Abstract
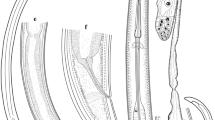
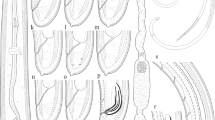
A new species of the dagger nematode genus Xiphinema was recovered from three different points in West Azarbaijan province, northwestern Iran, from the rhizosphere of grasses and described based on both morphological and molecular data. Xiphinema azarbaijanense n. sp. belongs to the Xiphinema non-americanum group and is characterized by having 3.8-5.3 mm long females with long odontostyle (129-151 μm), two equally developed genital tracts with crystalloid bodies in the tubular part of uterus, short tail, four juvenile developmental stages and males absent. It is similar to 14 known species belonging to morphospecies group 6, and is almost indistinguishable from most of them using traditional taxonomy; thus, is part of a complex of cryptic species. Molecular phylogenetic data using two genomic structural (18S, 28S D2-D3) and one ITS1 ribosomal DNA (rDNA) loci were used to separate the new species from close taxa. The new species formed an independent lineage in three reconstructed trees based upon the resolved topologies, and was also morphologically compared with phylogenetically related species.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Named after West Azarbaijan province, the origin of the new species.
References
Andrássy, I. (2009). In C. Csuzdi & S. Mahunka (Eds.), Free-living nematodes of Hungary (Nematoda errantia) (Vol. III. Pedozoologica Hungarica No. 5, 608 pp). Budapest: Hungarian Natural History Museum and Systematic Zoology Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Archidona-Yuste, A., Navas-Cortés, J. A., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2016). Cryptic diversity and species delimitation in the Xiphinema americanum-group complex (Nematoda: Longidoridae) as inferred from morphometrics and molecular markers. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 176, 231–265.
Barsi, L., & De Luca, F. (2008). Morphological and molecular characterisation of two putative Xiphinema americanumgroup species, X. parasimile and X. simile (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) from Serbia. Nematology, 10, 15–25.
Barsi, L., & Lamberti, F. (1999). Five undescribed species of Xiphinema (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) from the former territory of Yugoslavia. Nematologia Mediterranea, 27, 127–150.
Barsi, L., & Lamberti, F. (2000). Morphometric variation and juvenile stages of Xiphinema vuittenezi (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) in Serbia. Nematologia Mediterranea, 28, 3–12.
Chizhov, V. N., Tiev, R. A., & Turkina, A. Y. (1986). Two new nematode species of the genus Xiphinema (Nematoda, Longidoridae) from northern Caucasus. In D. J. F. Brown, R. Fortuner, & L. R. Creamer (Eds.), English translation of selected taxonomic papers in nematology, 5 (pp. 5–9). Sacramento: California Department of Food and Agriculture.
Chizhov, V. N., Subbotin, S. A., Romanenko, N. D., & Kruchina, S. N. (1991). New nematode species of the genera Xiphinema and Longidorus (Nematoda, Longidoridae) from the West Caucasus. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 70, 30–133.
Cobb, N. A. (1913). New nematode genera found inhabiting fresh water and non-brackish soils. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences, 3, 432–444.
Coomans, A., Huys, R., Heyns, J., & Luc, M. (2001). Character analysis, phylogeny, and biogeography of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda, Longidoridae) (Vol. 287). Belgique: Annales du Musée Royal de l’Afrique Centrale (Zoologie), Tervuren.
Dalmasso, A. (1969). Etude anatomique et taxonomique des genres Xiphinema, Longidorus et Paralongidorus. (Nematoda: Dorylaimidae). Mémoircs du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle Paris (Vol. 61, pp. 33–82). Série A, Zoologie.
De Grisse, A. T. (1969). Redescription ou modifications de quelques techniques utilisées dans l’étude des nematodes phytoparasitaires. Mededelingen Rijksfakulteit Landbouwwetenschappen. Gent, 34, 351–369.
de Man, J. G. (1884). Die frei in der reinen Erde und im süssen Wasser lebenden Nematoden der niederländischen Fauna (pp. 1–206). Leiden.
