Abstract
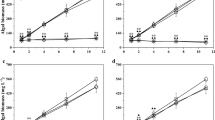
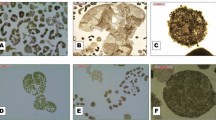
Cyanobacteria are a diverse group of Gram-negative bacteria that produce an array of secondary compounds with selective bioactivity against vertebrates, invertebrates, fungi, bacteria and cell lines. Recently the main methods of controlling cyanobacteria are using chemicals, medicinal plants and microorganism but fewer involved the safety research in hydrophytic ecosystems. In search of an environmentally safe compound, 53 chemicals were screened against the developed heavy cyanobacteria bloom Microcystis aeruginosa using coexistence culture system assay. The results of the coexistence assay showed that 9 chemicals inhibited M. aeruginosa effectively at 20 mg L−1 after 7 days of exposure. Among them dimethomorph, propineb, and paraquat were identified that they are safe for Chlorella vulgaris, Scenedesmus obliquus, Carassius auratus (Goldfish) and Bacillus subtilis within half maximal effective concentration (EC50) values 5.2, 4.2 and 0.06 mg L−1 after 7 days, respectively. Paraquat as the positive control observed to be more efficient than the other compounds with the inhibitory rate (IR) of 92 % at 0.5 mg L−1. For the potential inhibition mechanism, the chemicals could destroy the cell ultrastructure in different speed. The safety assay proved dimethomorph, propineb and paraquat as harmless formulations or products having potential value in M. aeruginosa controlling, with the advantage of its cell morphology degrading ability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi SA, Soni R (1986) An examination of environmentally safe levels of zinc (II), cadmium (II) and lead (II) with reference to impact on channelfish Nuria denricus. Environ Pollut Series A, Ecological and Biological 40:37–51
Altinok I (2004) Toxicity and therapeutic effects of chloramine-T for treating Flavobacterium columnare infection of goldfish. Aquaculture 239:47–56
Anderson DM, Glibert PM, Burkholder JM (2002) Harmful Algal Blooms and Eutrophication: Nutrient Sources, Composition, and Consequences. Estuaries 25:704–726
Azevedo SMFO, Carmichael WW, Jochimsen EM, Rinehart KL, Lau S, Shaw GR, Eaglesham GK (2002) Human intoxication by microcystins during renal dialysis treatment in Caruaru—Brazil. Toxicology 181:441–446
Backhaus T, Faust M, Scholze M, Gramatica P, Vighi M, Horst Grimme L (2004) Joint algal toxicity of phenylurea herbicides is equally predictable by concentration addition and independent action. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:258–264
Bonvehí JS, Coll FV (1994) The composition, active components and bacteriostatic activity of propolis in dietetics. J Am Oil Chem Soc 71:529–532
Brix H, Schierup HH (1989) The use of aquatic macrophytes in water-pollution control. Ambio Stockholm 18:100–107
Drabkova M, Marsalek B, Admiraal W (2007) Photodynamic therapy against cyanobacteria. Environ Toxicol 22:112–115
Embry MR, Belanger SE, Braunbeck TA, Galay-Burgos M, Halder M, Hinton DE, Léonard MA, Lillicrap A, Norberg-King T, Whale G (2010) The fish embryo toxicity test as an animal alternative method in hazard and risk assessment and scientific research. Aquat Toxicol 97:79–87
Feuga AM (2000) The role of microalgae in aquaculture: situation and trends. J App Phycol 12:527–534
Finney D (1971) Probit analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Fisher SH (1999) Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Bacillus subtilis: vive la difference. Mol Microbiol 32:223–232
Folmar LC, Sanders HO, Julin AM (1979) Toxicity of the herbicide glyphosate and several of its formulations to fish and aquatic invertebrates. Arch Environ Con Tox 8:269–278
Gorbach SL (2001) Editorial: antimicrobial use in animal feed—time to stop. New Engl J Med 345:1–3
