Abstract
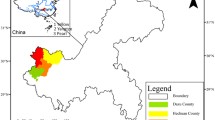
At present, sanitary landfill is mainly used for domestic waste treatment in Shannan City, Tibet. However, there are few studies on heavy metals in the soil around the landfill in Shannan city. Therefore, the surrounding soil of Luqionggang landfill in Shannan City, Tibet Autonomous Region, is taken as the research object. In the study, the geo-accumulation index method, Nemerow comprehensive pollution index method and potential ecological risk index method are mainly used to evaluate the pollution and risk of heavy metals in the soil around the landfill site. The main results are as follows: The average pH value of the soil around the landfill site is 9.37, belonging to the strong alkaline range. The average values of heavy metals Hg and Ni in soil exceeded the background content, and the average contents of other heavy metals Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, As and Cd did not exceed the background content. The average content of these eight heavy metals did not exceed the screening value of the national soil environmental quality standard. In the horizontal direction, the average content of heavy metal elements Cu, Cr, Cd, Hg and Ni is relatively high in the west. The average content of heavy metals As, Zn and Pb in the north, east and south is slightly higher than that in the west. And the farther away from the landfill, the less the soil is affected by heavy metals. The evaluation results of geo-accumulation index show that heavy metal Hg is the most affected. The average value of the comprehensive pollution index is 2.969, which is between 2 and 3, belonging to the moderate pollution level. And the west side of the landfill (downstream area) is greatly affected. The evaluation results of potential ecological hazard pollution index show that the potential risk index of single pollutants of heavy metals Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Ni, As and Cd belongs to low ecological hazard level, and the potential risk index of single pollutants of heavy metal Hg belongs to relatively heavy ecological hazard level. On the whole, the total potential risk coefficient belongs to medium pollution hazard degree. According to the correlation analysis, there is no significant correlation between heavy metal elements As and Hg and the other six heavy metal elements. In addition, the pollution source of heavy metal As may be mainly soil forming factors and the pollution source of Hg may be mainly human factors.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript and available from the corresponding author upon request. Supplementary information is available at Environmental Geochemistry and Health’s website.
References
Adelopo, A. O., Haris, P. I., Alo, B. I., & Huddersman, K., Jenkins R.O. (2018). Multivariate analysis of the effects of age, particle size and landfill depth on heavy metals pollution content of closed and active landfill precursors. Waste Management, 78, 227–237.
Alejandro, S. C., Cristina, P. M., Ciro, A. O. R., & Nadal, J. (2008). Bioaccumulation of metals and effects of a landfill in small mammals. Part II. The wood mouse. Apodemus sylvaticus. Chemosphere, 70(1), 101–109.
Allen, A. (2001). Containment landfills: The myth of sustainability. Engineering Geology, 60(1–4), 3–19.
Bakare, A. A., Pandey, A. K., Bajpayee, M., Bhargav, D., Chowdhuri, D., Singh, K. P., & Murthy, R. C. (2006). DNA damage induced in human peripheral blood lymphocytes by industrial solid waste and municipal sludge leachates. Environmental & Molecular Mutagenesis, 48(1), 30–37.
Barbieri, M., Sappa, G., Vitale, S., Parisse, B., & Battistel, M. (2014). Soil control of trace metals concentrations in landfills: a case study of the largest landfill in Europe, Malagrotta, Rome. Journal Geochemical Exploratin, 143, 146–154.
Berkun, M., Aras, E., & Nemlioglu, S. (2005). Disposal of solid waste in Istanbul and along the Black Sea coast of Turkey. Waste Management, 25(8), 847–855.
Booth, C. J., & Vagt, P. J. (1990). Hydrogeology and historical assessment of a classic sequential-land use landfill site, Illinois, U.S.A. Environmental Geology, 15(3), 165–178.
Cai, L. M., Xu, Z. C., Sun, G. X., Chen, Z., Bao, P., He, M., Dou, L., Chen, L. G., Zhou, Y. Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2015). Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and source of arsenic and heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunde, Southeast China. Journal of Geo-chemical Exploration, 148, 189–195.
Cevik, F., Goeksu, M. Z. L., Derici, O. B., & Findik, O. (2008). An assessment of metal pollution in surface sediments of Seyhan Dam by using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index and statistical analyses. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 152(1–4), 309–317.
Chai, X. L., Lou, Z. Y., Takayuki, S., Hirofumi, N., Zhu, Y., Cao, X. Y., Teppei, K., Toshio, I., & Zhao, Y. C. (2010). Characteristics of environmental factors and their effects on CH4 and CO2 emissions from a closed landfill: an ecological case study of Shanghai. Waste Management, 30(3), 446–451.