Decraemer, W., & Robbins, R. T. (2007). The who, what and where of longidoridae and trichodoridae. Journal of Nematology, 39, 295–297.
Ghaemi, R., Pourjam, E., Pedram, M., Robbins, R. T., Ye, W., & Decraemer, W. (2012). Morphological and molecular characterization of Xiphinema zagrosense sp. n. (Dorylaimida: Longidoridae) from Zagros Mountains. Nematology, 14, 445–455.
Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, C., Palomares-Rius, J. E., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Landa, B. B., Esmenjaud, D., & Castillo, P. (2010). Molecular analysis and comparative morphology to resolve a complex of cryptic Xiphinema species. Zoologica Scripta, 39, 483–498.
Gutiérrez-Gutiérrez, C., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Decraemer, W., Vovlas, N., Prior, T., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2012). Phylogeny, diversity, and species delimitation in some species of the Xiphinema americanum-group complex (Nematoda: Longidoridae), as inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA sequences and morphology. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 134, 561–597.
Holterman, M., Van Der Wurff, A., van den Elsen, S., van Megen, H., Bongers, T., Holovachov, O., Bakker, J., & Helder, J. (2006). Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 1792–1800.
Hunt, D. J. (1993). Aphelenchida, Longidoridae and Trichodoridae, Their Systematics and Bionomics. Wallingford, Oxon: CAB International.
Huson, D. H., & Scornavacca, C. (2012). Dendroscope 3: an interactive tool for rooted phylogenetic trees and networks. Systematic Biology, 61, 1061–1067.
Jahanshahi Afshar, F. (2019). The first molecular phylogenetic study of Xiphinema robbinsi Pedram, Niknam & Decraemer, 2008 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) based on specimens from the type locality. Nematology, 21, 333–335.
Joyce, S. A., Reid, A., Driver, F., & Curran, J. (1994). Application of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods to identification of entomopathogenic nematodes. In A. M. Burnell, R. U. Ehlers, & J. P. Masson (Eds.), COST 812 Biotechnology: Genetics of Entomopathogenic Nematode–Bacterium Complexes (pp 178–187). Proceedings of Symposium & workshop, St. Patrick’s College, Maynooth, Co. Kildare, Luxembourg: European Commission, DG XII.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 772–780.
Kruger, J. C. d. W. (1988). The uterine differentiation in Xiphinema. Phytophylactica, 20, 233–251.
Lamberti, F., Castillo, P., Gómez-Barcina, A., & Agostinelli, A. (1992). Description of six new species of Xiphinema (Nematoda, Dorylaimida) from the Mediterranean region. Nematologia Mediterranea, 20, 125–139.
Larget, B., & Simon, D. L. (1999). Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 750–759.
Loof, P. A. A., & Coomans, A. (1972). The oesophageal gland nuclei of Longidoridae (Dorylaimida). Nematologica, 18, 213–233.
Loof, P. A. A., & Luc, M. (1990). A revised polytomous key for the identification of species of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) with exclusion of the X. americanum-group. Systematic Parasitology, 16, 35–66.
Loof, P. A. A., & Luc, M. (1993). A revised polytomous key for the identification of species of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) with exclusion of the X. americanum group: Supplement 1. Systematic Parasitology, 24, 185–189.
Loof, P. A. A., Luc, M., & Baujard, P. (1996). A revised polytomous key for the identification of species of the genus Xiphinema Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) with exclusion of the X. americanum group: Supplement 2. Systematic Parasitology, 33, 23–29.
Luc, M., Lima, M. B., Weischer, B., & Flegg, J. J. M. (1964). Xiphinema vuittenezi n. sp. (Nematoda: Dorylaimidae). Nematologica, 10, 151–163.
Luc, M., Brown, D. J. F., & Cohn, E. (1982). Xiphinema israeliae n.sp. (Nematoda: Dorylaimoidea). Revue de Nematologie, 5, 233–239.
