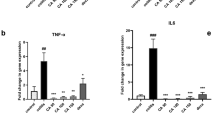
Abstract
Aim The aim of this investigation was to examine the effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on the development of colitis and antioxidant parameters in bilateral ovariectomized rats subjected to trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis. Materials and methods Twenty-one Wistar Albino ovariectomized female rats were divided into four subgroups (n = 5 or 6) (colitis control, vehicle control, CAPE 10 and 30 mg/kg, respectively). Colitis was induced using an enema of TNBS and ethanol, following which CAPE was administrated for 3 days to induce colitis and effect of CAPE was subsequently evaluated. Results Based on microscopic damage scores, there was no difference between rats of the TNBS-colitis and the vehicle-treated groups, whereas treatment with CAPE 10 and 30 mg/kg, respectively, caused a significant reduction in colon injury compared to that observed in rats of the TNBS-colitis and vehicle-treated groups. The histologies of both treatment groups were not significantly different. In terms of the biochemical analyses, myeloperoxidase levels in rats from the CAPE 10 and 30 mg/kg groups were significantly different from that of the colitis control rats; however, the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), catalase and reduced glutathione (GSH) were only significantly different from the levels found colitis control rats in rats administered 10 mg/kg. The levels of MDA, GSH and SOD in rats given CAPE were also significantly different from those of rats in the vehicle control group. These results were consistent with histological findings. Conclusion CAPE may have a positive effect on the inflammatory bowel disease treatment process and could, therefore, be used as an adjunct therapy in colitis. These effects of CAPE may occur through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grisham MB (1994) Oxidants and free radicals in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet 344:859–861
Keshavarzian A, Banan A, Farhadi A, Komanduri S, Mutlu E, Zhang Y, Fields JZ (2003) Increases in free radicals and cytoskeletal protein oxidation and nitration in the colon of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 52:720–728
Lih-Brody L, Powell SR, Collier KP, Reddy GM, Cerchia R, Kahn E, Weissman GS, Katz S, Floyd RA, McKinley MJ, Fisher SE, Mullin GE (1996) Increased oxidative stress and decreased antioxidant defenses in mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis Sci 41:2078–2086
Kruidenier L, Kuiper I, Van Duijn W, Mieremet-Ooms MA, van Hogezand RA, Lamers CB, Verspaget HW (2003) Imbalanced secondary mucosal antioxidant response in inflammatory bowel disease. J Pathol 201:17–27
Grisham MB, McCord JM (1986) Chemistry and cytotoxicity of reactive oxygen metabolites. In: Taylor AE, Matalon S, Ward PA (eds) Physiology of oxygen radicals. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 1–18
Weiss SJ (1986) Oxygen, ischemia and inflammation. Acta Physiol Scand 548:9–37
Williams JG, Hughes LE, Hallett MB (1990) Toxic oxygen metabolite production by circulating phagocytic cells in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 31:187–193
Grisham MB, Gaginella TS, von Ritter C, Tamai H, Be RM, Granger DN (1990) Effects of neutrophil-derived oxidants on intestinal permeability, electrolyte transport, and epithelial cell viability. Inflammation 14:531–542
Campbell-Thomson M, Lynch IJ, Bhardwaj B (2001) Expression of estrogen receptor (ER) subtypes and ER beta isoforms in colon cancer. Cancer Res 61:632–640
Konstantinopoulos PA, Kominea A, Vandoros G, Sykiotis GP, Andricopoulos P, Varakis I, Sotiropoulou-Bonikou G, Papavassiliou AG (2003) Oestrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) is abundantly expressed in normal colonic mucosa, but declines in colon adenocarcinoma paralleling the tumour’s dedifferentiation. Eur J Cancer 39:1251–1258
