Abstract
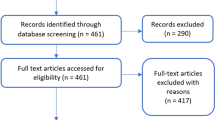
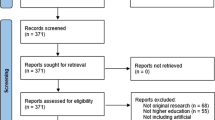
Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) have been widely used to enhance math learning, wherein teacher’s involvement is prominent to achieve their full potential. Usually, ITSs depend on direct interaction between the students and a computer. Recently, researchers started exploring handwritten input (e.g., from paper sheets) aiming to provide equitable access to ITSs’ benefits. However, research on math ITSs ability to handle handwritten input is limited and, to our best knowledge, no study has summarized its state of the art. This article fulfills that gap with a scoping review of handwritten recognition methods, characteristics, and applications of math ITSs compatible with handwritten input. Based on a search of 11 databases, we found eight primary studies that met our criteria. Mainly, we found that all ITSs depend on receiving handwritten input from a touchscreen interface, in contrast to recognizing solutions developed on paper. We also found that most ITSs focus on similar audiences (e.g., English speakers students), subjects (e.g., algebraic questions), and applications (e.g., in-class to understand student perceptions). Thus, towards enabling equitable access to ITSs, we propose ITS Unplugged (i.e., ITSs that i) run on low-cost, resource-restricted devices with little to no internet connection and ii) receive as well as return information in the format target users usually use) and contribute a research agenda concerning challenges of developing such ITSs.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Anthony, L., Yang, J., & Koedinger, K. R. (2007). Benefits of handwritten input for students learning algebra equation solving. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications, 158, 521.
Anthony, L., Yang, J., & Koedinger, K. R. (2012). A paradigm for handwriting-based intelligent tutors. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 70(11), 866–887.
Barthakur, A., Dawson, S., Kovanovic, V. (2023). Advancing leaner profiles with learning analytics: A scoping review of current trends and challenges. Lak23: 13th international learning analytics and knowledge conference (pp. 606–612).
Davis, S.R., DeCapito, C., Nelson, E., Sharma, K., Hand, E.M. (2020). Homework helper: Providing valuable feedback on math mistakes. Advances in Visual Computing: 15th international symposium, isvc 2020, San Diego, CA, USA, October 5–7, 2020, proceedings, part ii 15 (pp. 533–544).
Dermeval, D., & Bittencourt, I. I. (2020). Co-designing gamified intelligent tutoring systems with teachers. Revista Brasileira De Informática Na Educação, 28, 73–91.
Dermeval, D., Paiva, R., Bittencourt, I. I., Vassileva, J., & Borges, D. (2018). Authoring tools for designing intelligent tutoring systems: A systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 28, 336–384.
Education, E., Agency, C.E., Eurydice, Ranguelov, S., Motiejunaite, A., Kerpanova, V., Noorani, S. (2015). Mathematics education in europe : Common challenges and national policies. Publications Office.
Fang, Y., Ren, Z., Hu, X., & Graesser, A. C. (2019). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of aleks on learning. Educational Psychology, 39(10), 1278–1292.
Feng, S., Magana, A.J., Kao, D. (2021). A systematic review of literature on the effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems in stem. 2021 IEEE frontiers in education conference (fie) (pp. 1–9).
Feng, X., Okazaki, Y., Zhu, Y. (2009). Pen gestures based mathematics editing to an its on algebraic calculation. 2009 first international workshop on education technology and computer science (vol. 2, pp. 1042–1046).
Freitas, E., Batista, H.H., Barbosa, G.A., Wenceslau, M., Portela, C., Isotani, S., et al. (2022). Learning analytics desconectada: Um estudo de caso em análise de produçoes textuais. Anais do i workshop de aplicações práticas de learning analytics em instituições de ensino no brasil (pp. 40–49).
Gašević, D. (2018). Include us all! directions for adoption of learning analytics in the global south. Learning analyfics for the global south, 1–22.
