Abstract
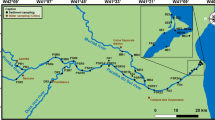
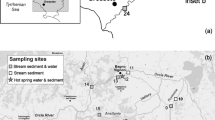
A survey of arsenic and phosphorus in Pampean streams of Buenos Aires province was performed. Nitrates and ammonia were also determined. Stream water was sampled as well as stream sediment and filamentous algae. Results show that 32 streams exceeded the arsenic recommended guidelines for human consumption of 10 μg L−1 and six exceeded recommended values for aquatic organisms’ protection of 50 μg L−1. The average concentration found was 36.54 μg L−1 and areas with more concentration of As are located in the southern region of the province, in streams that are tributaries of the Atlantic Ocean. Other regions with high As concentration are the Matanza River tributaries and the Arrecifes River tributaries. No differences of As concentration was found between stream sediments. Also, no seasonal pattern of As concentration was observed in one stream sampled during a year, but a positive correlation between As and the conductivity (p = 0.0002) and pH (p = 0.01) of the streams was found. Also, As bioaccumulation was detected for all the algae sampled, but no correlation between As accumulated and As in the stream water was found. Ammonia levels exceeded recommended guidelines for human consumption in the Argentinean law in 30 streams. The characterization performed in this study provides relevant information on the distribution of arsenic and its origin and mobility.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloupi, M., Angelidis, M., Gavriil, A. M., Koulousaris, M., & Varnavas, S. P. (2009). Influence of geology on arsenic concentrations in ground and surface water in central Lesvos, Greece. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 151(1–4), 383–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0280-z.
Alvarez, J., Marcó-Parra, L. M., Greaves, E. D., & Rivas, R. (2003). Determination of calcium, potassium, manganese, iron Koper. cooper and zinc levels in representative samples of two onion cultivars using TXRF and three preparation procedures. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 58, 2183–2189.
Anawar, H. M., Akai, J., Komaki, K., Terao, H., Yoshioka, T., Ishizuka, T., et al. (2003). Geochemical occurrence of arsenic in groundwater of Bangladesh: sources and mobilization processes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 77(2–3), 109–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(02)00273-X.
Andreae, M. O., Byrd, T. J., & Froelich, O. N. (1983). Arsenic, antimony, germanium and tin in the Tejo estuary, Portugal: modelling of a polluted estuary. Environmental Science and Technology, 17, 731–737.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. (A. D. Eaton, L. S. Clesceri, E. W. Rice, & A. E. Greenberg, Eds.). American Public Health Association.
Auge, M. P. (2014). Arsénico en el agua subterránea de la provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina. In M. I. Litter, H. B. Nicolli, J. M. Meichtry, N. Quici, J. Bundschuh, P. Bhattacharya, & R. Naidu (Eds.), Conference proceedings of the 5th international congress on arsenic in the environment (pp. 125–128). London: CRC Press.
Avigliano, E., Schenone, N. F., Volpedo, A. V., Goessler, W., & Fernández Cirelli, A. (2015). Heavy metals and trace elements in muscle of silverside (Odontesthes bonariensis) and water from different environments (Argentina): aquatic pollution and consumption effect approach. The Science of the Total Environment, 506-507, 102–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.119.
Blanck, H., Wängberg, S.-Å., Wangberg, S.-A., & Wängberg, S.-Å. (1988). Validity of an ecotoxicological test system: short-term and long-term effects of arsenate on marine periphyton communities in laboratory systems. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 45(10), 1807–1815. https://doi.org/10.1139/f88-212.
Bundschuh, J., Farias, B., Martin, R., Storniolo, A., & Bhattacharya, P. (2004). Groundwater arsenic in the Chaco-Pampean Plain, Argentina: case study from Robles county, Santiago del Estero Province. Applied Geochemistry, 19, 231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.009.
Cáceres, L., Gruttner, E., & Contreras, R. (1992). Water recycling in arid regions—Chilean case. Ambio, 21, 138–144.
Carvalho, L. H. M., Koe, T. D. E., Tavares, P. B., De Koe, T., & Tavares, P. B. (1998). An improved molybdenum blue method for simultaneous determination of inorganic phosphate and arsenate. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Restoration, 1(1), 13–19.
Coste, M., Boudou, A., Gold, C., Feurtet-Mazel, A., Coste, M., & Boudou, A. (2002). Field transfer of periphytic diatom communities to assess short-term structural effects of metals (Cd, Zn) in rivers. Water Research, 36(14), 3654–3664. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00051-9.
De la Calle, I., Cabaleiro, N., Romero, V., Lavilla, I., & Vendicho, C. (2013). Sample pretreatment strategies for total reflection X-ray fluorescence analysis: a tutorial review. Spectrochimica Acta Part B, 90, 23–54.
Dodds, W. K., Jones, J. R., & Welch, E. B. (1998). Suggested classification of stream trophic state: distributions of temperate stream types by chlorophyll, total nitrogen and phosphorus. Water Research, 32(5), 1455–1462.
Elosegi, A., Butturini, A., Armengol, J., & Sabater, S. (2009). El caudal circulante. In A. Elosegi & S. Sabater (Eds.), Conceptos y técnicas en ecología fluvial (pp. 51–69). Fundación BBVA.