Wada-Hiraike O, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2006) New developments in oestrogen signalling in colonic epithelium. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1114–1116
Wada-Hiraike O, Imamov O, Hiraike H, Hultenby K, Schwend T, Omoto Y, Warner M, Gustafsson JA (2005) Role of estrogen receptor β in colonic epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2959–2964
Herrington DM, Klein KP (2001) Effects of SERMs on important indicators of cardiovascular health: lipoproteins, hemostatic factors, endothelial function. Womens Health Issues 11:95–102
Stevenson M, Lloyd Jones M, De Nigris E, Brewer N, Davis S, Oakley J (2005) A systematic review and economic evaluation of alendronate, etidronate, risedronate, raloxifene and teriparatide for the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Health Technol Assess 9:1–160
Bernardi F, Pluchino N, Stomati M, Pieri M, Genazzani AR (2003) CNS: sex steroids and SERMs. Ann NY Acad Sci 997:378–388
Kume-Kick J, Ferris DC, Russo-Menna I, Rice ME (1996) Enhanced oxidative stress in female rat brain after gonadectomy. Brain Res 738:8–14
Strehlow K, Rotter S, Wassman S, Adam O, Grohe C, Laufs K, Bohm M, Nickenig G (2003) Modulation of antioxidant enzyme expression and function by estrogen. Circ Res 93:170–177
Munoz-Castaneda JR, Muntane J, Herencia C, Munoz MC, Bujolance I, Montilla P, Tunez I (2006) Ovariectomy exacerbates oxidative stress and cardiopathyinduced by adriamycin. Gynecol Endocrinol 22:74–79
Russo A, Longo R, Vanella A (2002) Antioxidant activity of propolis: role of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and galangin. Fitoterapia 73[Suppl 1]:21–29
Sud’ina GF, Mirzoeva OK, Puskareva MA, Korshunova GA, Sumbatyan NV, Varfolomeev SD (1993) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester as a lipoxygenase inhibitor with antioxidant properties. FEBS Lett 329:21–24
Cicala C, Morello S, Iorio C, Capasso R, Borrelli F, Mascolo N (2003) Vascular effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on isolated rat thoracic aorta. Life Sci 73:73–80
Fitzpatrick LR, Wang J, Le T (2001) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB, attenuates bacterial peptidoglycan polysaccharide-induced colitis in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:915–920
Su ZZ, Grunberger D, Fisher PB (1991) Suppression of adenovirus type 5 EIA-mediated transformation and expression of the transformed phenotype by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE). Mol Carcinogen 4:231–242
Marquez N, Sancho R, Macho A, Calzado MA, Fiebich BL, Munoz E (2004) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits T-cell activation by targeting both nuclear factor of activated T-cells and NF-kappaB transcription factors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:993–1001
Ozer MK, Parlakpinar H, Acet A (2004) Reduction of ischemia-reperfusion induced myocardial infarct size in rats by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE). Clin Biochem 37:702–705
Ozguner F, Oktem F, Ayata A, Koyu A, Yilmaz HR (2005) A novel antioxidant agent caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevents long-term mobile phone exposure-induced renal impairment in rat. Mol Cell Biochem 277:73–80
Nemcsik J, Morschl E, Egresits J, Kordas K, Laszlo F, Laszlo AF, Pavo I (2004) Raloxifene lowers ischemia susceptibility by increasing nitric oxide generation in the heart of ovariectomized rats in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 495:179–184
Konyalioglu S, Durmaz G, Yalcin A (2007) The potential antioxidant effect of raloxifene treatment: a study on heart, liver and brain cortex of ovariectomized female rats. Cell Biochem Funct 25:259–266
González R, Rodríguez S, Romay C, Ancheta O, González A, Armesto J, Remirez D, Merino N (1999) Anti-inflammatory activity of phycocyanin extract in acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Pharmacol Res 39:55–59