Hillmayr, D., Ziernwald, L., Reinhold, F., Hofer, S. I., & Reiss, K. M. (2020). The potential of digital tools to enhance mathematics and science learning in secondary schools: A context-specific meta-analysis. Computers & Education, 153, 103897.
Holmes, W., Porayska-Pomsta, K., Holstein, K., Sutherland, E., Baker, T., Shum, S.B., et al. (2021). Ethics of ai in education: Towards a community-wide framework. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 1–23.
Isotani, S., Bittencourt, I.I., Challco, G.C., Dermeval, D., Mello, R.F. (2023). Aied unplugged: Leapfrogging the digital divide to reach the underserved. Artificial intelligence in education. posters and late breaking results, workshops and tutorials, industry and innovation tracks, practitioners, doctoral consortium and blue sky.
Jordan, K. (2020). Beyond indicators: A scoping review of the academic literature related to sdg4 and educational technology. Addressing global challenges and quality education: 15th european conference on technology enhanced learning, ec-tel 2020, Heidelberg, Germany, September 14–18, 2020, proceedings 15 (pp. 353–357).
Kang, B., Kulshreshth, A., LaViola Jr, J.J. (2016). Analyticalink: An interactive learning environment for math word problem solving. Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Intelligent user Interfaces (pp. 419–430).
Lee, J.S., & Kim, J.H. (2009). Pen-based intelligent tutor for simultaneous equations. 2009 chinese conference on pattern recognition (pp. 1–5).
Li, B., Yuan, Y., Liang, D., Liu, X., Ji, Z., Bai, J., . . . Bai, X. (2022). When counting meets hmer: Counting-aware network for handwritten mathematical expression recognition. Computer vision–eccv 2022: 17th european conference, tel aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, proceedings, part XXVIII (pp. 197–214).
Morais, F., Bittencourt, I.I., Isotani, S., Jaques, P.A. (2017). The use of handwriting input in math tutoring systems: an use case with pat2math. 2017 IEEE 17th international conference on advanced learning technologies (icalt) (pp. 44–46).
Morais, F., & Jaques, P. A. (2022). Does handwriting impact learning on math tutoring systems? Informatics in Education, 21(1), 55–90.
Mouchère, H., Viard-Gaudin, C., Zanibbi, R., Garain, U. (2014). Icfhr 2014 competition on recognition of on-line handwritten mathematical expressions (crohme 2014). 2014 14th international conference on frontiers in handwriting recognition (pp. 791-796).
Mousavinasab, E., Zarifsanaiey, N., Niakan Kalhori, R., & S., Rakhshan, M., Keikha, L., Ghazi Saeedi, M. (2021). Intelligent tutoring systems: a systematic review of characteristics, applications, and evaluation methods. Interactive Learning Environments, 29(1), 142–163.
Munn, Z., Peters, M. D., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review or scoping review? guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC medical research methodology, 18, 1–7.
Nagashima, T., Britti, J.,Wang, X., Zheng, B., Turri, V., Tseng, S., Aleven, V. (2022). Designing playful intelligent tutoring software to support engaging and effective algebra learning. Educating for a new future: Making sense of technologyenhanced learning adoption: 17th european conference on technology enhanced learning, ec-tel 2022, toulouse, france, September 12–16, 2022, proceedings (pp. 258–271).
Nkambou, R., Mizoguchi, R., Bourdeau, J. (2010). Advances in intelligent tutoring systems (vol. 308). Springer Science & Business Media.
Pacheco-Venegas, N. D., López, G., & Andrade-Aréchiga, M. (2015). Conceptualization, development and implementation of a web-based system for automatic evaluation of mathematical expressions. Computers & Education, 88, 15–28.
Patel, N., Thakkar, M., Rabadiya, B., Patel, D., Malvi, S., Sharma, A., Lomas, D. (2022). Equitable access to intelligent tutoring systems through paper-digital integration. Intelligent tutoring systems: 18th international conference, its 2022, Bucharest, Romania, June 29–July 1, 2022, proceedings (pp. 255–263).
