Abstract
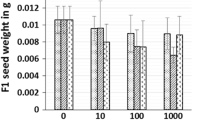
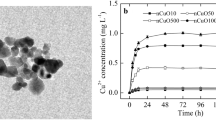
Multiple applications of nanoparticles (NPs) could result in their potential release into agricultural systems and raised concerns about food safety. The NPs once released in the environment may interact with numerous pollutants, including other NPs. Present study assessed the impact of a single (CuO and ZnO NPs) and binary mixture (CuO+ZnO NPs) on the germination of Raphanus sativus seeds with a wide range of exposure concentration (0–1000 mg/L). Both the NPs have shown a deleterious effect on seeds at exposure concentration greater than 10 mg/L. Antagonistic interaction between effects of CuO and ZnO NPs on seeds was noticed for all the exposed concentrations. CuO NPs showed higher absorption capacity on the seedling surface than ZnO NPs. Internal uptake of Zn in ZnO NP–exposed seedlings was found to be greater than that due to CuO NP–exposed seedlings. Three different types of exposure adversely affected seed germination (reduction in root length, shoot length, and fresh weight). Reduction in growth parameters (length and weight) with concentration was compared using log-logistic dose-response model of “DRC” package of the “R” software, and EC50 was determined. As per EC50 values, the toxicity of CuO NPs was found to be maximum followed by CuO+ZnO NPs and then minimum for ZnO NPs. Seedlings accumulated Cu and Zn metals, and higher uptake was recorded for Zn (reported as mg/g seedling dry weight). The order of toxicity was found as CuO NPs > binary mixture (CuO+ZnO) NPs > ZnO NPs. Exposure concentration greater than 10 mg/L resulted in significant toxicity and uptake in germinated seedlings. These findings indicated that exposure of the mixture of NPs during germination might give different effects and thus, further attempts could prove quite beneficial to the literature.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aruoja, V., Dubourguier, H.-C., Kasemets, K., & Kahru, A. (2009). Toxicity of nanoparticles of CuO, ZnO and TiO2 to microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. The Science of the Total Environment, 407(4), 1461–1468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.053.
Ates, M., Arslan, Z., Demir, V., Daniels, J., & Farah, I. O. (2015). Accumulation and toxicity of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles through waterborne and dietary exposure of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Environmental Toxicology, 30(1), 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22002.
Begum, P., & Fugetsu, B. (2012). Phytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on red spinach (Amaranthus tricolor L) and the role of ascorbic acid as an antioxidant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 243, 212–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.10.025.
Bradfield, S. J., Kumar, P., White, J. C., & Ebbs, S. D. (2016). Zinc, copper, or cerium accumulation from metal oxide nanoparticles or ions in sweet potato: yield effects and projected dietary intake from consumption. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.008.
Bradfield, S. J., Kumar, P., White, J. C., & Ebbs, S. D. (2017). Zinc, copper, or cerium accumulation from metal oxide nanoparticles or ions in sweet potato: yield effects and projected dietary intake from consumption. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 110, 128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.008.
Bundschuh, M., Gergs, R., Schadt, S., & Schulz, R. (2013). Do differences in sensitivity between native and invasive amphipods explain their coexistence in Lake Constance? A case study with lambda-cyhalothrin. Chemosphere, 92(5), 483–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.106.
Choi, O., Clevenger, T. E., Deng, B., Surampalli, R. Y., Ross, L., & Hu, Z. (2009). Role of sulfide and ligand strength in controlling nanosilver toxicity. Water Research, 43(7), 1879–1886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.01.029.
Hänsch, R., & Mendel, R. R. (2009). Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 12(3), 259–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.05.006.
Impa, S. M., Morete, M. J., Ismail, A. M., Schulin, R., & Johnson-Beebout, S. E. (2013). Zn uptake, translocation and grain Zn loading in rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes selected for Zn deficiency tolerance and high grain Zn. Journal of Experimental Botany, 64(10), 2739–2751. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert118.
Ivask, A., Juganson, K., Bondarenko, O., Mortimer, M., Aruoja, V., Kasemets, K., et al. (2014). Mechanisms of toxic action of Ag, ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to selected ecotoxicological test organisms and mammalian cells in vitro : a comparative review. Nanotoxicology, 8(sup1), 57–71. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2013.855831.
Jośko, I., Oleszczuk, P., & Skwarek, E. (2017). Toxicity of combined mixtures of nanoparticles to plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 331, 200–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.02.028.
Kim, S., Samanta, P., Yoo, J., Kim, W.-K., & Jung, J. (2017). Time-dependent toxicity responses in Daphnia magna exposed to CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 98(4), 502–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-2022-1.
Lee, W.-M., An, Y.-J., Yoon, H., & Kweon, H.-S. (2008). Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (Triticum aestivum): plant agar test for water-insoluble nanoparticles. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27(9), 1915–1921.
Lee, W. M., Kwak, J. I., & An, Y. J. (2012). Effect of silver nanoparticles in crop plants Phaseolus radiatus and Sorghum bicolor: media effect on phytotoxicity. Chemosphere, 86(5), 491–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.10.013.
Li, W.-X., Stampfl, C., & Scheffler, M. (2003). Insights into the function of silver as an oxidation catalyst by ab initio atomistic thermodynamics. Physical Review B, 68(16), 165412. Materials Science. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.68.165412.
