Pb > Zn > Cr, and suggested that Cd and Hg were respectively at high and considerable environmental health risks. In addition, multivariate statistical analyses indicated that Cd, Hg, Cu, and Zn were most likely from the waste of electroplating, metal, and battery industries at Shekou industrial district, while Pb and As originated from both natural processes and anthropogenic activities along the bank of Pear River such as coal transportation and combustion, glass manufacturing, and painting, and Cr came mostly from Cr-related industries especially leather tanning within Shenzhen City. This study provided useful reference information about heavy metal contamination in the sediments in the estuarine and coastal areas with rapid urbanization and industrialization, and should be very helpful for the local governments to make relevant policies and strategies of heavy metal contamination control and management in developing countries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asci, Y. A., Nurbas, M., & Acikel, Y. S. (2008). A comparative study for the sorption of Cd (II) by K-feldspar and sepiolite as soil components, and the recovery of Cd (II) using rhamnolipid biosurfactant. Journal of Environmental Management, 88(3), 383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2007.03.006.
Bai, J. H., Cui, B. S., Chen, B., Zhang, K. J., Deng, W., Gao, H. F., & Xiao, R. (2011). Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland, China. Ecological Modelling, 222(2), 301–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2009.12.002.
Bonelli, M. G., Ferrini, M., & Manni, A. (2017). Artificial neural networks to evaluate organic and inorganic contamination in agricultural soils. Chemosphere, 186, 124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.116.
Chai, L. Y., Li, H., Yang, Z. H., Min, X. B., Liao, Q., Liu, Y., Men, S. H., Yan, Y. N., & Xu, J. X. (2017). Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1), 874–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7872-x.
Chai, M. W., Li, R. L., Tam, N. F. Y., & Zan, Q. J. (2019a). Effects of mangrove plant species on accumulation of heavy metals in sediment in a heavily polluted mangrove swamp in Pearl River Estuary, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41(1), 175–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0107-y.
Chai, M. W., Li, R. L., Ding, H., & Zan, Q. J. (2019b). Occurrence and contamination of heavy metals in urban mangroves: A case study in Shenzhen, China. Chemosphere, 219, 165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.160.
Chen, Y. M., Li, X., Zheng, Y., Guan, Y. Y., & Liu, X. P. (2011). Estimating the relationship between urban forms and energy consumption: a case study in the Pearl River Delta, 2005-2008. Landscape and Urban Planning, 102(1), 33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2011.03.007.
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Centre). (1990). The background values of Chinese soils (pp. 15–505). Beijing: Environmental Science Press of China (in Chinese).
Doabi, S. A., Afyuni, M., & Karami, M. (2017). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals contamination in atmospheric dust of Kermanshah province, western Iran, during the spring and summer 2013. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 180, 61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.06.007.
Dong, X. Q., Li, C. L., Li, J., Huang, W. T., Wang, J., & Liao, R. B. (2012). Application of a system dynamics approach for assessment of the impact of regulations on cleaner production in the electroplating industry in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 20(1), 72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.08.014.
Duodu, G. O., Goonetilleke, A., & Ayoko, G. A. (2016). Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metal in Brisbane River sediment. Environmental Pollution, 219, 1077–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.008.
Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S. (2007). Sources and characteristics of lead pollution in the urban environment of Guangzhou. Science of the Total Environment, 385(1-3), 182–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.06.047.
Fang, Z. Q., Cheung, R. Y. H., & Wong, M. H. (2003). Heavy metals in oysters, mussels and clams collected from coastal sites along the Pearl River Delta, South China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 15(1), 9–24. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1001-0742.2003.01.003.
Frena, M., Quadros, D. P. C., Castilho, I. N. B., de Gois, J. S., Borges, D. L. G., Welz, B., & Madureira, L. A. S. (2014). A novel extraction-based procedure for the determination of trace elements in estuarine sediment samples by ICP-MS. Microchemical Journal, 117, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2014.05.014.
Garelick, H., Jones, H., Dybowska, A., & Valsami-Jones, E. (2009). Arsenic pollution sources. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination Volume 197 (pp. 17–60). New York: Springer.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8.
He, B., Li, R. L., Chai, M. W., & Qiu, G. Y. (2014). Threat of heavy metal contamination in eight mangrove plants from the Futian mangrove forest, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(3), 467–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9574-3.
He, Z. F., Li, F. L., Dominech, S., Wen, X. H., & Yang, S. Y. (2019). Heavy metals of surface sediments in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary: Distribution, speciation and environmental risks. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 198, 18–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.12.015.
Huang, R. Q., Du, Y., & Cheng, L. (2013). Intelligent urban space creation approach: Shenzhen shekou industrial district renovation. Planners, 29(2), 26–31. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-0022.2013.02.005.
Islam, M. S., Ahmed, M. K., Raknuzzaman, M., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., & Islam, M. K. (2015). Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecological Indicators, 48, 282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.016.
Jiang, X., Teng, A. K., Xu, W. Z., & Liu, X. S. (2014). Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in the Yellow Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 83(1), 366–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.03.020.