Rodrigues, L., Pereira, F., Santos, J., Oliveira, E., Gasparini, I., Mello, R., . . . Isotani, S. (2023). Question classification with constrained resources: A study with coding exercises. Artificial intelligence in education. posters and late breaking results, workshops and tutorials, industry and innovation tracks, practitioners, doctoral consortium and blue sky.
Schiff, D. (2022). Education for ai, not ai for education: the role of education and ethics in national ai policy strategies. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 32(3), 527–563.
Sharp, H., Rogers, Y., & Preece, J. (2007). Interaction design: Beyond human computer interaction. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Silva, L.C., Sobrinho, A.S., Cordeiro, T.D., Melo, R.F., Bittencourt, I.I., Marques, L.B., Isotani, S. (2023). Applications of convolutional neural networks in education: A systematic literature review. Expert Systems with Applications, 120621.
Soofi, A.A., & Ahmed, M.U. (2019). A systematic review of domains, techniques, delivery modes and validation methods for intelligent tutoring systems. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 10(3).
Steenbergen-Hu, S., & Cooper, H. (2013). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems on k-12 students’ mathematical learning. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(4), 970.
Steenbergen-Hu, S., & Cooper, H. (2014). A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of intelligent tutoring systems on college students’ academic learning. Journal of educational psychology, 106(2), 331.
Su, J., & Yang, W. (2022). Artificial intelligence in early childhood education: A scoping review. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 3, 100049.
Tricco, A. C., Lillie, E., Zarin, W., O’brien, K., Colquhoun, H., Kastner, M., et al. (2016). A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews. BMC medical research methodology, 16, 1–10.
UNESCO (2022). Reimagining our futures together: A new social contract for education. UN.
van der Bent, R., Jeuring, J., Heeren, B. (2019). The diagnosing behaviour of intelligent tutoring systems. Transforming learning with meaningful technologies: 14th european conference on technology enhanced learning, ec-tel 2019, Delft, the Netherlands, September 16–19, 2019, proceedings 14 (pp. 112–126).
VanLehn, K. (2006). The behavior of tutoring systems. International journal of artificial intelligence in education, 16(3), 227–265.
Vinuesa, R., Azizpour, H., Leite, I., Balaam, M., Dignum, V., Domisch, S., & Fuso Nerini, F. (2020). The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the sustainable development goals. Nature communications, 11(1), 233.
Wang, G., Bowditch, N., Zeleznik, R., Kwon, M., & LaViola, J. J. (2016). A tablet-based math tutor for beginning algebra (pp. 91–102). Revolutionizing Education with Digital Ink: The Impact of Pen and Touch Technology on Education.
Wang, T., & Cheng, E.C. (2021). Towards a tripartite research agenda: A scoping review of artificial intelligence in education research. International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education Technology (pp. 3–24).
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 3087.
Xia, Q., Chiu, T.K., Zhou, X., Chai, C.S., Cheng, M. (2022). Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 100118.
Yuan, Y., Liu, X., Dikubab, W., Liu, H., Ji, Z., Wu, Z., Bai, X. (2022). Syntax-aware network for handwritten mathematical expression recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4553–4562).
Zhao, W., & Gao, L. (2022). Comer: Modeling coverage for transformer-based handwritten mathematical expression recognition. S. Avidan, G. Brostow, M. Cissé, G.M. Farinella, & T. Hassner (Eds.), Computer vision - eccv 2022 (pp. 392–408). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland.
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian Ministry of Education - TED 11476.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors equally contributed to this research by designing, collecting data, analyzing data, and writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, L., Pereira, F.D., Marinho, M. et al. Mathematics intelligent tutoring systems with handwritten input: a scoping review. Educ Inf Technol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12245-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12245-y