Han FX, Hargreaves JA, Kingery WL, Huggett DB, Schlenk DK (2001) Accumulation, distribution, and toxicity of copper in sediments of catfish ponds receiving periodic copper sulfate applications. J Environ Qual 30:912–919
Hill IR (1985) Effects on non-target organisms in terrestrial and aquatic environments. In: Leahey JP (ed) The pyrethroid insecticides. Taylor & Francis, London, UK, pp 151–262
Imamura N, Motoike I, Shimada N, Nishikori M, Morisaki H, Fukami H (2001) An efficient screening approach for anti-microcystis compounds based on knowledge of aquatic microbial ecosystem. J Antibiotics 54:582–587
Jančula D, Drábková M, Černý J, Karásková M, Kořínková R, Rakušan J, Maršálek B (2008) Algicidal activity of phthalocyanines—Screening of 31 compounds. Environ Toxicol 23:218–223
Jensen BB, Cox RP (1983) Effect of oxygen concentration on dark nitrogen fixation and respiration in cyanobacteria. Arch Microbiol 135:287–292
Jeong JH, Jin HJ, Sohn CH, Suh KH, Hong YK (2000) Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J Appl Phycol 12:37–43
Kargioglu M, Serteser A, Kivrak E, Içaga Y, Konuk M (2012) Relationships between epipelic diatoms, aquatic macrophytes, and water quality in Akarçay Stream, Afyonkarahisar, Turkey. Oceanol Hydrobiol St 41:74–84
Kim BH, Hwang SJ, Park MH, Kim YJ (2010) Relationship between cyanobacterial biomass and total microcystin-LR levels in drinking and recreational water. B Environ Contam Toxicol 85:457–462
Kong CH, Wang P, Zhang CX, Zhang MX, Hu F (2005) Herbicidal potential of allelochemicals from Lantana camara against Eichhornia crassipes and the alga M. aeruginosa. Weed Res 46:290–295
Li FM, Hu HY (2005) Isolation and characterization of a novel antialgal allelochemical from Phragmites communis. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):6545–6553
Lo CC, Ho MH, Hung MD (1996) Use of high-performance liquid chromatographic and atomic absorption methods to distinguish propineb, zineb, maneb, and mancozeb fungicides. J Agr Food Chem 44:2720–2723
Lumaret JP, Errouissi F, Floate K, Römbke J, Wardhaugh K (2012) A review on the toxicity and non-target effects of macrocyclic lactones in terrestrial and aquatic environments. Curr. Pharm. biotechnol 13:1004–1060
Ma JY, Zheng RQ, Xu LG, Wang SF (2002) Differential Sensitivity of Two Green Algae, Scenedesmus obliqnus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa, to 12 Pesticides. Ecotox Environ Safe 52:57–61
Ma J, Lu N, Qin W, Xu R, Wang Y, Chen X (2006) Differential responses of eight cyanobacterial and green algal species, to carbamate insecticides. Ecotox Environ Safe 63:268–274
Ma J, Tong S, Wang P, Chen J (2010) Toxicity of Seven Herbicides to the Three Cyanobacteria Anabaena flos-aquae, Microcystis flos-aquae and Mirocystis aeruginosa. Int J Environ Res 4:347–352
Masojídek J, Souček P, Machova J, Frolik J, Klem K, Maly J (2011) Detection of photosynthetic herbicides: Algal growth inhibition test vs. electrochemical photosystem II biosensor. Ecotox Environ safe 74:117–122
Morin S, Proia L, Ricart M, Bonnineau C, Geiszinger A, Ricciardi F, Guasch H, Romani AM, Sabater S (2010) Effects of a bactericide on the structure and survival of benthic diatom communities. Vie et milieu 60:109–116
Nakai S, Inoue Y, Hosomi M, Murakami A (1999) Growth inhibition of blue-green algae by allelopathic effects of macrophytes. Water Sci Technol 39:47–53
Ni L, Acharya K, Hao X, Hao XY, Li SY (2012) Isolation and identification of an anti-algal compound from Artemisia annua and mechanisms of inhibitory effect on algae. Chemosphere 88:1051–1057
Oh HM, Lee SJ, Jang MH, Yoon BD (2000) Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa in a phosphorus-limited chemostat. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:176–179
