Abstract
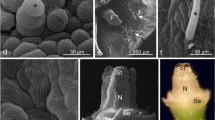
The morphology of apple and pear stigma was investigated with confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The floral colonization process by Erwinia amylovora was studied with gfp-labelled bacteria and confocal laser scanning microscopy to allow the in vivo observation of the pathogen colonization on intact, viable plant tissues without any kind of staining of the specimens. The interaction on the stigma between Erwinia amylovora and Pantoea agglomerans, both labelled with genes encoding for fluorescent proteins (DsRed-GFP), was also investigated. A stylar groove, covered by papillae and dwelling from the stigma along the style, was visualized. In laboratory conditions, this groove was shown to be an important way for E. amylovora migration towards the nectarthodes. Due to its anatomical structure the groove can sustain bacterial multiplication and thus may play an important role on the interactions between the pathogen and the bacterial antagonist P. agglomerans.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Confocal laser scanning microscopy:
-
CLSM
- scanning electron microscopy:
-
SEM
References
GS Baird DA Zacharias R Tsien (2000) ArticleTitleBiochemistry, mutagenesis, and oligomerization of DsRed, a red fluorescent protein from coral Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 97 11984–11989 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnvVSgtro%3D
GV Bloemberg GA O’Toole BJJ Lugtenber R Kolter (1997) ArticleTitleGreen fluorescent protein as a marker for Pseudomonas spp Applied and Environonmental Microbiology 63 4543–4551 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnt12ntbc%3D
GV Bloemberg AHM Wijfjes GEM Lamers N Stuurman BJJ Lugtenberg (2000) ArticleTitleSimultaneous imaging of Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 populations expressing three different autofluorescent proteins in the rhizosphere: New perspectives for studying microbial communities Molecular Plant–Microbe Interactions 13 1170–1176 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnslaisL0%3D Occurrence Handle11059483
J Bogs I Bruchmüller C Erbar K Geider (1998) ArticleTitleColonization of host plants by the fireblight pathogen Erwinia amylovora marked with genes for bioluminescence and fluorescence Phytopathology 88 416–421
TJ Burrill (1883) ArticleTitleNew species of Micrococcus American Naturalist 17 319
M Cresti F Ciampolini S Sansavini (1980) ArticleTitleUltrastructural and histochemical features of the pistil of Malus communis: the stylar transmitting tissue Scientia Horticulturae 12 327–337 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-4238(80)90047-3
M Cresti F Ciampolini S Sansavini (1985) ArticleTitleThe morphological characteristics of the stigma in various fruit plants Rivista della Ortoflorofrutticoltura Italiana 69 49–62
SJ Eden-Green E Billing (1974) ArticleTitleFireblight Review of Plant Pathology 53 353–365
H Falkenstein P Bellemann S Walter W Zeller K Geider (1988) ArticleTitleIdentification of Erwinia amylovora, the fireblight pathogen, by colony hybridization with DNA from plasmid pEA29 Applied and Environmental Microbiology 54 2798–2802 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXjsVOrtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle16347778
K Geider R Baldes P Bellemann M Metzger T Schwartz (1995) ArticleTitleMutual adaptation of bacteriophage fd, pfd plasmids␣and their host strains Microbiological Research 15 337–346
MJ Hattingh SV Beer EW Lawson (1986) ArticleTitleScanning electron microscopy of apple blossom colonized by Erwinia amylovora and Erwinia herbicola Phytopathology 76 900–904
EM Hildebrand (1937) The blossom-blight phase of fireblight? and methods of control Cornell University Agriculture Experiment Station Memoirs 207 Ithaca, New York 17–40
CA Ishimaru EJ Klos RR Brubaker (1988) ArticleTitleMultiple antibiotic production by Erwinia herbicola Phytopathology 78 746–750 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlsVKhsr0%3D
S Jock V Donat MM López C Bazzi K Geider (2002) ArticleTitleFollowing spread of fire blight in western, central and southern Europe by molecular differentiation of Erwinia amylovora strains with PFGE analysis Environmental Microbiology 4 106–114 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00277.x Occurrence Handle11972620
KB Johnson VO Stockwell (2000) Biological control of fire blight JL Vanneste (Eds) Fire Blight: the Disease and its Causative Agent Erwinia amylovora CAB International Wallingford Oxon, United Kingdom
KB Johnson VO Stockwell MJ JE McLaughlin Loper RG Roberts (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of bacterial antagonists on establishment of honey bee-dispersed Erwinia amylovora in pear blossom and on fire blight control Phytopathology 83 995–1002