Chen, X. M., Zhu, B. H., Yang, W., & Ji, H. B. (2015). Sources, spatial distribution and contamination assessments of heavy metals in gold mine area soils of Miyun Reservoir upstream, Beijing China. Environmental Chemistry, 34(12), 2248–2256. (in Chinese).
Christophoridis, C., Dedepsidis, D., & Fytianos, K. (2009). Occurrence and distribution of selected heavy metals in the surface sediments of Thermaikos Gulf, N. Greece Assessment using pollution indicators. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(2–3), 1082–1091.
Dai, L., Wang, L., Liang, T., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Xiao, J., Dong, L., & Zhang, H. (2019). Geostatistical analyses and co-occurrence correlations of heavy metals distribution with various types of land use within a watershed in eastern QingHai-Tibet Plateau, China. The Science of the Total Environment, 653(25), 849–859.
Dan, Z., Zhou, W., Zhou, P., Che, Y., Han, Z., Qiong, A., Duo, B., Lv, X., Zhuoma, Q., Wang, J., & Yang, W. (2021). Characterization of municipal solid waste incineration and flue gas emission under anoxic environment in Tibet Plateau. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(29), 1–14.
Ding, Z. H., Tang, Q. H., Liu, C. E., Wang, W. H., Zhuang, M., & Lin, Y. M. (2007). Distribution and ecological effect of mercury in Laogang landfill, Shanghai China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(2), 200–204.
Dorothy, D. H. B., Matthew, C. S., David, K. G., & Das, K. C. (2001). Characterization of microbial populations in landfill leachate and bulk samples during aerobic bioreduction. Advances in Environmental Research, 5(3), 285–294.
Elliott, P., Briggs, D. J., Morris, S., Hoogh, K. D., Hurt, C., Jensen, T. K., Maitland, I., Richardson, S., Wakefield, J., & Jarup, L. (2001). Risk of adverse birth outcomes in populations living near landfill sites. BMJ Clinical Research, 323(7309), 363–368.
Fan, M. Y., Yang, H., Huang, X. F., Cao, R. S., Zhang, Z. D., Hu, J. W., & Qin, F. X. (2016). Chemical forms and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around a typical coal-fired power plant located in the mountainous area. China Environmental Science, 36(8), 2425–2436. (in Chinese).
Fang, X. H., Peng, B., Wang, X., Song, Z. L., Zhou, D. X., Wang, Q., Qin, Z. L., & Tan, C. Y. (2019). Distribution, contamination and source identification of heavy metals in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan province, China - ScienceDirect. Science of The Total Environment, 689, 557–570.
Geschwind, S. A., Stolwijk, J. A. J., Michael, B., Edward, F., Alice, S., Carolyn, O., & James, M. (1992). Risk of congenital malformations associated with proximity to hazardous waste sites. American Journal of Epidemiology, 135(11), 1197–1207.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
He, L. H., & Gao, X. H. (2016). Assessment of potential ecological risk for soil heavy metals in Sanjiang Source Region: A case study of Yushu County Qinghai Province. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 35(6), 1071–1080. (in Chinese).
Hu, Z. Y., Haneklaus, S., Sparovek, G., & Schnug, E. (2006). rare earth elements in soils. Communications in Soil ence & Plant Analysis, 37(9–10), 1381–1420.
Huang, J. Y., Minasny, B., Mcbratney, A. B., Padarian, J., & Triantafilis, J. (2018). The location- and scale- specific correlation between temperature and soil carbon sequestration across the globe. Science of the Total Environment, 615(15), 540–548.
Jarup, L., Briggs, D., De, H. C., Morris, S., Hurt, C., Lewin, A., Maitland, I., Richardson, S., Wakefield, J., & Elliott, P. (2002). Cancer risks in populations living near landfill sites in Great Britain. British Journal of Cancer, 86(11), 1732–1736.
Jiang, F. C., Li, Y. L., Yang, S., & Yang, G. D. (2018). Source analysis, distribution and pollution assessment of the soil heavy metals in the Qinwangchuan Basin. China Environmental Science, 38(6), 2243–2252. (in Chinese).
Jin, G. Q., Fang, W., Shafi, M., Wu, D. T., Li, Y. Q., Zhong, B., Ma, J. W., & Liu, D. (2019). Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil with application of APCS-MLR model: A pilot study for restoration of farmland in Shaoxing City Zhejiang China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 184, 109495.