Papageorgiou GC (1996) The photosynthesis of cyanobacteria (blue bacteria) from the perspective of signal analysis of chlorophyll a fluorescence. J Sci Res India 55:596–617
Pimentel R, Bulkley RV (1983) Influence of water hardnesson fluoride toxicity to rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 2:381–386
Prado R, García R, Rioboo C, Herrero C, Abalde J, Cid A (2009) Comparison of the sensitivity of different toxicity test endpoints in a microalga exposed to the herbicide paraquat. Environ Int 35:240–247
Ricardo GA, Virgile Q, René R (2013) The effects of eight single microalgal diets on sex-ratio and gonad development throughout European flat oyster (Ostrea edulis L.) conditioning. Aquaculture 400:1–5
Sáenz ME, Alberdi JL, Di Marzio WD, Accorinti J, Tortorelli MC (1997) Paraquat toxicity to different green algae. B Environ Contam Toxicol 58:922–928
Schrader KK, Bommer JC, Jori G (2010) In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial agent AquaFrin as a bactericide and selective algicide for use in channel catfish aquaculture. N Am Aquac 72:304–308
Singh R, Jain A, Panwar S, Gupta D, Khare SK (2005) Antimicrobial activity of some natural dyes. Dyes Pigments 66:99–102
Sjollema SB, Van Beusekom SAM, Van Der Geest HG, Booij P, De Zwart D, Vethaak AD, Admiraa M (2014) Laboratory algal bioassays using PAM fluorometry: Effects of test conditions on the determination of herbicide and field sample toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 33:1017–1022
Sprague JB (1971) Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish. III. Sublethal effect and Asafe B concentration. Water Res 5:245–266
Stein JM, Kirk WW (2004) The generation and quantification of resistance to dimethomorph in Phytophthora infestans. Plant Dis 88:930–934
Su W, Zhao L, Liu J, Chen HL, Gong ZQ (2007) Study on bacteriostasis and anti-oxidation of polyonatic sibiricum polysaccharides. Food Sci 8:55–57
Toussaint MW, Shedd TR, Van Der Schalie WH, Leather GR (1995) A comparison of standard acute toxicity tests with rapid-screening toxicity tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 14:907–915
Vasconcelos VM, Pereira E (2001) Cyanobacteria diversity and toxicity in a wastewater treatment plant (Portugal). Water Res 35:1354–1357
Wong PK (2000) Effects of 2,4-D, glyphosate and paraquat on growth, photosynthesis and chlorophyll-a synthesis of Scenedesmus quadricauda Berb 614. Chemosphere 41:177–182
Yi YL, Lei Y, Yin YB, Zhang HY, Wang GX (2012) The antialgal activity of 40 medicinal plants against Microcystis aeruginosa. J App Phycol 24:847–856
Zhang C, Yi YL, Hao K, Liu GL, Wang GX (2013) Algicidal activity of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bung on Microcystis aeruginosa—Towards identification of algicidal substance and determination of inhibition mechanism. Chemosphere 93:997–1004
Zhao M, Xie SQ, Zhu XM, Yang YX, Gan NQ, Song LR (2006) Effect of dietary cyanobacteria on growth and accumulation of microcystins in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 261:960–966
Zhou GJ, Peng FQ, Zhang LJ, Ying GG (2012) Biosorption of zinc and copper from aqueous solutions by two freshwater green microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:2918–2929
Zou X, Zhang LZ, Liu JY, Wang Y, Huang XR, Zhuang P (2012) Acute toxicity of the five fishery drugs on Siganus guttatus. Marine Fisheries 34:189–194 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the China Spark Program (2012GA651002). We would like to thanks the anonymous referees for their writing assistance on this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, XB., Hao, K., Ling, F. et al. Aquatic environmental safety assessment and inhibition mechanism of chemicals for targeting Microcystis aeruginosa . Ecotoxicology 23, 1638–1647 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1303-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1303-x