Abstract
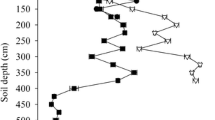
Desert riparian forests are the main body of natural oases in the lower reaches of inland rivers; its growth and distribution are closely related to water use sources. However, how does the desert riparian forest obtains a stable water source and which water sources it uses to effectively avoid or overcome water stress to survive? This paper describes an analysis of the water sources, using the stable oxygen isotope technique and the linear mixed model of the isotopic values and of desert riparian Populus euphratica forests growing at sites with different groundwater depths and conditions. The results showed that the main water source of Populus euphratica changes from water in a single soil layer or groundwater to deep subsoil water and groundwater as the depth of groundwater increases. This appears to be an adaptive selection to arid and water-deficient conditions and is a primary reason for the long-term survival of P. euphratica in the desert riparian forest of an extremely arid region. Water contributions from the various soil layers and from groundwater differed and the desert riparian P. euphratica forests in different habitats had dissimilar water use strategies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asbjornsen, H., Mora, G., & Helmers, M. J. (2007). Variation in water uptake dynamics among contrasting agricultural and native plant communities in the Midwestern U.S. Agriculture. Ecosystems and Environment, 121, 343–356.
Bailey, R. G. (1996). Ecosystem geography (1st ed.). Berlin: Springer.
Busch, D. E., Ingraham, N. L., & Smith, S. D. (1992). Water uptake in woody riparian phreatophytes of the southwestern United States: a stable isotope study. Ecological Applications, 2, 450–459.
Chen, Y. N., Cui, W. C., Li, W. H., Chen, Y. P., & Zhang, H. F. (2003). Utilization of water resources and ecological protection in the Tarim River. Acta Geographica Sinica, 58, 215–222 (in Chinese).
Chen, Y. N., Li, W. H., Chen, Y. P., Zhang, H. F., & Zhuang, L. (2004). Physiological response of natural plants to the change of groundwater level in the lower reaches of Tarim River, Xinjiang. Progress in Natural Science, 14, 975–983 (in Chinese).
Chen, Y. N., Li, W. H., Chen, Y. P., Zhao, R. F., & Wan, J. H. (2006). Ecological response of dried channel water transfer of the lower Tarim River and Ecological restoration. Arid Zone Research, 23, 521–530 (in Chinese).
Chu, J. M. (2007). Study of selective water use of plants in arid zone. Beijing, Academy of Forestry Scientific Research, Beijing. Doctoral Dissertation.
Clark, I. D., & Fritz, P. (1997). Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Dawson, T. E. (1998). Fog in the California redwood forest: ecosystem inputs and use by plants. Oecologia, 117, 476–485.
Dawson, T. E., & Ehleringer, J. R. (1991). Streamside trees that do not use stream water. Nature, 350, 335–337.
Dawson, T. E., & Pate, J. S. (1996). Seasonal water uptake and movement in root systems of Australian phraeatophytic plants of dimorphic root morphology: a stable isotope investigation. Oecologia, 107, 13–20.
Drake, P. L., & Franks, P. J. (2003). Water resource partitioning, stem xylem hydraulic properties, and plant water use strategies in a seasonally dry riparian tropical rainforest. Oecologia, 137, 321–329.
Ehleringer, J. R., Phillips, S. L., Schuster, W. S. F., & Sandquist, D. R. (1991). Differential utilization of summer rains by desert plants. Oecologia, 88, 430–434.
Fan, Z. L., Ma, Y. J., Zhang, H., Wang, R. H., Zhao, Y. J., & Zhou, H. F. (2004). Research of eco-water table and rational depth of groundwater of Tarim River drainage basin. Arid Land Geography, 27, 8–13 (in Chinese).
Han, L., Wang, H. Z., Chen, J. L., & Yu, J. (2011). Disturbance regimes and gaps characteristics of the desert riparian forest at the middle reaches of Tarim Rivers. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31, 4699–4708 (in Chinese).
Hao, X. M., Chen, Y. N., Li, W. H., Guo, B., & Zhao, R. F. (2010). Hydraulic lift in P. euphratica from the desert riparian vegetation of the Tarim River Basin. Journal of Arid Environments, 74, 905–911.
Huang, T. M., & Pang, Z. H. (2010). Changes in groundwater induced by water diversion in the Lower Tarim River, Xinjiang Uygur, NW China: Evidence from environmental isotopes and water chemistry. Journal of Hydrology, 387, 188–201.