Jin, Q., Gao, H., Yue, B., Huang, Q. F., Wang, Y. T., Wu, X. H., Yu, J. Y., & Yang, H. Y. (2018). Heavy metal content of rural living solid waste and related source and distribution analysis. Environmental Science, 39(9), 4385–4392. (in Chinese).
Jing, C. X., Kong, Q. M., & Feng, Z. G. (2020). Heavy metal pollution in a uranium mining and metallurgy area in South China. China Environmental Science, 40(1), 338–349. (in Chinese).
Karimi, N. M. T., Tabatabaii, S. M., & Gholami, A. (2015). Geochemical assessment of steel smelter-impacted urban soils, Ahvaz Iran. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 152, 91–109.
Kaschl, A., Romheld, V., & Chen, Y. (2002). The influence of soluble organic matter from municipal solid waste compost on trace metal leaching in calcareous soils. Science of the Total Environment, 291(1–3), 45–57.
Kumari, A., Panda, R., Jha, M. K., Kumar, J. R., & Lee, J. Y. (2015). Process development to recover rare earth metals from monazite mineral: A review. Minerals Engineering, 79, 102–115.
Lee, K., Hur, S. D., Hou, S. G., Burn, L. J., Hong, S., Barbante, C., Boutron, C. F., & Rosman, K. J. R. (2011). Isotopic signatures for natural versus anthropogenic Pb in high-altitude Mt. Everest ice cores during the past 800 years. Science of the Total Environment, 412, 194–202.
Liang, Y. Y., Yi, X. J., Dang, Z., Wang, Q., Gao, S. Q., Tang, J., & Zhang, Z. F. (2019). Pollution and risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around a Pb-Zn tailing pond. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 38(1), 103–110. (in Chinese).
Licht, L. A., & Isebrands, J. G. (2005). Linking phytoremediated pollutant removal to biomass economic opportunities. Biomass & Bioenergy, 28(2), 203–218.
Lin, W. T., Wu, K. M., Lao, Z. L., Hu, W., Lin, B. J., Li, Y. L., Fan, H. B., & Hu, J. J. (2019). Assessment of trace metal contamination and ecological risk in the forest ecosystem of dexing mining area in northeast Jiangxi Province, China. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 167, 76–82.
Liu, L. F., Long, J., Wan, H. F., & Li, J. (2013). Distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils in An Abandoned Antimony Smelter in Guizhou Karst Areas. Soils, 45(6), 1036–1047. (in Chinese).
Ludvigsen, L., Albrechtsen, H. J., Heron, G., Bjerg, P. L., & Christensen, T. H. (1998). Anaerobic microbial redox processes in a landfill leachate contaminated aquifer (Grindsted, Denmark). Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 33(3–4), 273–291.
Lv, Y. F., Xie, L., Sun, H., & Gu, W. (2019). Criterion selection in assessment of soil heavy metal pollution in farmland on county scale. China Environmental Science, 39(11), 4743–4751. (in Chinese).
Lv, Z. L., Zhang, J. L., Lu, S. Y., Zou, T. S., Liu, K., Zhang, H., & Gu, Y. Y. (2019). Pollution characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in surface soil around a municipal solid waste incineration power plant. Environmental Science, 40(5), 2483–2492. (in Chinese).
Ma, W. C., Tai, L. Y., Qiao, Z., Zhong, L., Wang, Z., Fu, K. X., & Chen, G. Y. (2018). Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: A case study in North China. Science of the Total Environment, 63–632(8), 348–357.
Minichilli, F., Bartolacci, S., Buiatti, E., Pallante, V., Scala, D., & Bianchi, F. (2005). A study on mortality around six municipal solid waste landfills in Tuscany Region. Epidemiologia & Prevenzione, 29(5–6 Suppl), 53–56.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2(3), 109–118.
Nemerow N L C, 1974. Scientific stream pollution analysis. Scripta Book Co.
Pawlowska, T. E., Chaney, R. L., Chin, M., & Charvat, I. (2000). Effects of metal Phytoextraction practices on the indigenous community of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi at a Metal-Contaminated Landfill. Appl Environ Microbiol, 66(6), 2526–2530.
Raskin, I., Kumar, P. N., Dushenkov, S., & Salt, D. E. (1994). Bioconcentration of heavy metals by plants. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 5(3), 285–290.
Remedios, M. G., Paches, M., Romero, I., & Aguado, D. (2019). Enrichment and contamination level of trace metals in the Mediterranean marine sediments of Spain. Science of The Total Environment, 693(3), 133566.
Sheng, J. J., Wang, X. P., Gong, P., Tian, L. D., & Yao, T. D. (2012). Heavy metals of the Tibetan top soils. Environmental Science&Pollution Research, 19(8), 3362–3370.