Jiang, X. J., Hong, C. P., Zheng, Y. X., Zheng, B., Guan, D. B., Gouldson, A., Zhang, Q., & He, K. B. (2015). To what extent can China’s near-term air pollution control policy protect air quality and human health? A case study of the Pearl River Delta region. Environmental Research Letters, 10(10), 104006. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/10/10/104006.
Ke, X., Gui, S. F., Huang, H., Zhang, H. J., Wang, C. Y., & Guo, W. (2017). Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere, 175, 473–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.029.
Lanocha-Arendarczyk, N., Kosik-Bogacka, D. I., Kalisinska, E., Sokolowski, S., Kolodziej, L., Budis, H., Safranow, K., Kot, K., Ciosek, Z., Tomska, N., & Galant, K. (2016). Influence of environmental factors and relationships between vanadium, chromium, and calcium in human bone. BioMed Research International, 8340425. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8340425.
Legorburu, I., Rodríguez, J. G., Borja, Á., Menchaca, I., Solaun, O., Valencia, V., Galparsoro, I., & Larreta, J. (2013). Source characterization and spatio–temporal evolution of the metal pollution in the sediments of the Basque estuaries (Bay of Biscay). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 66(1-2), 25–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.11.016.
Li, T. H., Li, W. K., & Qian, Z. H. (2010). Variations in ecosystem service value in response to land use changes in Shenzhen. Ecological Economics, 69(7), 1427–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2008.05.018.
Li, F., Huang, J. H., Zeng, G. M., Yuan, X. Z., Li, X. D., Liang, J., Wang, X. Y., Tang, X. J., & Bai, B. (2013a). Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Dongting Lake, Middle China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 132, 75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.05.007.
Li, F., Zeng, X. Y., Wu, C. H., Duan, Z. P., Wen, Y. M., Huang, G. R., Long, X. L., Li, M.-J., Li, M.-J., & Xu, J. Y. (2013b). Ecological risks assessment and pollution source identification of trace elements in contaminated sediments from the Pearl River Delta, China. Biological Trace Element Research, 155(2), 301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9789-2.
Li, G. G., Hu, B. Q., Bi, J. Q., Leng, Q. N., Xiao, C. Q., & Yang, Z. C. (2013c). Heavy metals distribution and contamination in surface sediments of the coastal Shandong Peninsula (Yellow Sea). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1-2), 420–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.08.032.
Li, C., Sun, M. H., Song, C. W., Tao, P., Yin, Y. Y., & Shao, M. H. (2017a). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of the Shuangtaizi estuary using multivariate statistical techniques. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 26(1), 45–58. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2017.1245710.
Li, H. M., Kang, X. M., Li, X. M., Li, Q., Song, J. M., Jiao, N. Z., & Zhang, Y. Y. (2017b). Heavy metals in surface sediments along the Weihai coast, China: distribution, sources and contamination assessment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 115(1-2), 551–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.12.039.
Liang, X. M., Song, J. M., Duan, L. Q., Yuan, H. M., Li, X. G., Li, N., Qu, B. X., Wang, Q. D., & Xing, J. W. (2018). Source identification and risk assessment based on fractionation of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 128, 548–556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.02.008.
Lu, X. W., Wang, L. J., Li, L. Y., Lei, K., Huang, L., & Kang, D. (2010). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji, NW China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173(1-3), 744–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.001.
Manzoor, R., Zhang, T. W., Zhang, X. J., Wang, M., Pan, J. F., Wang, Z. M., & Zhang, B. (2018). Single and combined metal contamination in coastal environments in China: current status and potential ecological risk evaluation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(2), 1044–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0526-9.
Neto, J. A. G., Montes, R., & Cardoso, A. A. (1999). Spectrophotometric detection of arsenic using flow-injection hydride generation following sorbent extraction preconcentration. Talanta, 50(5), 959–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00184-8.
Pan, K., & Wang, W. X. (2012). Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Science of the Total Environment, 421, 3–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.03.013.
Peshut, P. J., Morrison, R. J., & Brooks, B. A. (2008). Arsenic speciation in marine fish and shellfish from American Samoa. Chemosphere, 71(3), 484–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.014.
Poté, J., Haller, L., Loizeau, J. L., Bravo, A. G., Sastre, V., & Wildi, W. (2008). Effects of a sewage treatment plant outlet pipe extension on the distribution of contaminants in the sediments of the Bay of Vidy, Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Bioresource Technology, 99(15), 7122–7131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.12.075.
Saravanan, P., Krishnakumar, S., Pradhap, D., Silva, J. D., Arumugam, K., Magesh, N. S., & Srinivasalu, S. (2018). Elemental concentration based potential ecological risk (PER) status of the surface sediments, Pulicat lagoon, Southeast coast of India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 133, 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.025.
Sarin, V., & Pant, K. K. (2006). Removal of chromium from industrial waste by using eucalyptus bark. Bioresource Technology, 97(1), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.010.
