Abstract
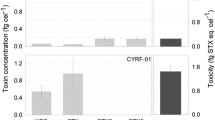
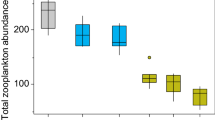
Impacts of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on phytoplankton, particularly, the tolerability and changes to the toxin profiles of harmful toxic algal species remain unknown. The degree to which oil-affected sympatric Karenia brevis, Prorocentrum minimum, and Heterosigma akashiwo, all of which are ecologically important species in the Gulf of Mexico, was investigated. Comparison of their tolerability to that of non-toxic species showed that the toxin-production potential of harmful species does not provide a selective advantage. Investigated toxin profiles for K. brevis and P. minimum demonstrated an increase in toxin productivity at the lowest crude oil concentration (0.66 mg L−1) tested in this study. Higher crude oil concentrations led to significant growth inhibition and a decrease in toxin production. Findings from this study could assist in the assessment of shellfish bed closures due to high risk of increased toxin potential of these phytoplankton species, especially during times of stressed conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams CM, Hernandez E, Cato JC (2004) The economic significance of the Gulf of Mexico related to population, income, employment, minerals, fisheries and shipping. Ocean Coast Manag 47(11):565–580
Adekunle I, Ajijo M, Adcofun C, Omoniyi I (2010) Response of four phytoplankton species found in some sectors of nigerian coastal waters to crude oil in controlled ecosystem. Int J Environ Res 4(1):65–74
Almeda R, Wambaugh Z, Wang Z, Hyatt C, Liu Z, Buskey EJ (2013) Interactions between zooplankton and crude oil: toxic effects and bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. PLoS One 8(6):e67212. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0067212
Anderson DM, Cembella AD, Hallegraeff GM (2012) Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Ann Rev Mar Sci 4:143–176
Backer LC, Kirkpatrick B, Fleming LE, Cheng YS, Pierce R, Bean JA, Clark R, Johnson D, Wanner A, Tamer R (2005) Occupational exposure to aerosolized brevetoxins during Florida red tide events: effects on a healthy worker population. Environ Health Perspect 113(5):644
Baden DG, Tomas CR (1988) Variations in major toxin composition for six clones of Ptychodiscus brevis. Toxicon 26(10):961–963
Bagchi M, Bagchi D, Balmoori J, Ye X, Stohs SJ (1998) Naphthalene-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in cultured macrophage J774A.1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 25(2):137–143
Brain P, Cousens R (2006) An equation to describe dose responses where there is stimulation of growth at low doses. Weed Res 29(2):93–96
Brown AMF, Dortch Q, Dolah FMV, Leighfield TA, Morrison W, Thessen AE, Steidinger K, Richardson B, Moncreiff CA, Pennock JR (2006) Effect of salinity on the distribution, growth, and toxicity of Karenia spp. Harmful Algae 5(2):199–212
Cohen JH, Tester PA, Forward RB (2007) Sublethal effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia brevis on marine copepod behavior. J Plankton Res 29(3):301–315
Crone TJ, Tolstoy M (2010) Magnitude of the 2010 Gulf of Mexico oil leak. Science 330(6004):634
CROSERF (2005) Cooperative aquatic toxicity testing of dispersed oil and the “chemical response to oil spills: ecological effects research forum (CROSERF). vol Technical Report 07-03. Ecosystem Management and Associates, Inc, Lusby, MD
Dortch Q, Parsons M, Rabalais N, Turner R (1999) What is the threat of harmful algal blooms in Louisiana coastal waters? In: Proceedings of recent research in Coastal Louisiana: Natural system function and response to human influences, pp 1-11