Yavuz Y, Yuksel M, Yegen BC, Alican I (1999) The effect of antioxidant therapy on colonic inflammation in the rat. Res Exp Med (Berlin) 199:101–110
Ademoglu E, Erbil Y, Tam B, Barbaros U, Ilhan E, Olgac V, Mutlu-Turkoglu U (2004) Do vitamin E and selenium have beneficial effects on trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced experimental colitis. Dig Dis Sci 49:102–108
Gué M, Bonbonne C, Fioramonti J, Moré J, Del Rio-Lachèze C, Coméra C, Buéno L (1997) Stress-induced enhancement of colitis in rats: CRF and arginine vasopressin are not involved. Am J Physiol 272:84–91
Lowry OH, Risebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randal RJ (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–270
Suzuki K, Ota H, Sasagawa S, Sakatani T, Fujikura T (1983) Assay method for myeloperoxidase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Anal Biochem 132:345–352
Buege JA, Aust SD (1976) Lactoperroxidase catalysed lipid peroxidation of microsomal and artificial membranes. Biochem Biophys Acta 444:192–201
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Method Enzymol 105:121–126
Fairbanks VF, Klee GG (1999) Biochemical aspects of hematology. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER (eds) Tietz textbook of clinical chemistry. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1642–1710
Yi S, Oberley LW ,Ying L (1998) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34/3:497–500
Lutoslawska G, Tkaczyk J, Panczenko-Kresowska B, Hubner-Wozniaka E, Skierskab E, Gajewski AK (2003) Plasma TBARS, blood GSH concentrations, and erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in regularly menstruating women with ovulatory and anovulatory menstrual cycles. Clin Chim Acta 331:159–163
Chao T, Alten PV, Walter RJ (1994) Steroid sex hormones and macrophages function. Modulation of reactive oxygen intermediates and nitrite release. Am J Reprod Immunol 32:43–52
Babbs CF (1992) Oxygen radicals in ulcerative colitis. Free Radic Biol Med 13:169–181
Keshavarzian A, Sedghi S, Kanofsky J, List T, Robinson C, İbrahim C, Winship D (1992) Excessive production of reactive oxygen metabolites by inflamed colon: analysis by chemiluminescence probe. Gastroenterology 103:177–185
Nieto N, Torres MI, Fernandez MI, Giron MD, Rios A, Suarez MD, Gil A (2000) Experimental ulcerative colitis impairs antioxidant defense system in rat intestine. Dig Dis Sci 45:1820–1827
Grisham MB, Yamada T (1996) Neutrophils, nitrogen oxides, and inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest 98:136–141
McKenzie SJ, Baker MS, Buffington GD, Doe WF (1996) Evidence of oxidant-induced injury to epithelial cells during inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Invest 98:136–141
D’Odorico A, Bortolan S, Cardin R, D’Inca R, Martines D, Ferronato A, Sturniolo GC (2001) Reduced plasma antioxidant concentrations and increased oxidative DNA damage in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 36:1289–1294
Koch TR, Yuan LX, Stryker SJ, Ratliff P, Telforg GL, Opara EC (2000) Total antioxidant capacity of colon in patients with chronic ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 45:1814–1819
Southey A, Tanaka S, Murakami T, Miyoshi H, Ishizuka T, Sugiura M, Kawashima K, Sugita T (1997) Pathophysiological role of nitric oxide in rat experimental colitis. Int J Immunopharmacol 19:669–676
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS, Depew WT, Szewczuk MR, Wallace JL (1989) Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology 96:795–803
Grisham MB, Volkmer C, Tso P, Yamada T (1991) Metabolism of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid by the rat colon produces reactive oxygen species. Gastroenterology 101:540–547
Nosal’ova V, Cerna S, Bauer V (2000) Effect of N-acetylcysteine on colitis induced by acetic acid in rats. Gen Pharmacol 35:77–81
Pentney PT, Bubenik GA (1995) Melatonin reduces the severity of dextran-induced colitis in mice. J Pineal Res 19:31–39