Mullin, P. G., Harris, T. S., & Powers, T. O. (2005). Phylogenetic relationships of Nygolaimina and Dorylaimina (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) inferred from small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Nematology, 7, 59–79.
Nunn, G. B. (1992). Nematode molecular evolution. An investigation of evolutionary patterns among nematodes based on DNA sequences. Nottingham: University of Nottingham.
Nylander, J. A. A. (2004). MrModeltest v2. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre: Uppsala University.
Oliveira, C. M. G., & Neilson, R. (2006). Taxonomy of Longidorid Nematodes and Dichotomous Keys for the Identification of Xiphinema and Xiphidorus Species Recorded in Brazil (Vol. 73, pp. 131–141). Arquivos do Instituto Biology Sao Paulo.
Oliveira, C. M. G., Ferraz, L. C. C. B., & Neilson, R. (2006). Xiphinema krugi, species complex or complex of cryptic species. Journal of Nematology, 38, 418–428.
Pearse, A. S. (1942). Introduction to Parasitology (p. 357). Baltimore: Springfield, Ill.
Pedram, M. (2017). Cryptaphelenchus varicaudatus n. sp. (Rhabditida: Ektaphelenchinae) from Tehran Province, Iran. Journal of Nematology, 49, 223–230.
Pedram, M., Niknam, G., & Decraemer, W. (2008). Xiphinema robbinsi sp. n. (Nematoda, Dorylaimida), an amphimictic species from Iran. Russian Journal of Nematology, 16, 49–57.
Pedram, M., Niknam, G., Robbins, R. T., Ye, W., & Karegar, A. (2009). Xiphinem iranicum n. sp. (Nematoda: longidoridae) from northwestern Iran. Nematology, 11, 11–21.
Pedram, M., Pourjam, E., Robbins, R. T., Ye, W., Atighi, M. R., & Decraemer, W. (2012a). Morphological and molecular characterization of Xiphinema mazandaranense n. sp. (Dorylaimida: Longidoridae), a new member to X. pyrenaicum species complex. Nematology, 14, 109–119.
Pedram, M., Pourjam, E. G., Palomares-Rius, G. R., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., & Castillo, P. (2012b). Molecular and morphological characterisation of Xiphinema granatum n. sp. and Longidorus pisi Edward, Misra and Singh, 1964 (Dorylaimida: Longidoridae) from Iran. Nematology, 14, 949–960.
Pedram, M., Pourjam, E., Namjou, S., Atighi, M. R., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Liébanas, G., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2012c). Molecular and morphological characterisation of Paralongidorus iranicus n. sp. and Paralongidorus bikanerensis (Lal & Mathur, 1987) Siddiqi, Baujard & Mounport, 1993 (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from Iran. Nematology, 14, 427–443.
Peraza-Padilla, W., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Zamora-Araya, T., Palomares-Rius, J. E., Castillo, P., & Archidona-Yuste, A. (2018). A new dagger nematode, Xiphinema tica n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidoridae), from Costa Rica with updating of the polytomous key of Loof and Luc (1990). European Journal of Plant Pathology, 150, 73–90.
Robbins, R. T., Brown, D. J. F., Halbrendt, J. M., & Vrain, T. C. (1996). Compendium of juvenile stages of Xiphinema species (Nematoda: Longidoridae). Russian Journal of Nematology, 4, 163–171.
Roca, F., & Bravo, M. A. (1993). The occurrence of Xiphinema sphaerocephalum Lamberti et al. and X. hispanum Lamberti et al. (Nematoda: Longidoridae) in Portugal with descriptions of X. lanceolatum sp. n. and X. lapidosum sp. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 16, 455–465.
Roca, F., & Lamberti, F. (1988). Xiphinema aequum sp. n. (Nematoda: Dorylaimida) from Italy, with description of the male of Longidorus eridanicus. Nematologia Mediterranea, 16, 87–91.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19, 1572–1574.