Dunstan WM, Atkinson LP, Natoli J (1975) Stimulation and inhibition of phytoplankton growth by low molecular weight hydrocarbons. Mar Biol 31(4):305–310
El-Sheekh MM, El-Naggar AH, Osman ME, Haieder A (2000) Comparative studies on the green algae Chlorella homosphaera and Chlorella vulgaris with respect to oil pollution in the river Nile. Water Air Soil Pollut 124(1–2):187–204
Errera RM, Bourdelais A, Drennan M, Dodd E, Henrichs D, Campbell L (2010) Variation in brevetoxin and brevenal content among clonal cultures of Karenia brevis may influence bloom toxicity. Toxicon 55(2):195–203
Geesey M, Tester PA (1993) Gymnodinium breve: ubiquitous in Gulf of Mexico waters. Toxic phytoplankton blooms in the sea. In: Proceedings of the fifth international conference on toxic marine phytoplankton. Elsevier Science Publishing, Inc, New York
Gonzalez J, Figueiras FG, Aranguren-Gassis M, Crespo BG, Fernandez E, Morin XAG, Nieto-Cid M (2009) Effect of a simulated oil spill on natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton enclosed in microcosms. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 83:265–276
Goutx H, Berland B, Leveau M, Bertrand J (1984) Effects of petroleum biodegradation products on phytoplankton growth. In: 2. Colloque International de Bacteriologie Marine, Brest (France), pp 1–5
Guillard RL (1975) Culture of Phytoplankton for Feeding Marine Invertebrates. In: Smith W, Chanley M (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Springer, USA, pp 29–60
Hagstrom JA, Graneli E, Moreira MO, Odebrecht C (2011) Domoic acid production and elemental composition of two Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries strains, from the NW and SW Atlantic Ocean, growing in phosphorus-or nitrogen-limited chemostat cultures. J Plankton Res 33(2):297–308
Hardison DR, Sunda WG, Wayne Litaker R, Shea D, Tester PA (2012) Nitrogen limitation increases brevetoxins in Karenia Brevis (Dinophyceae): implications for bloom toxicity. J Phycol 48(4):844–858
Hardison DR, Sunda WG, Shea D, Litaker RW (2013) Increased toxicity of Karenia brevis during phosphate limited growth: ecological and evolutionary implications. PLoS One 8(3):e58545
Harper TL (2005) Improved methods of detection for the difficult to identify marine toxin, Okadaic acid. Master Thesis, The University of North Carolina Wilmington (UNCW)
Heil DC (2009) Karenia brevis monitoring, management, and mitigation for Florida molluscan shellfish harvesting areas. Harmful Algae 8(4):608–610
Heil CA, Glibert PM, Fan C (2005) Prorocentrum minimum (Pavillard) Schiller: a review of a harmful algal bloom species of growing worldwide importance. Harmful Algae 4(3):449–470
Hong J, Talapatra S, Katz J, Tester PA, Waggett RJ, Place AR (2012) Algal toxins alter copepod feeding behavior. PLoS One 7(5):e36845
Hook SE, Osborn HL (2012) Comparison of toxicity and transcriptomic profiles in a diatom exposed to oil, dispersants, dispersed oil. Aquat Toxicol 124‚125(0):139–151. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2012.08.005
Jenke-Kodama H, Sandmann A, Müller R, Dittmann E (2005) Evolutionary implications of bacterial polyketide synthases. Mol Biol Evol 22(10):2027–2039
Jiang Z, Huang Y, Xu X, Liao Y, Shou L, Liu J, Chen Q, Zeng J (2010) Advance in the toxic effects of petroleum water accommodated fraction on marine plankton. Acta Ecol Sin 30(1):8–15
Justić D, Rabalais NN, Turner RE (2005) Coupling between climate variability and coastal eutrophication: evidence and outlook for the northern Gulf of Mexico. J Sea Res 54(1):25–35
Khosla C, Gokhale RS, Jacobsen JR, Cane DE (1999) Tolerance and specificity of polyketide synthases. Annu Rev Biochem 68(1):219–253
