Abstract
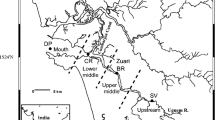
Bacterial indicators in relation to tidal variations were studied at five locations for over 2 days covering three tidal cycles in the southwestern region of Gulf of Kachchh, India. Tidal flow here is predominantly in the east west direction and can transport particles up to 32 km. Tidal amplitude appears to play a prominent role in abundance, distribution, and dispersal of coliform bacteria examined during this study. Shallow depths, clayey sediments, strong currents, and higher tidal amplitudes appear to rise by an order of magnitude in total bacterial abundance up to 2.4×104 ml − 1 due to their resuspension from the churned up sediments. Dispersal of allochthonous microflora far into coastal marine regions appears to be governed by the strong tidal amplitude in this region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1985). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (16th ed., p. 1628). Washington DC: American Public Health Association (APHA).
Babu, M. T., Vethamony, P., & Desa, E. (2005). Modelling tide driven currents and residual eddies in the Gulf of Kachchh and their seasonal variability: A marine environmental planning perspective. Ecological Modelling, 184, 299–312.
Brookings, K. G., & Epifanio, C. E. (1985). Abundance of brachyuran larvae in a small coastal inlet over six consecutive tidal cycles. Estudios, 8, 60–67.
Chandra, R., Singh, S., & Raj, A. (2006). Seasonal bacteriological analysis of Gola river water contaminated with pulp paper mill waste in Uttaranchal, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118, 393–406.
Cronin, T. W., & Forward, Jr., R. B. (1979). Tidal vertical migration an endogenous rhythm in estuarine crab larvae. Science, 205, 1020–1022.
Davies, C. M., Long, J. A., Donald, M., & Ashbolt, N. J. (1995). Survival of fecal microorganism in marine and freshwater sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61(5), 1888–1896.
Desa, E., Zingde, M. D., Vethamony, P., Babu, M. T., D’Souza, S. N., & Verlecar, X. N. (2005). Dissolved oxygen—A target indicator in determining use of the Gulf of Kachchh waters. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 73–79.
Goyal, S. M., Gerba, C. P., & Melnik, J. L. (1977). Occurrence and distribution of bacterial indicators and pathogens in canal communities along the Texas coast. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 34(2), 139–149.
Harder, B. (2005). Bacteria ride the tide: Moon‘s phases predict water quality at beaches. Science News, 168, 4.
Lindquist, R. (1993). Dispersal of bacteria in ground water-mechanism, kinetics and consequences for facilitated transport. http://www.kem.ekol.lu.se/theses.html.
MIKE21 (2001). User guide and reference manual (p. 70). Horsholm: Danish Hydraulic Institute, Agern Alle, Denmark.
Ramaiah, N., Rodrigues, E., Alvares, E., Rodrigues, C., Baksh, R., Jayan, S., et al. (2007). Sewage pollution indicator bacteria. The Mandovi and Zuari Estuaries (p. 139). Bangalore: Lotus printers.
Vethamony, P., Reddy, G. S., Babu, M. T., Desa, E., & Sudheesh, K. (2005). Tidal eddies in a semi-enclosed basin: A model study. Marine Environmental Research, 59, 519–532.
Wilson, C. A., & Stevenson, L. H. (1980). The dynamics of bacterial populations associated with a salt Marsh. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 48, 126–127.
Wright, R. T., & Coffin, R. B. (1984). Measuring microzooplankton grazing on planktonic marine bacteria by its impact on bacterial production. Microbial Ecology, 10, 137–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohandass, C., Kumar, S.J., Ramaiah, N. et al. Dispersion and retrievability of water quality indicators during tidal cycles in coastal Salaya, Gulf of Kachchh (West coast of India). Environ Monit Assess 169, 639–645 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1203-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-1203-3