Silva, T. R., Testa, A., Baptista, C. R. J. A., Marques, W., & Mattiello-Sverzut, A. C. (2014). Balance and muscle power of children with Charcot-Marie-Tooth. Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy, 18(4), 334–342. https://doi.org/10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0055.
Sinharay, S. (2010). An Overview of Statistics in Education. In International Encyclopedia of Education (3rd ed., pp. 1–11). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-044894-7.01719-X.
Tian, H. Z., Wang, Y., Xue, Z. G., Qu, Y. P., Chai, F. H., & Hao, J. M. (2011). Atmospheric emissions estimation of Hg, As, and Se from coal-fired power plants in China, 2007. Science of the Total Environment, 409(16), 3078–3081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.039.
Wang, S. L., Cao, X. Z., Lin, C. Y., & Chen, X. G. (2010). Arsenic content and fractionation in the surface sediments of the Guangzhou section of the Pearl River in Southern China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1-3), 264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.07.020.
Wang, S. L., Xu, X. R., Sun, Y. X., Liu, J. L., & Li, H. B. (2013). Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: A Review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1-2), 7–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.08.025.
Wang, W., Wang, C. J., & Jin, F. J. (2018). Spatial evolution of coal transportation at coastal ports in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 28(2), 238–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-018-1470-4.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 58(301), 236–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1963.10500845.
Xiong, C. H., Li, Y. L., Wang, G. T., Fang, L., Zhou, S. G., Yao, C. P., Chen, Q., Zheng, X. M., Qi, D. M., Fu, Y. Q., & Zhu, Y. F. (2015). Selective removal of Hg (II) with polyacrylonitrile-2-amino-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole chelating resin: Batch and column study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 259, 257–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.114.
Xu, D. Q., Wang, Y. H., Zhang, R. J., Guo, J., Zhang, W., & Yu, K. F. (2016). Distribution, speciation, environmental risk, and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the karst aquatic environment of the Lijiang River, Southwest China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(9), 9122–9133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6147-x.
Xu, F. J., Liu, Z. Q., Cao, Y. C., Qiu, L. W., Feng, J. W., Xu, F., & Tian, X. (2017). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in urban river sediments in the Jiaozhou Bay catchment, Qingdao, China. Catena, 150, 9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.004.
Zhang, J. F., & Gao, X. L. (2015). Heavy metals in surface sediments of the intertidal Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China: Distributions, sources and contamination assessment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 98(1-2), 320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.06.035.
Zhang, Z. X., Lu, Y., Li, H. P., Tu, Y., Liu, B. Y., & Yang, Z. G. (2018). Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Science of the Total Environment, 645, 235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.026.
Zhao, L., Xu, Y. F., Hou, H., Shangguan, Y. X., & Li, F. S. (2014). Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 468, 654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.094.
Zhao, G. M., Ye, S. Y., Yuan, H. M., Ding, X. G., & Wang, J. (2017). Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(3), 2966–2979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8003-4.
Zhou, M., Liao, B., Shu, W. S., Yang, B., & Lan, C. Y. (2015). Pollution assessment and potential sources of heavy metals in agricultural soils around four Pb/Zn mines of Shaoguan city, China. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 24(1), 76–89. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2014.914152.
Zhou, Y., Liu, C. H., Pu, Y., Cheng, G. G., Yu, X. G., Zhou, L. X., Lin, D. M., Zhu, K., & Alfano, R. R. (2017). Resonance Raman Spectroscopy of human brain metastasis of lung cancer analyzed by blind source separation. In Neural Imaging and Sensing, Proceedings of SPIE Proceedings (p. 10051). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2254465.
Zhu, L. M., Guo, L. D., Gao, Z. Y., Yin, G. A., Lee, B., Wang, F., & Xu, J. A. (2010). Source and distribution of lead in the surface sediments from the South China Sea as derived from Pb isotopes. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(11), 2144–2153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.07.026.
Zhuang, Q. F., Li, G., & Liu, Z. Y. (2018). Distribution, source and pollution level of heavy metals in river sediments from South China. Catena, 170, 386–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.06.037.
Zuo, P., Wang, Y. P., Cheng, J., & Min, F. Y. (2008). Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in surface sediments and core sediments of the Shenzhen Bay in Guangdong Province, China. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 30(4), 71–79. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2008.04.009.
Zuo, P., Wang, Y. P., Cheng, J., & Min, F. Y. (2009). Pollution assessment of heavy metals in coastal surface sediments of the Shenzhen Bay. Marine Science Bulletin, 28(1), 50–54. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2009.01.008.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0901106), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 31871734, 31540012, 81501213), Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2018A0303130054, 2016A030313051), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province (2020B121202014), Guangdong MEPP Fund (NO. GDOE(2019)A37), Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee Grants (JCYJ20180305124211995, JCYJ20180305125619343, JCYJ20180507182405562, JSGG20160229120821300, JCYJ20170818143107733), and the National Key Project for Synthetic Biology (SQ2018YFA090029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Xu, Y., Wen, H. et al. Contamination evaluation and source identification of heavy metals in sediments near outlet of Shekou industrial district of Shenzhen City. Environ Monit Assess 192, 772 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08755-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08755-8