Lin, D., & Xing, B. (2007). Phytotoxicity of nanoparticles: inhibition of seed germination and root growth. Environmental Pollution, 150(2), 243–250.
Lin, D., & Xing, B. (2008). Root uptake and phytotoxicity of ZnO nanoparticles. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(15), 5580–5585.
Lindsay, W. L. (1979). Chemical equilibria in soils.
Ma, X., Wang, Q., Rossi, L., Ebbs, S. D., & White, J. C. (2016). Multigenerational exposure to cerium oxide nanoparticles: physiological and biochemical analysis reveals transmissible changes in rapid cycling Brassica rapa. NanoImpact, 1, 46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2016.04.001.
Milewska-Hendel, A., Zubko, M., Stróż, D., & Kurczyńska, E. U. (2019). Effect of nanoparticles surface charge on the Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) roots development and their movement into the root cells and protoplasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(7), E1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071650.
Mortimer, M., Kasemets, K., & Kahru, A. (2010). Toxicity of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles to ciliated protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila. Toxicology, 269(2–3), 182–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.07.007.
Mwaanga, P., Carraway, E. R., & van den Hurk, P. (2014). The induction of biochemical changes in Daphnia magna by CuO and ZnO nanoparticles. Aquatic Toxicology, 150, 201–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.03.011.
Norwood, W. P., Borgmann, U., Dixon, D. G., & Wallace, A. (2003). Effects of metal mixtures on aquatic biota: a review of observations and methods. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 9(4), 795–811. https://doi.org/10.1080/713610010.
Ritz, C., Baty, F., Streibig, J. C., Gerhard, D., Baun, A., & Nyholm, N. (2015). Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS One, 10(12), e0146021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0146021.
Seefeldt, S. S., Jensen, J. E., & Fuerst, E. P. (1995). Log-logistic analysis of herbicide dose-response relationships. Weed Technology, 9(2), 218–227. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0890037x00023253.
Singh, D., & Kumar, A. (2015). Effects of nano silver oxide and silver ions on growth of Vigna radiata. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 95, 379–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1595-4.
Singh, D., & Kumar, A. (2016). Impact of irrigation using water containing CuO and ZnO nanoparticles on Spinach oleracea grown in soil media. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 97(4), 548–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1872-x.
Singh, D., & Kumar, A. (2018). Investigating long-term effect of nanoparticles on growth of Raphanus sativus plants: a trans-generational study. Ecotoxicology, 27(1), 23–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1867-3.
Sunda, W. G., & Huntsman, S. A. (1998). Interactions among Cu2+, Zn2+, and Mn2+ in controlling cellular Mn, Zn, and growth rate in the coastal alga Chlamydomonas. Limnology and Oceanography, 43(6), 1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1998.43.6.1055.
Trujillo-Reyes, J., Majumdar, S., Botez, C. E., Peralta-Videa, J. R., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2014). Exposure studies of core-shell Fe/Fe(3)O(4) and Cu/CuO NPs to lettuce (Lactuca sativa) plants: are they a potential physiological and nutritional hazard? Journal of Hazardous Materials, 267, 255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.11.067.
Trujillo-Reyes, J., Vilchis-Nestor, A. R., Majumdar, S., Peralta-Videa, J. R., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2013). Citric acid modifies surface properties of commercial CeO2 nanoparticles reducing their toxicity and cerium uptake in radish (Raphanus sativus) seedlings. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 263, 677–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.10.030
Wei, L., Donat, J. R., Fones, G., & Ahner, B. A. (2003). Interactions between Cd, Cu, and Zn influence particulate phytochelatin concentrations in marine phytoplankton: laboratory results and preliminary field data. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(16), 3609–3618.
Wu, S. G., Huang, L., Head, J., Chen, D.-R., Kong, I.-C., & Tang, Y. J. (2012). Phytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles is related to both dissolved metals ions and adsorption of particles on seed surfaces. Journal of Petroleum & Environmental Biotechnology, 3(4), 1000126.
Zhang, W. (2003). Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 5(3/4), 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025520116015.
Zhou, D., Jin, S., Li, L., Wang, Y., & Weng, N. (2011). Quantifying the adsorption and uptake of CuO nanoparticles by wheat root based on chemical extractions. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23(11), 1852–1857. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60646-8.
Zuverza-Mena, N., Armendariz, R., Peralta-Videa, J. R., & Gardea-Torresdey, J. L. (2016). Effects of silver nanoparticles on radish sprouts: root growth reduction and modifications in the nutritional value. Frontiers in Plant Science, 7, 90. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00090.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Indian Institute of Technology (IIT Delhi) and Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR, India) for help in conducting this study.
Funding
Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR, India) funded this study (grant number: Sr. No. 1121020571 Ref. No: 19-12/2010 (i) EU-IV).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Divya Singh has received research grants from CSIR, India. Arun Kumar has not received any research grant for this work. Divya Singh declares that she has no conflict of interest. Arun Kumar declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Capsule: Mixture of CuO and ZnO NPs gives antagonistic toxic effects with Raphanus sativus seedlings.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 765 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, D., Kumar, A. Assessment of toxic interaction of nano zinc oxide and nano copper oxide on germination of Raphanus sativus seeds . Environ Monit Assess 191, 703 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7902-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7902-5