Kendall, C., & Caldwell, E. A. (1998). Fundamentals of isotope geochemistry. In C. Kendall & J. J. McDonnell (Eds.), Isotope tracers in catchments hydrology (pp. 5–86). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science B.V.
Kolb, T. E., Hart, S. C., & Amundson, R. (1997). Boxelder water source and physiology at perennial and ephemeral stream sites in Arizona. Tree Physiology, 17, 151–160.
Li, X. M., & Zhang, X. M. (2003). Water condition and restoration of natural vegetation in the southern margin of the Taklimakan Desert. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 23, 1449–1453 (in Chinese).
Li, W. H., Hao, X. M., Qin, X. W., Chen, Y. N., & Huang, X. (2008). Ecological process of desert riparian forest communities and its hydrological mechanism of inland river basin in arid area. Journal of Desert Research, 28, 1113–1117 (in Chinese).
Mensforth, L. J., Thorburn, P. J., Tyerman, S. D., & Walker, G. R. (1994). Source of water used by riparian Eucalyptus camaldulensis overlying highly saline groundwater. Oecologia, 100, 21–28.
Phillips, D. L., & Gregg, J. W. (2003). Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too many sources. Oecologia, 136, 261–269.
Rietti-Shati, M., Yam, R., Karlen, W., & Shemesh, A. (2000). Stable isotope composition of tropical high-altitude fresh-waters on Mt. Kenya, Equatorial East Africa. Chemical Geology, 166, 341–350.
Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. (2000). Ecohydrology: a hydrologic perspective of climate-soil-vegetation dynamics. Water Resources Research, 36, 3–9.
Schachtschneider, K., & February, E. C. (2010). The relationship between fog, floods, groundwater and tree growth along the lower Kuiseb River in the hyperarid Namib. Journal of Arid Environments, 74, 1632–1637.
Smith, S. D., Welling, A. B., Nachlinger, J. A., & Fox, C. A. (1991). Functional responses of riparian vegetation to streamflow diversions in eastern Sierra Nevada. Ecological Applications, 1, 89–97.
Snyder, K. A., & Williams, D. G. (2000). Water sources used by riparian trees varies among stream types on the San Pedro River, Arizona. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 105, 227–240.
Sun, S. F., Huang, J. H., Lin, G. H., Zhao, W., & Han, X. G. (2005). Application of stable isotope technique in the study of plant water use. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 25, 2362–2371 (in Chinese).
Thorburn, P. J., & Walker, G. R. (1993). The source of water transpired by Eucalyptus camaldulensis: soil, groundwater, or streams? In J. R. Ehleringer, A. E. Hall, & G. D. Farquhar (Eds.), Stable isotopes and plant carbon-water relations (pp. 511–527). San Diego: Academic Press.
Thorburn, P. J., & Walker, G. R. (1994). Variations in stream water uptake by Eucalyptus camaldulensis with differing access to stream water. Oecologia, 100, 293–301.
Turner, J. V., Arad, A., & Johnston, C. D. (1987). Environmental isotope hydrology of salinized experimental catchments. Journal of Hydrology, 94, 89–107.
Wang, P. Y., Liu, W. J., & Li, P. J. (2010). Advance in the study of plant water use strategy. Guangxi Plants, 30, 82–88 (in Chinese).
White, J. W. C., Cook, E. R., Lawrence, J. R., & Broecker, W. S. (1985). The D/H ratios of sap in trees: implications for water sources and tree ring D/H ratios. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49, 237–246.
Zhang, G. X., He, Y., & Deng, W. (2004). Advance in the application of isotope D and 18O in water environment study. Arid Zone Research, 21, 225–229 (in Chinese).
Zhao, L. J., Xiao, H. L., Cheng, G. D., Song, Y. Y., Zhao, L., Li, C. Z., et al. (2008). A preliminary study of water sources of riparian plants in the lower reaches of the Heihe Basin. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 29, 709–718 (in Chinese).
Zhong, H. P., Liu, H., & Wang, Y. (2002). Relations between Ejina Oasis and water resources in the lower reaches of the Heihe River. Advances in Water Science, 13, 223–228 (in Chinese).
Zimmermann, U., Ehhalt, D. H., & Münnich, K. O. (1967). Soil water movement and evapotranspiration: changes in the isotopic composition of the water. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Isotopes in Hydrology. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp. 567–585.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation Major Research Plan (91025024), Key Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZZD-EW-04-05) and the ‘Western Light’ Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Si, J., Feng, Q., Cao, S. et al. Water use sources of desert riparian Populus euphratica forests. Environ Monit Assess 186, 5469–5477 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3796-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3796-4