Shimbo, S., Zhang, Z. W., Watanabe, T., Nakatsuka, H., Matsuda, I. N., Higashikawa, K., & Ikeda, M. (2001). Cd and Zn contents in rice and other cereal products in Japan in 1998–2000. The Science of Total Environment, 281(1), 165–175.
Tang, Y. F., Wang, L. Y., Wu, D., Dai, C., & Han, J. G. (2019). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and bearing capacity estimation of continuous biogas slurry application on cropland: A case study of the coastal rice-wheat rotated farmland in Jiangsu China. China Environmental Science, 39(4), 1687–1695. (in Chinese).
Tu, P,. 2013 Current situation analysis and evaluation on heavy metal pollution for the soil around Chang-an landfill site. Chengdu:Sichuan Agricultural University, Master's thesis, 13-24(in Chinese).
Vrijheid, M., Dolk, H., Armstrong, B., Abramsky, L., Bianchi, F., Fazarinc, I., Garne, E., Ide, R., Nelen, V., Robert, E., Scott, J. E. S., & Stone, D. (2002). Chromosomal congenital anomalies and residence near hazardous waste landfill sites. Lancet, 359(9303), 320–322.
Wang, F., Shan, R. Y., Chen, Y. Z., Lin, D. L., Zang, C. R., Chen, C. S., You, Z. M., & Yu, W. Q. (2018). Concentrations and health risk assessment of heavy metals in tea garden soil and tea leaf from a mine county in central Fujian province. China Environmental Science, 38(3), 1064–1072. (in Chinese).
Wang, G. X., Yan, X. D., Zhang, F., Zeng, C., & Gao, D. (2013). Traffic-related trace element accumulation in roadside soils and wild grasses in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. International Journal of Environmental Research & Public Health, 11(1), 456–472.
Wang, S. Y., Wu, W. Y., Liu, F., Zhao, M., Qiu, J. Q., & Wu, J. J. (2018). Assessment of human health risks of heavy metals in the typical sewage irrigation areas. China Environmental Science, 38(4), 1550–1560. (in Chinese).
Wang, X., Dan, Z., Cui, X., Zhang, R., Zhou, S., Wenga, T., Yan, B., Chen, G., Zhang, Q., & Zhong, L. (2020). Contamination, ecological and health risks of trace elements in soil of landfill and geothermal sites in Tibet. Science of The Total Environment, 715, 136639.
Wu, J. N., Long, J., Liu, L. F., Li, J., Liao, H. K., Peng, S. Q., & Wan, H. F. (2018). Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil of a lead-zinc mining area. China Environmental Science, 38(3), 1054–1063. (in Chinese).
Wu, W. C., Song, Q. M., Liu, X. C., Wu, J. H., & Cai, X. D. (2018). Distribution pattern of heavy metals in soils with respect to typical land uses in electronic waste recycling waste recycling region. China Environmental Science, 38(7), 2632–2638. (in Chinese).
Xiao, H., Shahab, A., Li, J. Y., Xi, B. D., Sun, X. J., He, H. J., & Yu, G. (2019). Distribution, ecological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in surface sediments of Huixian karst wetland China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safty, 185, 109700.
Xiao, Q., Zong, Y. T., & Lu, S. G. (2015). Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 120, 377–385.
Xu, D. Y., Gao, B., Chen, S., Peng, W. Q., Zhang, M., Qu, X. D., Gao, L., & Li, Y. Y. (2019). Release risk assessment of trace metals in urban soils using in-situ DGT and DIFS model. Science of The Total Environment, 694, 133624.
Yan, X. D., Zhang, F., Gao, D., Zeng, C., Wang, X., & Zhang, M. (2013). Accumulations of heavy metals in roadside soils close to Zhaling, Eling and Nam Co Lakes in the Tibetan Plateau. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(6), 2384–2400.
Yao, R. J., Yang, J. S., Xie, W. P., Wu, D. H., Bai, Y. C., Yu, S. P., & Zhang, X. (2016). Contents and spatio-temporal variability of soil heavy metals in the coastal mudflat area of north Jiangsu province. China Environmental Science, 36(6), 1810–1820. (in Chinese).
Yu, Z., Chen, F., Zhang, J. F., Huang, D. K., Yu, E. J., & Liu, H. Y. (2019). Contamination and risk of heavy metals in soils and vegetables from zine smelting area. China Environmental Science, 39(5), 2086–2094. (in Chinese).