Koshikawa H, Xu KQ, Liu ZL, Kohata K, Kawachi M, Maki H, Zhu MY, Watanabe M (2007) Effect of the water-soluble fraction of diesel oil on bacterial and primary production and the trophic transfer to mesozooplankton through a microbial food web in Yangtze estuary, China. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 71(1–2):68–80. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2006.08.008
Ladizinsky NC (2003) The influence of dissolved copper on the production of domoic acid by Pseudo-nitzschia species in Monterey Bay. Laboratory experiements and field observations, California
Licea S, Zamudio M, Luna R, Okolodkov YB, Gómez-Aguirre S (2002) Toxic and harmful dinoflagellates in the southern Gulf of Mexico. Harmful Algae 2004:380–382
Licea S, Zamudio ME, Luna R, Soto J (2004) Free-living dinoflagellates in the southern Gulf of Mexico: report of data (1979–2002). Phycol Res 52(4):419–428
Lohrenz SE, Dagg MJ, Whitledge TE (1990) Enhanced primary production at the plume/oceanic interface of the Mississippi River. Cont Shelf Res 10(7):639–664
Loret P, Tengs T, Villareal T, Singler H, Richardson B, McGuire P, Morton S, Busman M, Campbell L (2002) No difference found in ribosomal DNA sequences from physiologically diverse clones of Karenia brevis (Dinophyceae) from the Gulf of Mexico. J Plankton Res 24(7):735–739
Morales-Loo M, Goutx M (1990) Effects of water-soluble fraction of the Mexican crude oil Isthmus Cactus on growth, cellular content of chlorophylla, and lipid composition of planktonic microalgae. Mar Biol 104(3):503–509
Morton SL, Bomber JW, Tindall PM (1994) Environmental effects on the production of okadaic acid from Prorocentrum hoffmannianum Faust I. temperature, light, and salinity. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 178(1):67–77
Naar J, Bourdelais A, Tomas C, Kubanek J, Whitney PL, Flewelling L, Steidinger K, Lancaster J, Baden DG (2002) A competitive ELISA to detect brevetoxins from Karenia brevis (formerly Gymnodinium breve) in seawater, shellfish, and mammalian body fluid. Environ Health Perspect 110(2):179
Needham J, McLachlan JL, Walter JA, Wright JL (1994) Biosynthetic origin of C-37 and C-38 in the polyether toxins okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-1. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 22:2599–2600
Ozhan K, Bargu S (2014) Distinct responses of Gulf of Mexico phytoplankton communities to crude oil and the dispersant Corexit® EC9500A under different nutrient regimes. Ecotoxicology 23(3):370–384. doi:10.1007/s10646-014-1195-9
Ozhan K, Miles SM, Gao H, Bargu S (2014) Relative phytoplankton growth responses to physically- and chemically-dispersed South Louisiana sweet crude oil. Environ Monit Assess 186(6):3941–3956. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-3670-4
Parab SR, Pandit RA, Kadam AN, Indap MM (2008) Effect of Bombay high crude oil and its water-soluble fraction on growth and metabolism of diatom Thalassiosira sp. Indian J Mar Sci 37:251–255p
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) Manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. Pergamon press, Oxford
Paul JH, Hollander D, Coble PG, Daly K, Murasko S, English D, Basso J, Delaney J, McDaniel L, Kovach CW (2013) Toxicity and mutagenicity of Gulf of Mexico Waters during and after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ Sci Technol 47(17):9651–9659
Pierce R, Henry M, Blum P, Hamel S, Kirkpatrick B, Cheng Y, Zhou Y, Irvin C, Naar J, Weidner A (2005) Brevetoxin composition in water and marine aerosol along a Florida beach: assessing potential human exposure to marine biotoxins. Harmful Algae 4(6):965–972
Pierce R, Henry M, Blum P (2008) Brevetoxin abundance and composition during ECOHAB-Florida field monitoring cruises in the Gulf of Mexico. Cont Shelf Res 28(1):45–58