Farias, S., Casa, V., Vazquez, C., Ferpozzi, L., Pucci, G., & Cohen, I. (2003). Natural contamination with arsenic and other trace elements in ground waters of Argentine Pampean Plain. Science of the Total Environment, 309(1–3), 187–199.
Feijoó, C. S., & Lombardo, R. J. (2007). Baseline water quality and macrophyte assemblages in Pampean streams: a regional approach. Water Research, 41(7), 1399–1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2006.08.026.
Feijoó, C. S., Giorgi, A., & Ferreiro, N. (2011). Phosphate uptake in a macrophyte-rich Pampean stream. Limnologica - Ecology and Management of Inland Waters, 41(4), 285–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2010.11.002.
Fendorf, S., Michael, H. A., & van Geen, A. (2010). Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science (New York, N.Y.), 328(5982), 1123–1127.
Fiorentino, C. E., Paoloni, J. D., Sequeira, M. E., Esp, E., Blanco, C., Espósito, M. E., et al. (2009). Arsenic in water resources of the southern pampa plains, Argentina. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, 2009, 216470. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/216470.
Frenguelli, J. (1956). Rasgos generales de la hidrogeografía de la provincia de Buenos Aires. LEMIT, II, 3–19.
Froelich, P. N., Kaul, L. W., Byrd, J. T., Andreae, M. O., & Roe, K. K. (1985). Arsenic, barium, germanium, tin, dimethyl-sulfide and nutrient biogeochemsitry in Charlotte Harbour, Florida, a phosphorus-enriched estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 20, 239–264.
Giorgi, A. (2016). La modificación antrópica de los ciclos de la materia. Lecture presented at Jornadas del Ciclo del Agua en los Ecosistemas. Facultad de Veterinaria- UBA.
Guasch, H., Bonet, B., Corcoll, N., Ricart, M., Serra, A., & Clements, W. H. (2012). How to link field observations with causality? Field and experimental approaches linking chemical pollution with ecological alterations. In H. Guasch, A. Ginebreda, & A. Geizsinger (Eds.), Emerging and Priority Pollutants in rivers: Bringing Science into River Management Plans. The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry (Vol. 19). Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Harold, F. M., & Baarda, J. R. (1966). Interaction of arsenate with phosphate-transport systems in wild-type and mutant Streptococcus faecalis. Journal of Bacteriology, 91(6), 2257–2262.
Jarvie, H. P., Withers, P. J. A., Bowes, M. J., Palmer-Felgate, E. J., Harper, D. M., Wasiak, K., et al. (2010). Streamwater phosphorus and nitrogen across a gradient in rural–agricultural land use intensity. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 135(4), 238–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.10.002.
Lagadic, L., & Caquet, T. (1998). Invertebrates in testing of environmental chemicals: are they alternatives? Environmental Health Perspectives, 106(Suppl 2), 593–611.
Lerda, D. E., & Prosperi, C. H. (1996). Water mutagenicity and toxicology in Río Tercero, Córdoba, Argentina. Water Research, 30, 819–824.
Matteucci, S. D. (2012). Ecorregión Pampa. In J. Morello, S. Matteucci, & A. Rodríguez (Eds.), Ecorregiones y Complejos Ecosistémicos Argentinos (1st ed., pp. 391–445). Buenos Aires: Orientación Gráfica Editora.
Neschuk, N. C., Gabellone, N. A., Claps, M. C., Solari, L. C., & Neschuk, N. C. (2005). Nutrients, conductivity and plankton in a landscape approach to a Pampean saline lowland river (Salado River, Argentina). Biogeochemistry, 75(3), 455–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-005-3273-9.
O’Farrell, I., Lombardo, R. J., Pinto, P. D. T., Loez, C., & Farrell, O. (2002). The assessment of water quality in the Lower Luján River (Buenos Aires, Argentina): phytoplankton and algal bioassays. Environmental Pollution, 120, 207–218.
Pell, A., Márquez, A., López-Sánchez, J. F., Rubio, R., Barbero, M., Stegen, S., et al. (2013). Occurrence of arsenic species in algae and freshwater plants of an extreme arid region in northern Chile, the Loa River Basin. Chemosphere, 90(2), 556–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.08.028.
Peters, S. C., Blum, J. D., Karagas, M. R., Chamberlain, C. P., & Sjostrom, D. J. (2006). Sources and exposure of the New Hampshire population to arsenic in public and private drinking water supplies. Chemical Geology, 228(1–3), 72–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.11.020.
Planas, D., & Healey, F. P. (1978). Effects of arsenate on growth and phosphorus metabolism of phytoplankton. Journal of Phycology, 14(3), 337–341. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8817.1978.tb00309.x.
Rahman, M. A., Hasegawa, H., Peter, R., & Lim, R. P. (2012). Bioaccumulation, biotransformation and trophic transfer of arsenic in the aquatic food chain. Environmental Research, 116, 118–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2012.03.014.
Rand, G. M. (1995). Fundamentals of aquatic toxicology. (G. M. Rand, Ed.). Taylor & Francis Group.
