Summary
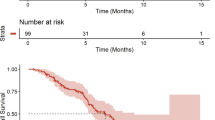
Background Sorafenib is the only systemic treatment that has shown a significant benefit in overall survival (OS) and in progression-free survival (PFS) in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. No standard of care currently exists for second-line treatment. The association of Gemcitabine-Oxaliplatine (GEMOX) has shown efficacy in the first-line setting. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of GEMOX after failure of at least one line of anti-angiogenic (AA) therapy. Patient and methods We performed a multicenter retrospective analysis of advanced HCC patients that received GEMOX chemotherapy after progression on at least one line of AA therapy. Results We analyzed a total of 40 patients that received a median of 7 cycles of GEMOX over a 6-year period. Grade 3/4 toxicity was observed in 25 % of patients, mainly neurotoxicity, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia in 12.5 %, 5 % and 5 % of patients respectively. Grade <3 toxicity was mainly hematological and neurotoxicity. In the sub-cohort of 35 patients evaluable for response, partial response was observed in 20 % of patients, while 46 % had stable disease. Median OS was 8.3 months, with a 6-month OS rate of 59 %. Median PFS was 3.1 months. Prognostic factors for OS in univariable analysis were the performance status and AFP levels at GEMOX start, and the BCLC score at diagnosis. None of these factors were prognostic for PFS or tumor response. Conclusion The GEMOX schedule seems to show clinical activity and an acceptable toxicity profile in advanced HCC patients who progressed after anti-angiogenic treatment. The observed median OS of over 8 months is encouraging in this population of heavily pretreated patients. These results would merit confirmation in a prospective randomized study.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman E (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, Schwartz M, Porta C, Zeuzem S, Bolondi L, Greten TF, Galle PR, Seitz JF, Borbath I, Häussinger D, Giannaris T, Shan M, Moscovici M, Voliotis D, Bruix J, SHARP Investigators Study Group (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359:378–390
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, Xu J, Sun Y, Liang H, Liu J, Wang J, Tak WY, Pan H, Burock K, Zou J, Voliotis D, Guan Z (2009) Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:25–34
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Lin DY, Park JW, Kudo M, Qin S, Chung HS, Song X, Xu J, Poggi G, Omata M, Pitman Lowenthal S, Lanzalone S, Yang L, Lechuga M, Raymond E (2013) Sunitinib versus Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular cancer: results of a randomised phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 31:4067–4075
Johnson PJ, Qin S, Park JW, Poon RT, Raoul JL, Philip PA, Hsu CH, Hu TH, Heo J, Xu J, Lu L, Chao Y, Boucher E, Han KH, Paik SW, Robles-Aviña J, Kudo M, Yan L, Sobhonslidsuk A, Komov D, Decaens T, Tak WY, Jeng LB, Liu D, Ezzeddine R, Walters I, Cheng AL (2013) Brivanib versus sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with unresectable, advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results from the randomized phase III BRISK-FL study. J Clin Oncol 31(28):3517–3524
Llovet JM, Decaens T, Raoul JL, Boucher E, Kudo M, Chang C, Kang YK, Assenat E, Lim HY, Boige V, Mathurin P, Fartoux L, Lin DY, Bruix J, Poon RT, Sherman M, Blanc JF, Finn RS, Tak WY, Chao Y, Ezzeddine R, Liu D, Walters I, Park JW (2013) Brivanib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who were intolerant to sorafenib or for whom sorafenib failed: results from the randomized phase III BRISK-PS study. J Clin Oncol 31(28):3509–3516
Zhu AX, Kudo M, Assenat E, Cattan S, Kang YK, Lim HY, Poon RTP, Blanc JF, Vogel A, Chen CL, Dorval E, Peck-Radosaviljevic M, Santoro A, Daniele B, Furuse J, Jappe A, Perraud K, Anak O, Sellami DB, Chen LT (2014). EVOLVE-1: Phase 3 study of everolimus for advanced HCC that progressed during or after sorafenib. J Clin Oncol 32,2014 (suppl 3; astr 172)
Taïeb J, Bonyhay L, Golli L, Ducreux M, Boleslawski E, Tigaud JM, de Baere T, Mansourbakht T, Delgado MA, Hannoun L, Poynard T, Boige V (2003) Gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma using two different schedules. Cancer 98(12):2664–2670