Rabalais NN, Turner RE, Justić D, Dortch Q, Wiseman WJ, Gupta BKS (1996) Nutrient changes in the Mississippi River and system responses on the adjacent continental shelf. Estuaries 19(2):386–407
Rao DS, Pan Y, Zitko V, Bugden G, Mackeigan K (1993) Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) associated with a subsurface bloom of dinophysis norvegica in Bedford Basin, eastern Canada. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 97(2):117–126
Ritz C, Streibig JC (2005) Bioassay analysis using R. J Stat Softw 12(5):1–22
Roszell L, Schulman L, Baden D (1988) Toxin profiles are dependent on growth stages in cultured Ptychodiscus brevis. Toxic marine phytoplankton. Elsevier, New York
Roth PB, Twiner MJ, Wang Z, Bottein Dechraoui MY, Doucette GJ (2007) Fate and distribution of brevetoxin (PbTx) following lysis of Karenia brevis by algicidal bacteria, including analysis of open A-ring derivatives. Toxicon 50(8):1175–1191
Schaeffer BA, Kurtz JC, Hein MK (2012) Phytoplankton community composition in nearshore coastal waters of Louisiana. Mar Pollut Bull 64(8):1705–1712
Shimizu Y (1993) Microalgal metabolites. Chem Rev 93(5):1685–1698
Souto M, Fernandez J, Norte M, Fernandez M, Martínez A (2001) Influence of amino acids on okadaic acid production. Toxicon 39(5):659–664
Steidinger KA (2009) Historical perspective on Karenia brevis red tide research in the Gulf of Mexico. Harmful Algae 8(4):549–561
Tang XX, Huang J, Wang YL (2002) Interaction of UV-B radiation and anthracene on DNA damage of Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Acta Ecol Sin 22(3):375–378
Teal JM, Howarth RW (1984) Oil spill studies: a review of ecological effects. Environ Manag 8(1):27–43. doi:10.1007/bf01867871
Tester PA, Steidinger KA (1997) Gymnodinium breve red tide blooms: initiation, transport, and consequences of surface circulation. Limnol Oceanogr 42(5):1039–1051
Tester PA, Shea D, Kibler SR, Varnam SM, Black MD, Wayne Litaker R (2008) Relationships among water column toxins, cell abundance and chlorophyll concentrations during Karenia brevis blooms. Cont Shelf Res 28(1):59–72
Tukaj Z, Bohdanowicz J, Aksmann A (1998) A morphometric and stereological analysis of ultrastructural changes in two Scenedesmus (Chlorococcales, Chlorophyta) strains subjected to diesel fuel oil pollution. Phycologia 37(5):388–393. doi:10.2216/i0031-8884-37-5-388.1
Turner RE, Rabalais NN (1994) Coastal eutrophication near the Mississippi river delta. Nature 368:619–621
Wade TL, Sweet ST, Walpert JN, Sericano JL, Singer JJ, Guinasso NL (2013) Evaluation of possible pnputs of oil from the Deepwater Horizon Spill to the loop current and associated eddies in the Gulf of Mexico. In: Liu Y, Macfadyen A, Ji Z-G, Weisberg RH (eds) Monitoring and modeling the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: a record-breaking enterprise. American Geophysical Union, Washington. doi:10.1029/2011GM001095
Waggett RJ, Hardison DR, Tester PA (2012) Toxicity and nutritional inadequacy of Karenia brevis: synergistic mechanisms disrupt top-down grazer control. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 444:15–30
Wright JL, Cembella AD (1998) Ecophysiology and biosynthesis of polyether marine biotoxins. Nato Asi Ser G Ecol Sci 41:427–452
Wright J, Hu T, McLachlan J, Needham J, Walter J (1996) Biosynthesis of DTX-4: confirmation of a polyketide pathway, proof of a Baeyer-Villiger oxidation step, and evidence for an unusual carbon deletion process. J Am Chem Soc 118(36):8757–8758
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özhan, K., Bargu, S. Responses of sympatric Karenia brevis, Prorocentrum minimum, and Heterosigma akashiwo to the exposure of crude oil. Ecotoxicology 23, 1387–1398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1281-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1281-z