Simmonds NJ, Millar AD, Blake DR, Rampton DS (1999) Antioxidant effects of aminosalicylates and potential new drugs for inflammatory bowel disease: assessment in cell-free systems and inflamed human colorectal biopsies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 13:363–372
Sud’ina GF; Mirzoeva OK, Puskareva MA Korshunova GA, Sumbatyan NV, Varfolomeev SD (1993) Caffeic acid phenehyl ester as a lipoxygenase inhibitor with antioxidant properties. FEBS Lett 329:21
Ozyurt H, Ozyurt B, Koca K, Ozgocmen S (2007) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) protects rat skeletal muscle against ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative stress. Vas Pharmacol 47:108–112
Akyol A, Ulusoy H, İmamoglu M, Cay A, Yulug E, Alver A, Erturk E, Kosucu M, Besir A, Akyol A, Ozen I (2006) Does propofol or caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevent lung injury after hindlimb ischemia-reperfusion in ventilated rats? Injury 37:380–387
Bobin-Dubigeon X, Collin N, Grimaud JM, Robert G, Le Baut L, Petit JY (2001) Effects of tumor necrosis factor-α synthesis inhibitors on rat trinitrobenzene sulphonic acid-induced chronic colitis. Eur J Pharmacol 42:103–110
Abreu MT (2002) The pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: translational implications for clinicians. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 4:481–489
Krıidenier L, Verspaget HW (2002) Oxidative stress as apathogenic factor in inflammatory bowel disease-radicals or ridiculous? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16:1997–2015
Girgin F, Karaoglu O, Erkus M Tuzun S, Ozutemiz O, Dincer C, Batur Y, Tanyalcın T (2000) Effects of trimetazidine on oxidant/antioxidant status in trinitrobezenesulfonic acid-induced chronic colitis. J Toxicol Environ Health A 59:641–652
Verspaget HW, Pena AS, Weterman IT, Lamers CBHW (1988) Diminished neutrophil function in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis identified by decreased oxidative metabolism and low superoxide dismutase content. Gut 29:223–228
Kuralay F, Yildiz C, Ozutemiz O. Islekel H, Caliskan S, Bingol B, Ozkal S (2003) Effects of trimetazidine on acetic acid-induced colitis in female swiss rats. J Toxicol Environ Health A 66:169–179
Zhou YH, Yu JP, Teng XJ, Ming M, Lv P, An P, Liu SQ, Yu HG (2006) Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on inflammatory mediators (SOD, MDA, TNF-α, NF-κBp65, IL–6) in TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Mediators Inflamm 5:1–9
Loeper J, Goy J, Rozensztajn L, Bedu O, Moisson P (1991) Lipid peroxidation and protective enzymes during myocardial infarction. Clin Chim Acta 196:119–125
Beno I, Staruchova M, Volkovova K, Mekinova D, Bobek P, Jurcovicova M (1994) Activity of the antioxidant system in patients with idiopathic proctocolitis and the effect of 5-aminosalicylic acid (Salofalk). Bratisl Lek Listy 95:99–102
Beno I, Staruchova M, Batovsky M, Volkovova K (1996) Adenomatous and inflammatory colorectal polyps: antioxidant enzyme activity in the colon. Cas Lek Cesk 135:208–210
Dong WG, Liu SP, Yu BP, Wu DF, Luo HS, Yu JP (2003) Ameliorative effects of sodium ferulate on experimental colitis and their mechanisms in rats. World J Gastroenterol 9:2533–2538
Liu SP, Dong WG, Wu DF, Luo HS, Yu JP (2003) Protective effect of angelica sinensis polysaccharide on experimental immunological colon injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol 9:2786–2790
Szabo S (1984) Role of sulfhydryls and early vascular lesions in gastric mucosal injury. Acta Physiol Hung 64:203–214
Buffington GD, Doe WF (1995) Depleted mucosal antioxidant defenses in inflammatory bowel disease. Free Radic Biol Med 19:911–918
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ek, R.O., Serter, M., Ergin, K. et al. The Effects of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE) on TNBS-induced Colitis in Ovariectomized Rats. Dig Dis Sci 53, 1609–1617 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0056-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0056-2