Abstract
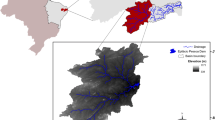
Soil erosion is an open topic, not only because soil fertility is lost, but also because nutrients are spilled into water bodies, thereby causing pollution. Research carried out in this field has amply described this process, but the interaction between these factors is complex and experimental research is needed to understand the production of loads of nutrients for different land uses. This paper describes a long-term monitoring case study using high-resolution rainfall data and runoff samples, carried out in the Lake Vico basin (Central Italy) to determine the phosphorus (P) export during erosive rainfall events. State of the art GIS-based basin characterization and advanced rainfall-runoff models are employed in order to describe the relationship between nutrient export and rainfall or runoff time distribution. Results show that the phosphorus export is strongly related to such time distributions, and less to the cumulative amount of rainfall or runoff.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnese, C., Bagarello, V., Corrao, C., D’Agostino, L., & D’Asaro, F. (2006). Influence of the rainfall measurement interval on the erosivity determinations in the Mediterranean area. Journal of Hydrology, 329, 39–48.
Arheimer, B., Andersson, L., Larsson, M., Lindström, G., Olsson, J., & Pers, B. C. (2004). Modelling diffuse nutrient flow in eutrophication control scenarios. Water Science and Technology, 49(3), 37–45.
Brakensiek, D. L., & Rawls, W. J. (1983). Agricultural management effects on soil water processes, part II: Green and Ampt parameters for crusting soils. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 26(6), 1753–1757.
Brakensiek, D. L., Rawls, W.-J., & Stephenson, G. R. (1984). Modifying SCS hydrologic soil groups and curve numbers for rangeland soils. PNR-84-203, American Society of Agricultural Engineers, St. Joseph, Mo.
Chen, H., Teng, Y., & Wang, J. (2013). Load estimation and source apportionment of nonpoint source nitrogen and phosphorus based on integrated application of SLURP model, ECM, and RUSLE: a case study in the Jinjiang River, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 2009–2021.
CORINE (Coordination of Information on Environment) Project. (2000). CORINE Database, a key database for European integrated environmental assessment. Programme of the European Commission, European Environmental Agency (EEA). http://dataservice.eea.europa.eu/dataservice/metadetails.asp?id=950.
Eli, R. N., & Lamont, S. J. (2010). Curve numbers and urban runoff modeling—application limitations. Low impact development 2010: redefining water in the city. Proceedings of the 2010 International Low Impact Development Conference, 405–418.
Gao, Y., Zhou, P., Zhu, B., Wang, T., & Tang, J.-L. (2008). Effects of gradients and rainfall intensities on phosphorus loss under simulated rainfall. 2nd International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, iCBBE 2008.
Garen, D. C., & Moore, D. S. (2005). Curve number hydrology in water quality modeling: uses, abuses, and future directions. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 41(2), 377–388.
Garnier, M., Recanatesi, F., Ripa, M. N., & Leone, A. (2010). Agricultural nitrate monitoring in a lake basin in central Italy: a further step ahead towards an integrated nutrient management aimed at controlling water pollution. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 170, 273–286.
Gerten, D., Schaphoff, S., Haberlandt, U., Lucht, W., & Sitch, S. (2004). Terrestrial vegetation and water balance—hydrological evaluation of a dynamic global vegetation model. Journal of Hydrology, 286, 249–270.
Green, W. H., & Ampt, G. A. (1911). Studies on soil physics. Journal of Agricultural Science, 4(1), 1–24.
Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., Alonso, G., & Nardi, F. (2010). Flow time estimation with variable hillslope velocity in ungauged basins. Advances in Water Resources, 33(10), 1216–1223.
Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., & Nardi, F. (2012a). A parsimonious geomorphological unit hydrograph for rainfall–runoff modelling in small ungauged basins. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 57(1), 73–83. doi:10.1080/02626667.2011.636045.
Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., & Serinaldi, F. (2012b). A continuous simulation model for design-hydrograph estimation in small and ungauged watersheds. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 57(6), 1035–1051.
Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., & Romano, N. (2013a). Green-Ampt Curve Number mixed procedure as an empirical tool for rainfall-runoff modelling in small and ungauged basins. Hydrological Processes, 27(8), 1253–1264. doi:10.1002/hyp.9303.
Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., & Romano, N. (2013b). Curve-Number/Green-Ampt mixed procedure for streamflow predictions in ungauged basins: parameter sensitivity analysis. Hydrological Processes, 27(8), 1265–1275. doi:10.1002/hyp.9749.
Grimaldi, S., & Petroselli, A. (2014). Do we still need the Rational Formula? An alternative empirical procedure for peak discharge estimation in small and ungauged basins. In press on Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2014.
Haygarth, P. M., & Jarvis, S. C. (1997). Soil derived phosphorus in surface runoff from grazed grassland lysimeters. Water Research, 31(1), 140–146.
Hoorman, J., Hone, T., Sudman, J., Dirksen, T., Iles, J., & Islam, K. R. (2008). Agricultural impacts on lakes and stream quality in grand lake St. Marys, Western Ohio. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 193, 309–322.
Jin, K., Cornelis, W. M., Gabriels, D., Baert, M., Wu, H. J., Sciettecatte, W., Cai, D. X., De Neve, S., Jin, J. Y., Hartmann, R., & Hofman, G. (2009). Residue cover and rainfall intensity effects on runoff soil organic carbon losses. Catena, 78, 81–96.
Kim, J., Oh, S., & Oh, K. (2006). Nutrient runoff from a Korean rice paddy watershed during multiple storm events in the growing season. Journal of Hydrology, 327, 128–139.
Krishna Prasad, V., Ortiz, A., Stinner, B., McCartney, D., Parker, J., Hudgins, D., Hoy, C., & Moore, R. (2005). Exploring the relationship between hydrologic parameters and nutrient loads using digital elevation model and GIS—a case study from Sugarcreek headwaters, Ohio, U.S.A. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 110, 141–169.
Lazzarotto, P., Prasuhn, V., Butscher, E., Crespi, C., Fluhler, H., & Stamm, C. (2005). Phosphorus export dynamics from two Swiss grassland catchments. Journal of Hydrology, 304, 139–150.
Law, B. E., Arkebauer, J. L., Campbell, J., Chen, O., Sun, M., Schwartz, C., & Van Ingen, S. (2008). Terrestrial carbon observations: protocols for vegetation sampling and data submission. Report 55, Global Terrestrial Observing System. FAO. http://www.fao.org/gtos/doc/pub55.pdf.
Leone, A., & Marini, R. (1993). Assessment and mitigation of the effects of land use in a lakebasin (Lake Vico in central Italy). Journal of Environmental Management, 39, 39–50.
Leone, A., Ripa, M. N., Boccia, L., & Lo Porto, A. (2008). Phosphorus export from agricultural land: a new simple quantitative methodology. Biosystems Engineering, 101, 270–280.
Lulli, L., Bidini, D., Lorenzoni, P., Quantin, P., & Raglione, M. (1990). I suoli caposaldo dell’apparato vulcanico di Vico. Ministero dell’Agricoltura e delle Foreste, Istituto sperimentale per la difesa del suolo, Firenze, Italy, 158–167 (in Italian). http://opac.bncf.firenze.sbn.it/opac/controller?action=search_bydeweysearch&query_fieldname_1=coddewey&query_querystring_1=631.4745622.
Mesa, O. J., & Mifflin, E. R. (1986). On the relative role of hillslope and network geometry in hydrologie response. In V. K. Gupta, I. Rodriguez-Iturbe, & E. F. Wood (Eds.), Scale problems in hydrology (pp. 1–17). Dordrecht: D. Reidel Publishing Co.
Naden, P. (1992). Spatial variability in flood estimation for large catchments: the exploitation of channel network structure. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 37(1), 53–71.
Nardi, F., Grimaldi, S., Santini, M., Petroselli, A., & Ubertini, L. (2008). Hydrogeomorphic properties of simulated drainage patterns using DEMs: the flat area issue. Hydrological Sciences–Journal–des Sciences Hydrologiques, 53(6), 1176–1192.
Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). (1997). Ponds-planning, design, construction. Agriculture Handbook No 590. U.S. Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington D.C.
Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). (2008). Part 630 hydrology, National Engineering Handbook. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington D.C.
Novotny, V. (2005). Diffuse pollution from Agriculture in the World. Proceedings from the International Workshop: ‘Where do fertilizers go?’. Belgirate, Italy, June, 28–29th.
Olem, H., & Simpson, J. (1994). Lake and reservoir management. Water Environment Research, 66, 489–496.
Pelorosso, R., Leone, A., & Boccia, L. (2009). Land cover and land use change in the Italian central Apennines: a comparison of assessment methods. Applied Geography, 29, 35–48.
Petroselli, A. (2012). LIDAR data and hydrological applications at the basin scale. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 49(1), 139–162. doi:10.2747/1548-1603.49.1.139.
Petroselli, A., & Alvarez, A. (2012). The flat area issue in DEMs and its consequences on the rainfall-runoff modeling. GIScience & Remote Sensing, 49(5), 711–734. doi:10.2747/1548-1603.49.5.711.
Rawls, W. J., Brakensiek, D. L., & Miller, N. (1983). Green-Ampt infiltration parameters from soil data. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 109(1), 62–70.
Recanatesi, F., Ripa, M. N., Leone, A., Perini, L., & Salvati, L. (2013). Land use, climate and transport of nutrients: evidence emerging from the Lake Vico case study. Environmental Management, 52(2), 503–513.
Ripa, M. N., Lone, A., Garnier, M., & Lo Porto, A. (2006). Agricultural land use and best management practices to control nonpoint water pollution. Environmental Management, 38, 253–266.
Rodríguez-Blanco, M. L., Taboada-Castro, M. M., & Taboada-Castro, M. T. (2013). Phosphorus transport into a stream draining from a mixed land use catchment in Galicia (NW Spain): significance of runoff events. Journal of Hydrology, 481, 12–21.
Santini, M., Grimaldi, S., Petroselli, A., Nardi, F., & Rulli, M. C. (2009). Preprocessing algorithms and landslide modelling on remotely sensed DEMs. Geomorphology, 113, 110–125.
Sharpley, A. N., Gburek, W. J., Folmar, G., & Pionke, H. B. (1999). Sources of phosphorus exported from an agricultural watershed in Pennsylvania. Agricultural Water Management, 41, 77–89.
Sharpley, A. N., McDowell, R. W., Weld, J. L., & Kleinman, P. J. A. (2001). Assessing site vulnerability to phosphorus loss in an agricultural watershed. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 2026–2036.
Sharpley, A. N., Kleinman, P., Heathwaite, A., Gburek, W. J., Folmar, G., & Schmidt, J. (2008). Phosphorus loss from an agricultural watershed as a function of storm size. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 362–368.
Serinaldi, F., & Grimaldi, S. (2011). Synthetic design hydrograph based on distribution functions with finite support. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering, 16, 434–446. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000339. ISSN: 1084-0699.
Soil Conservation Service (SCS). (1972). National Engineering Handbook, section 4, hydrology, (NEH-4), U.S. Department of Agriculture, Washington D.C.
Ulen, B., & Persson, K. (1999). Field-scale phosphorus losses from a drained clay soil in Sweden. Hydrological Processes, 13, 2801–2812.
Vidon, P., & Cuadra, P. E. (2011). Phosphorus dynamics in tile-drain flow during storms in the US Midwest. Agricultural Water Management, 98(4), 532–540.
Woodward, D. E., Hoeft, C. C., Hawkins, R. H., Van Mullem, J., & Ward, T. J. (2010). Discussion of “Modifications to SCS-CN method for long-term hydrologic simulation” by K. Geetha, S. K. Mishra, T. I. Eldho, A. K. Rastogi, and R. P. Pandey. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, 136(6), 444–446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petroselli, A., Leone, A., Ripa, M.N. et al. Linking phosphorus export and hydrologic modeling: a case study in Central Italy. Environ Monit Assess 186, 7849–7861 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3972-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3972-6