Raychowdhury, N., Mukherjee, A., Bhattacharya, P., Johannesson, K., Bundschuh, J., Bejarano Sifuentes, G., et al. (2013). Provenance and fate of arsenic and other solutes in the Chaco-Pampean Plain of the Andean foreland, Argentina: From perspectives of hydrogeochemical modeling and regional tectonic setting. Journal of Hydrology, 518(c), 300–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.07.003.
Rodríguez Castro, M. C., Urrea, G., & Guasch, H. (2014). Influence of the interaction between phosphate and arsenate on periphyton’s growth and its nutrient uptake capacity. Science of The Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.094.
Rodríguez Castro, M. C., Vilches, C., Torremorell, A., Vázquez, C. (2016). Total reflection X ray fluorescence in environmental and geochemical studies: unveiling solute provenance in streams during a rain episode. X-Ray Spectrometry, In Press. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/xrs.2694.
Rosso, J. J., Troncoso, J. J., & Fernández Cirelli, A. (2011). Geographic distribution of arsenic and trace metals in lotic ecosystems of the Pampa Plain, Argentina. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 86(1), 129–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-010-0177-8.
Rosso, J. J., Schenone, N. F., Carrera, A. P., Fernández, A., Pérez Carrera, A., & Fernández Cirelli, A. (2013). Concentration of arsenic in water, sediments and fish species from naturally contaminated rivers. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35(2), 201–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9476-9.
Sabater, S., Guasch, H., Ricart, M., Romaní, A., Vidal, G., Klünder, C., & Schmitt-jansen, M. (2007). Monitoring the effect of chemicals on biological communities. The biofilm as an interface. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 387(4), 1425–1434.
Schenone, N. F., Volpedo, A. V., & Fernández Cirelli, A. (2007). Trace metal contents in water and sediments in Samborombón Bay wetland, Argentina. Wetlands Ecology and Management, 15(4), 303–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-006-9030-6.
Schenone, N. F., Avigliano, E., Goessler, W., Fernández Cirelli, A., & Cirelli, A. F. (2014). Toxic metals, trace and major elements determined by ICPMS in tissues of Parapimelodus valenciennis and Prochilodus lineatus from Chascomus Lake, Argentina. Microchemical Journal, 112, 127–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2013.09.025.
Serra, A., Corcoll, N., & Guasch, H. (2009). Copper accumulation and toxicity in fluvial periphyton: the influence of exposure history. Chemosphere, 74(5), 633–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.10.036.
Seyler, P., & Martin, J. M. (1991). Arsenic and selenium in a pris- tine river-estuarine system: the Krka, Yugoslavia. Marine Chemistry, 34, 137–151.
Smedley, P. L., & Kinniburgh, D. G. (2002). A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 517–568.
Smedley, P. L., Kinniburgh, D. G., Macdonald, D. M. J., Nicolli, H. B., Barros, A. J., Tullio, J. O., et al. (2005). Arsenic associations in sediments from the loess aquifer of La Pampa, Argentina. Applied Geochemistry, 20(5), 989–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.10.005.
Viglizzo, E.F., & Jobbágy, E. (2006). Expansión de la Frontera Agropecuaria en Argentina y su Impacto Ecológico-Ambiental Agropecuaria en Argentina y su Impacto Ecológico-Ambiental Editores : (E. F. Viglizzo & E. Jobbágy, Eds.). Instituto Nacional de Tecnologia Agropecuaria.
Vilches, C., & Giorgi, A. (2010). Metabolism in a macrophyte-rich stream exposed to flooding. Hydrobiologia, 654(1), 57–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0368-7.
Villa-bellosta, R., & Sorribas, V. (2010). Arsenate transport by sodium/phosphate cotransporter type IIb. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 247(1), 36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2010.05.012.
Wang, N.-X., Li, Y., Deng, X., Miao, A.-J., Ji, R., & Yang, L. (2013). Toxicity and bioaccumulation kinetics of arsenate in two freshwater green algae under different phosphate regimes. Water Research, 47(7), 2497–2506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2013.02.034.
Wieland, M., Ren, Q., & Tan, J. S. Y. (2004). New developments in dam engineering proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Dam Engineering, 18-20 October 2004, Nanjing China. (M. Wieland, Q. Ren, & J. Tan, Eds.). London, UK: Taylor & Francis Group.
World Health Organization, & WHO. (1984). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. (World Health Organization (WHO), Ed.)WHO chronicle (4th ed., Vol. 38). Geneva: World Health Organization ; Albany, NY : WHO Publications Center USA [distributors].
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to thank Eduardo Zunino for his collaboration in the sampling. Also, we would like to thank the reviewers for their suggestions.
Funding information
This project was financed partially by PICT Number 1017/14 and the National University of Luján. Also, this project was financed partially by an UBACYT project of the Universidad de Buenos Aires, code 20020150100177BA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 28 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez Castro, M.C., Marcó P, L., Ranieri, M.C. et al. Arsenic in the health of ecosystems: spatial distribution in water, sediment and aquatic biota of Pampean streams. Environ Monit Assess 189, 542 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6255-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6255-1