CM Labarca M Kroh F Loewus (1970) ArticleTitleThe composition of stigmatic exudate from Lilium longiflorum labelling studies with myo-inositol, d-glucose and l-proline Plant Physiology 46 150–156 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3MXhtFem
SE Lindow MT Brandl (2003) ArticleTitleMicrobiology of the phyllosphere Applied and Environmental Microbiology 69 1875–1883 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.69.4.1875-1883.2003 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXivFKrur8%3D Occurrence Handle12676659
TD Miller MN Schroth (1972) ArticleTitleMonitoring the epiphytic population of Erwinia amylovora on pear with a selective medium Phytopathology 62 1175–1182
JM Monier SE Lindow (2003) ArticleTitleDifferential survival of solitary and aggregated bacterial cells promotes aggregate formation on leaf surface Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 100 15977–15982 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtVCrtQ%3D%3D
JM Monier SE Lindow (2004) ArticleTitleFrequency, size and localization of bacterial aggregates on bean leaf surface Applied and Environmental Microbiology 70 346–355 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.70.1.346-355.2004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXmvFansQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle14711662
AL Pierstorff (1931) Studies on the fire-blight organism, Bacillus amylovorus Cornell University Agricultural Experiment Station Memoir 136 Ithaca, New York
Rosen HR (1936) Mode of penetration and progressive invasion of fire-blight bacteria into apple and pear blossoms. University of Arkansas College of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin no 331
JR Rundle S Beer (1987) ArticleTitlePopulation dynamics of Erwinia amylovora and biological control agent, Erwinia herbicola, on? apple blossom parts Acta Horticulturae 217 221–222
Spinelli F, Marcazzan GL and Sabatini AG (2000) Effetto degli inibitori delle diossigenasi sulla composizione glucidica del nettare di pomacee e sulle dinamiche di biocontrollo del colpo di fuoco batterico. Atti VI Giornate Scientifiche SOI, Spoleto 23–25 aprile 2002. 1: 109–110.
VO Stockwell KB Johnson JE Loper (1996) ArticleTitleCompatibility of bacterial antagonists of Erwinia amylovora with antibiotics used for fire blight control Phytopathology 86 834–840
VO Stockwell JE Loper KB Johnson (1992) ArticleTitleEstablishment of bacterial antagonists on pear blossom Phytopathology 82 1128
VO Stockwell D Sugar R Spotts KB Johnson JE Loper (1998) ArticleTitleEstablishment of bacterial antagonists of Erwinia amylovora on pear and apple blossoms as influenced by inoculum preparation Phytopathology 88 506–513
A Takhtajan (1991) Evolutionary trends in flowering plants Columbia University Press New York
SV Thomson (1986) ArticleTitleThe role of the stigma in fire blight infections Phytopathology 76 476–482
JL Vanneste (1995) Erwinia amylovora US Singh RP Singh K Kohomoto (Eds) Pathogenesis and Host Specificity in Plant Disease: Histopathological, Biochemical, Genetic and Molecular Basis NumberInSeriesVol. 1 Prokaryotes, Pergammon Press Oxford and London 21–46
JL Vanneste (2000) Fire Blight, the Disease and its Causative Agent Erwinia amylovora CABI Publishing Wallingford, UK 370
JL Vanneste J Yu (1996) ArticleTitleBiological control of fire blight using Erwinia herbicola Eh252 and Pseudomonas fluorescens A506 separately or in combination Acta Horticulturae 411 351–353
M Wilson HAS Epton DC Sigee (1989) ArticleTitleErwinia amylovora infection of hawthorn blossom: II. The stigma Journal of Phytopathology 127 15–28
M Wilson HAS Epton DC Sigee (1990a) ArticleTitleErwinia amylovora infection of hawthorn blossom: III. The nectary Journal of Phytopathology 187 62–74
M Wilson HAS Epton DC Sigee (1990b) ArticleTitleBiological control of fire blight of hawthorn (Crateagus monogyna) with Erwinia herbicola under protected conditions Plant Pathology 39 301–308
M Wilson HAS Epton DC Sigee (1992) ArticleTitleInteractions between Erwinia herbicola and Erwinia amylovora on the stigma of hawthorn blossom Phytopathology 82 914–918
M Wilson SE Lindow (1993) ArticleTitleInteractions between the biological control agent Pseudomonas fluorescens strain A506 and Erwinia amylovora in pear blossom Phytopathology 83 117–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spinelli, F., Ciampolini, F., Cresti, M. et al. Influence of Stigmatic Morphology on Flower Colonization by Erwinia amylovora and Pantoea agglomerans. Eur J Plant Pathol 113, 395–405 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-4511-7
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-005-4511-7