Louafi S, Boige V, Ducreux M, Bonyhay L, Mansourbakht T, de Baere T, Asnacios A, Hannoun L, Poynard T, Taïeb J (2007) Gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin (GEMOX) in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): results of a phase II study. Cancer 109(7):1384–1390
Zaanan A, Williet N, Hebbar M, Dabakuyo TS, Fartoux L, Mansourbakht T, Dubreuil O, Rosmorduc O, Cattan S, Bonnetain F, Boige V, Taïeb J (2013) Gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a large multicenter AGEO study. J Hepatol 58(1):81–88
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein VJ, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors: European Organization for research and treatment of cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Mir O, Coriat R, Boudou-Rouquette P, Ropert S, Durand JP, Cessot A, Mallet V, Sogni P, Chaussade S, Pol S, Goldwasser F (2012) Gemcitabine and oxaliplatin as second-line treatment in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma pre-treated with sorafenib. Med Oncol 29(4):2793–2799
Takimoto CH, Graham MA, Lockwood G, Ng CM, Goetz A, Greenslade D, Remick SC, Sharma S, Mani S, Ramanathan RK, Synold TW, Doroshow JH, Hamilton A, Mulkerin DL, Ivy P, Egorin MJ, Grem JL (2007) Oxaliplatin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in adult cancer patients with impaired renal function. Clin Cancer Res 13(16):4832–4839
Synold TW, Takimoto CH, Doroshow JH, Gandara D, Mani S, Remick SC, Mulkerin DL, Hamilton A, Sharma S, Ramanathan RK, Lenz HJ, Graham M, Longmate J, Kaufman BM, Ivy P (2007) Dose-escalating and pharmacologic study of oxaliplatin in adult cancer patients with impaired hepatic function: a National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group study. Clin Cancer Res 13(12):3660–3666
Nowak AK, Chow PK, Findlay M (2004) Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Eur J Cancer 40:1474–1484
Chou YY, Cheng AL, Hsu HC (1997) Expression of P-glycoprotein and p53 in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated by single agent chemotherapy: clinical correlation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:569–575
Ng IO, Liu CL, Fan ST, Ng M (2000) Expression of P-glycoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. A determinant of chemotherapy response. Am J Clin Pathol 113:355–363
Zhu AX, Blaszkowsky LS, Ryan DP, Clark JW, Muzikansky A, Horgan K, Sheehan S, Hale KE, Enzinger PC, Bhargava P, Stuart K (2006) Phase II study of gemcitabine and oxaliplatin in combination with bevacizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 24(12):1898–1903
Asnacios A, Fartoux L, Romano O, Tesmoingt C, Louafi SS, Mansoubakht T, Artru P, Poynard T, Rosmorduc O, Hebbar M, Taieb J (2008) Gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin (GEMOX) combined with cetuximab in patients with progressive advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a multicenter phase 2 study. Cancer 112(12):2733–2739
Assenat E, Boige V, Thézenas S, Pageaux GP, Peron JM, Becouarn Y, Dahan L, Merle P, Blanc JF, Bouche O, Ramdani M, Mazard T, Bleuse JP, Ychou M (2013). Sorafenib (S) alone versus S combined with gemcitabine and oxaliplatin (GEMOX) in first-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Final analysis of the randomized phase II GONEXT trial (UNICANCER/FFCD PRODIGE 10 trial). J Clin Oncol 31, 2013 (suppl; abstr 4028)
Goyal L, Muzumdar MD, Zhu AX (2013) Targetting the HGF/c-MET pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 19(9):2310–2318
Jia SW, Fu S, Wang F, Shao Q, Huang HB, Shao JY (2014) ALK gene copy number gain and its clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 20(1):183–192
Gianneli G, Mazzocca A, Fransvea E, Lahn M, Antonaci S (2011) Inhibiting TGF-β signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta 1815(2):214–223
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patrikidou, A., Sinapi, I., Regnault, H. et al. Gemcitabine and oxaliplatin chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after failure of anti-angiogenic therapies. Invest New Drugs 32, 1028–1035 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0100-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0100-y