Abstract
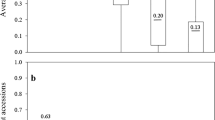
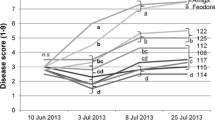
Pleiochaeta root rot (PRR) caused by Pleiochaeta setosa is a serious, widespread fungal disease in lupin crops, especially in Lupinus albus (broad-leaf lupin, or white lupin). PRR resistance is common in the gene pool of L. albus with various landraces from the Mediterranean region being the most resistant, and suitable for use in breeding new cultivars. Heritability of resistance is sufficient to make good gains from selection but only when controlled-environment (CE) screening is used. Field disease nurseries on loamy soil gave much lower heritability of resistance. Field disease nurseries had spatially variable spore counts despite continuous lupin cropping, and this was partly responsible (along with climatic conditions) for their reduced precision compared to tests conducted in a CE. Giving infected L. albus roots a single, most-severe-lesion score on a 0–9 scale was adequate for CE screening but not as precise or discriminating as the more time-consuming method of six scores per root. Replication in CE experiments was reduced to two pots of 16 seedlings each without sacrificing genotype discrimination.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BLS:
-
Brown leaf spot
- CE:
-
Controlled environment
- DN:
-
Disease nursery
- PRR:
-
Pleiochaeta root rot
- REML:
-
Residual maximum likelihood
References
Bateman, G. L. (1997). Pathogenicity of fungi associated with winter loss and injury in white lupin. Plant Pathology, 46, 157–167. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3059.1997.d01-215.x.
Bradley, F., Oram, R. N., & Malafant, K. W. (2002). Inheritance of partial resistance to brown spot disease in Lupinus angustifolius L. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 53, 919–929. doi:10.1071/AR01155.
Coombes, N. E. (2002). The reactive tabu search for efficient correlated experimental designs. PhD thesis, John Moores University, Liverpool UK.
Cowling, W. A., Sweetingham, M. W., Diepeveen, D., & Cullis, B. R. (1997). Heritability of resistance to brown spot and root rot of narrow-leafed lupins caused by Pleiochaeta setosa (Kirchn.) Hughes in field experiments. Plant Breeding, 116, 341–345. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.1997.tb01009.x.
Cullis, B. R., Smith, A. B., & Coombes, N. E. (2006). On the design of early generation cultivar trials with correlated data. Journal of Agricultural Biological & Environmental Statistics, 11, 381–393. doi:10.1198/108571106X154443.
FAO-Unesco. (1974). Soil map of the world, Vol 1, Legend, p. 59. Paris: UNESCO.
Finney, D. J. (1964). Statistical method in biological assay (2nd ed.). Charles Griffin & Co Ltd.
Gondran, J., Bournoville, R., & Duthion, C. (1994). Identification of diseases, pests and physical constraints in white lupin. Versailles, France: INRA Editions.
Hill, G. D. (1998). Diseases of lupins. In D. J. Allen & J. M. Lenne (Eds.), The pathology of food and pasture legumes, pp. 559–589. Wallingford, UK: CAB International.
Infantino, A., Kharrat, M., Riccioni, L., Coyne, C., McPhee, K., & Grünwald, N. (2006). Screening techniques and sources of resistance to root diseases in cool season food legumes. Euphytica, 147, 201–221. doi:10.1007/s10681-006-6963-z.
Luckett, D. J., Cowley, R. B., Richards, M. F., & Roberts, D. M. (2008). Improved methodology for screening for resistance to Pleiochaeta setosa root rot in Lupinus albus. In J. A. Palta & J. Berger (Eds.), 12th International Lupin conference. Fremantle, Western Australia: International Lupin Association.
Noffsinger, S. L., & Santen, Ev. (2005). Evaluation of Lupinus albus L. germplasm for the southeastern USA. Crop Science, 45, 1941–1950. doi:10.2135/cropsci2004.0575.
Pilet-Nayel, M. L., Muehlbauer, F. J., McGee, R. J., Kraft, J. M., Baranger, A., & Coyne, C. J. (2005). Consistent quantitative trait loci in pea for partial resistance to Aphanomyces euteiches isolates from the United States and France. Phytopathology, 95, 1287–1293. doi:10.1094/PHYTO-95-1287.
Raza, S., Christiansen, J. L., Jornsgard, B., & Ortiz, R. (2000). Partial resistance to a Fusarium root disease in Egyptian white lupin landraces. Euphytica, 112, 233–237. doi:10.1023/A:1003904805737.
Simmonds, N. W., & Smartt, J. (1999). Principles of crop improvement (2nd ed.). UK: Blackwell Science Oxford.
Sweetingham, M., & Yang, H. (1998). New sources of resistance to Pleiochaeta and Eradu patch disease in Lupinus spp. Perth, WA: CLIMA (Centre for Legumes in Mediterranean Agriculture.
Sweetingham, M. W. (1991). The effect of inoculum distribution and sowing depth on Pleiochaeta root rot of lupins. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 42, 121–128. doi:10.1071/AR9910121.
Sweetingham, M. W., Jones, R. A. C., & Cowling, W. A. (1996). Advances in lupin disease management in Australia. In G. D. Hill (Ed.), Towards the 21st century. Proceedings of the 8th international lupin conference, pp. 466–486. Canterbury, New Zealand: International Lupin Association. Asilomar, California, USA.
Tivoli, B., Baranger, A., Avila, C. M., Banniza, S., Barbetti, M., Chen, W. D., et al. (2006). Screening techniques and sources of resistance to foliar diseases caused by major necrotrophic fungi in grain legumes. Euphytica, 147, 223–253. doi:10.1007/s10681-006-3131-4.
Wunderlich, N., Ash, G. J., Harper, J. D. I., Cowley, R. B., & Luckett, D. J. (2008). Penetration and symptom development of Pleiochaeta root rot in susceptible and resistant Lupinus albus cultivars. Australasian Plant Pathology, 37, 387–391. doi:10.1071/AP08014.
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the GRDC (Grains Research & Development Corporation, Australia). We thank Bev Orchard for help with statistical advice. Colin Smith and Jon Clements provided seed from the Australian Lupin Germplasm Collection held at DAFWA in Perth, Western Australia. We thank John Harper and Gavin Ash for encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luckett, D.J., Cowley, R.B., Richards, M.F. et al. Breeding Lupinus albus for resistance to the root pathogen Pleiochaeta setosa . Eur J Plant Pathol 125, 131–141 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9465-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-009-9465-8