Yuan, J., Yang, F., Li, G. X., Li, N., & Luo, W. H. (2014). Physicochemical properties and resource utilization of aged refuse in informal landfill. China Environmental Science, 34(7), 1811–1817. (in Chinese).
Zhang H, 2012. The analysis on the enrichment of traffic related heavy metals in soils and plants in the Tibet Plateau. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Master's thesis (in Chinese).
Zhang Y H, 2015c. Research and evaluate on the heavy metals pollution characteristics of the landfill soil. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, Master's thesis,19-31(in Chinese).
Zhang, D., & Zhang, C. E. (2015). Risk assessment and impact factor analysis of soil heavy metal pollution in Baihe River Basin. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 28(5), 2187–2193. (in Chinese).
Zhang, H., Zhang, Y. L., Wang, Z. F., & Ding, M. J. (2013). Heavy metal enrichment in the soil along the Delhi-Ulan section of the Qinghai-Tibet railway in China. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 185(7), 5435–5447.
Zhang, Q., Chen, Z. J., Peng, C. S., Li, F. S., & Gu, Q. B. (2015). Heavy metals pollution in topsoil from Dagang industry area and its ecological risk assessment. Environmental Science, 36(11), 4232–4240. (in Chinese).
Zhang, W. G., Feng, H., Chang, J. N., Qu, J. G., Xie, H. X., & Yu, L. Z. (2009). Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone: An assessment from different indexes. Environmental Pollution, 157(5), 1533–1543.
Zhang, X. P. (1994). Research on the environmental background values of soils in Xizang. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 14(1), 49–55. (in Chinese).
Zhang, X. W., WeiI, S., Sun, Q. Q., Wadood, S. A., & Guo, B. L. (2018). Source identification and spatial distribution of arsenic and heavy metals in agricultural soil around Hunan industrial estate by positive matrix factorization model, principle components analysis and geo statistical analysis. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 159, 354–362.
Zhao, X., Huang, Y., Li, J., Cheng, G., Song, L. H., Lu, K. D., & Ning, C. (2015). Environmental levels, spatial distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soils surrounding a large solid waste incinerator. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 24(6), 1013–1021. (in Chinese).
Zheng, G. Z. (2008). The vertical distribution regularity of heavy metal elements in Guanzhong Tier soil profile. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(1), 109–115. (in Chinese).
Zhong, G. H., Tian, F. Y., Wang, M., Zhang, H. F., Liu, C. H., & Ci, B. (2005). Soil fertility of croplands in major agricultural areas in Tibet. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 45(6), 1030–1034. (in Chinese).
Zhou W W, 2020. Study on status and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil of Shannan landfill in Tibet. Lhasa:T ibet University, Master's thesis, 11-12(in Chinese).
Zhou, W. W., Chen, G. Y., Dan, Z., Qiong, D. Z. M., Zhou, P., & Wang, J. (2020). Comparison and selection of rehabilitation schemes for groundwater lead in landfill area: A case study of Lhasa. Environmental Engineering, 38(6), 163–168. (in Chinese).
Zhou, W. W., Chen, G. Y., Qiong, D. Z. M., Zhou, P., Wang, J., & Dan, Z. (2020). Health risk assessment of groundwater quality in Lhasa landfill. Environmental Chemistry, 39(6), 1513–1522. (in Chinese).
Zhou, W. W., Chen, G. Y., Qiong, D. Z. M., Zhou, P., Wang, J., Li, Y., & Dan, Z. (2020). Impact Study of Landfill on Groundwater Environmental Quality in Lhasa. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 32(4), 20–23. (in Chinese).
Zhou, W. W., Chen, G. Y., Zhou, P., Qiong, D. Z. M., Wang, J., Li, Y., & Dan, Z. (2019). Situation analysis and suggestion on food waste in Lhasa city of Tibet. Environment and Sustainable Development, 44(1), 60–63. (in Chinese).
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Key Research &Development Program of China (No.2019YFC1904101), National Natural Science Foundation of China Project (No.52160026), and Key R & D projects of Tibet Autonomous Region(No. XZ202101ZY0010G).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zeng Dan and Guanyi Chen provided the research ideas and experimental equipment. Wenwu Zhou, Dean Meng, Peng Zhou, Keke Chang, Qiongda Zhuoma, Jing Wang, and Fei Xu completed the experimental operation and the arrangement and processing of experimental data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This paper mainly studies the heavy metals in landfill soil, not involving human and animal research.
Consent to participate
All authors were participated in this work.
Consent to publish
All authors agree to publish.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, W., Dan, Z., Meng, D. et al. Distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around Shannan landfill site, Tibet. Environ Geochem Health 45, 393–407 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01349-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01349-y