Roshan-Bakhsh, A., Pourjam, E., Pedram, M., Robbins, R. T., & Decraemer, W. (2014). Description of Xiphinema castilloi sp. n. (Dorylaimida: Longidoridae) from Iran and its phylogenetic relationships. Nematology, 16, 359–368.
Siddiqi, M. R. (2000). Tylenchida Parasites of Plants and Insects (2nd ed.p. 833). Wallingford: UK, CABI Publishing.
Silvestro, D., & Michalak, I. (2011). raxmlGUI: a graphical frontend for RAxML. Organisms Diversity and Evolution, 12, 335–337.
Subbotin, S., Halford, P. D., Warry, A., & Perry, R. N. (2000). Variations in ribosomal DNA sequences and phylogeny of Globodera parasitising solanaceous plants. Nematology, 2, 591–604.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., & Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 30, 2725–2729.
Thorne, G. (1935). Notes on free-living and plant-parasitic nematodes. II-Higher classification groups of Dorylaimoidea. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 2, 96–98.
Tzortzakakis, E. A., Archidona-Yuste, A., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Nasiou, E., Lazanaki, M. S., Kabourakis, E. M., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2014). Integrative diagnosis and molecular phylogeny of dagger and needle nematodes of olives and grapevines in the island of Crete, Greece, with description of Xiphinema cretense n. sp. (Nematoda, Longidoridae). European Journal of Plant Pathology, 140, 563–590.
Tzortzakakis, E. A., Archidona-Yuste, A., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Nasiou, E., Palomares-Rius, J. E., & Castillo, P. (2015). Description and molecular characterisation of Xiphinema herakliense n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidoridae) from wild and cultivated olives in Crete. Nematology, 17, 231–245.
Williams, T. D. (1961). Xiphinema bakeri n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidorivae) from the Fraser river Valley, British Columbia, Canada. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 39, 407–412.
Ye, W., & Robbins, R. T. (2004). Longidorus biformis n. sp. and L. glycines n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidoridae), two amphimictic species from Arkansas. Journal of Nematology, 36, 1–13.
Zhao, L., Ye, W., Munawar, M., Pedram, M., & Gu, L. (2017). Xiphinema japonicum n. sp. (Nematoda: Longidorinae) from the Rhizosphere of Japanese Podocarpus macrophyllus (Thunb.), a cryptic species related to Xiphinema bakeri Williams, 1961. Journal of Nematology, 49, 404–417.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate valuable help of Dr. Karen Freeman (Research Director of Madagascar Fauna and Flora Group, Stirling, United Kingdom) for her technical comments and reviewing the manuscript, and Tarbiat Modares University and Iranian National Science foundation (INSF) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors certify that they do not have any conflict of interest, the presented data are original and the described species is not published, and is not under evaluation for publication elsewhere, all prevailing local, national and international regulations and conventions, and normal scientific ethical practices, have been respected. They also certify that the final version of this manuscript has been reviewed by all authors.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
No specific permits were required for this study. The soil samples analyzed in this study were obtained in public areas, forests, and grasslands, which are not under protection.
Informed consent
The authors certify that they have accepted the principles of ethical standards and that guidelines of professional conduct have been followed. The funders had no role in designing of this study, collecting and analyzing of the data, preparing the manuscript and are not involved in evaluating or publishing process of this research.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1.
Pairwise genetic distances for selected 28S rDNA D2-D3 sequences of species used in 28S phylogenetic tree of Xiphinema azarbaijanense n. sp. (XLS 38 kb)
Supplementary Table 2.
Pairwise genetic distances for selected ITS1 rDNA sequences of species used in ITS1 phylogenetic tree of Xiphinema azarbaijanense n. sp. (XLS 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahanshahi Afshar, F., Shahryari, F., Gharibzadeh, F. et al. Description of Xiphinema azarbaijanense n. sp. (Nematoda; Longidoridae) from West Azarbaijan province, northwestern Iran. Eur J Plant Pathol 155, 417–434 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01776-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-019-01776-1