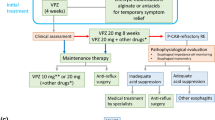
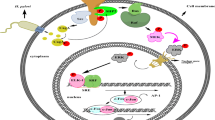
Abstract
The recognition of Helicobacter pylori infection as a cause of peptic ulcer disease, medical regimens to eradicate the organism, and the widespread use of proton pump inhibition to suppress gastric acid secretion have revolutionized the management of peptic ulcer disease. As a result, successful medical management of peptic ulcer disease has largely supplanted the need for gastric surgery by general surgeons. Surgery is reserved for complications of the disease, refractory disease, or rare causes of ulcer disease such as gastrinoma and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. In this report, we describe a case of intractable peptic ulcer disease that progressed to gastric outlet obstruction despite maximal medical therapy. We review the diagnostic studies utilized to evaluate the potential etiologies of peptic ulcer disease and the difficulty in diagnosing gastrinoma and Zollinger–Ellison in the setting of potent medical acid suppression therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soll AH: Medical treatment of peptic ulcer disease. JAMA 275:622, 1996
Walsh JH, Peterson WL: The treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in the management of peptic ulcer disease. N Engl J Med333:984, 1995
Hopkins RJ, Girardi LS, Turney EA: Relationship between H. pylori eradication and reduced duodenal and gastric ulcer recurrence: A review. Gastroenterology 110:1244, 1996
Verma S, Giaffer MH: Helicobacter pylori eradication ameliorates symptoms and improves quality of life in patients on long-term acid suppression. a large prospective study in primary care. Dig Dis Sci 47(7):1567–1574, 2002
Bardhan KD, Nayyar AK, Royston C: History in our lifetime: the changing nature of refractory duodenal ulcer in the era of histamine H2 receptor antagonists. Dig Liver Dis 35(8):529–536, 2003
Ford A, Delaney B, Forman D, Moayyedi P: Eradication therapy for peptic ulcer disease in Helicobacter pylori positive patients. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4):CD003840, 2004
Liu CC, Lee CL, Chan CC, Tu TC, Liao CC, Wu CH, Chen TK: Maintenance treatment is not necessary after Helicobacter pylori eradication and healing of bleeding peptic ulcer: a 5-year prospective, randomized, controlled study. Arch Intern Med 163(17):2020–2024, 2003
Bardhan KD, Williamson M, Royston C, Lyon C: Admission rates for peptic ulcer in the trent region, UK, 1972–2000. changing pattern, a changing disease? Dig Liver Dis 36(9):577–588, 2004
Miwa H, Sakaki N, Sugano K, Sekine H, Higuchi K, Uemura N, Kato M, Murakami K, Kato C, Shiotani A, Ohkusa T, Takagi A, Aoyama N, Haruma K, Okazaki K, Kusugami K, Suzuki M, Joh T, Azuma T, Yanaka A, Suzuki H, Hashimoto H, Kawai T, Sugiyama T: Recurrent peptic ulcers in patients following successful Helicobacter pylori eradication: a multicenter study of 4940 patients. Helicobacter 9(1):9–16, 2004
Lanas AI, Remacha B, Esteva F, et al.: Risk factors associated with refractory peptic ulcers. Gastroenterology 109:1124, 1995
Rosenstock S, Jorgensen T, Bonnevie O, Andersen L: Risk factors for peptic ulcer disease: a population based prospective cohort study comprising 2416 Danish adults. Gut 52(2):186–193, 2003
Anda RF, Williamson DF, Escobedo LG, Remington PL: Smoking and the risk of peptic ulcer disease among women in the United States. Arch Intern Med 150(7):1437–1441, 1990
Reynolds JC, Schoen RE, Maislin G, Zangari GG: Risk factors for delayed healing of duodenal ulcers treated with famotidine and ranitidine. Am J Gastroenterol 89(4):571–580, 1994
Laine L: Proton pump inhibitor co-therapy with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-nice or necessary? Rev Gastroenterol Disord 4 (Suppl 4):S33–S41, 2004
Goldstein JL: Challenges in managing NSAID-associated gastrointestinal tract injury. Digestion 69 (Suppl 1):25–33, 2004
Lai KC, Lam SK, Chu KM, Hui WM, Kwok KF, Wong BC, Hu HC, Wong WM, Chan OO, Chan CK: Lansoprazole reduces ulcer relapse after eradication of Helicobacter pylori in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug users—a randomized trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 18(8):829–836, 2003
Goddard AF, Logan RP: Diagnostic methods for Helicobacter pylori detection and eradication. Br J Clin Pharmacol 56(3):273–283, 2003
Howden CW, Hunt RH: Guidelines for the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Ad Hoc Committee on Practice Parameters of the American College of Gastroenterology. Am J Gastroenterol 93(12):2330–2338, 1998
Branca G, Spanu T, Cammarota G, Schito AM, Gasbarrini A, Gasbarrini GB, Fadda G: High levels of dual resistance to clarithromycin and metronidazole and in vitro activity of levofloxacin against Helicobacter pylori isolates from patients after failure of therapy. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24(5):433–438, 2004
Cammarota G, Martino A, Pirozzi G, Cianci R, Branca G, Nista EC, Cazzato A, Cannizzaro O, Miele L, Grieco A, Gasbarrini A, Gasbarrini G: High efficacy of 1-week doxycycline- and amoxicillin-based quadruple regimen in a culture-guided, third-line treatment approach for Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 19(7):789–795, 2004
Duck WM, Sobel J, Pruckler JM, Song Q, Swerdlow D, Friedman C, Sulka A, Swaminathan B, Taylor T, Hoekstra M, Griffin P, Smoot D, Peek R, Metz DC, Bloom PB, Goldschmidt S, Parsonnet J, Triadafilopoulos G, Perez-Perez GI, Vakil N, Ernst P, Czinn S, Dunne D, Gold BD: Antimicrobial resistance incidence and risk factors among Helicobacter pylori-infected persons, United States. Emerg Infect Dis 10(6):1088–1094, 2004
Fischbach LA, Zanten SV, Dickason J: Meta-analysis: the efficacy, adverse events, and adherence related to first-line anti-Helicobacter pylori quadruple therapies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20(10):1071–1082, 2004
Furuta T, Shirai N, Xiao F, Takashita M, Sugimoto M, Kajimura M, Ohashi K, Ishizaki T: High-dose rabeprazole/amoxicillin therapy as the second-line regimen after failure to eradicate H. pylori by triple therapy with the usual doses of a proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin and amoxicillin. Hepatogastroenterology 50(54):2274–2248, 2003
Ruggiero P, Peppoloni S, Rappuoli R, Del Giudice G: The quest for a vaccine against Helicobacter pylori: how to move from mouse to man? Microbes Infect 5(8):749–756, 2003
Freston JW: Helicobacter pylori-negative peptic ulcers: frequency and implications for management. J Gastroenterol 35 (Suppl 12):29–32, 2000
Freston JW: Review article: role of proton pump inhibitors in non-H. pylori-related ulcers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 15 (Suppl 2):2–5, 2001
Bonapace ES, Fisher RS, Parkman HP: Does fasting serum gastrin predict gastric acid suppression in patients on proton-pump inhibitors? Dig Dis Sci 45(1):34–39, 2000
Ellison EC, Sparks J: Zollinger-Ellison syndrome in the era of effective acid suppression: Are we unknowlingly growing tumors? Am J Surg 186(3):245–248, 2003
Kaneko E, Hoshihara Y, Sakaki N, Harasawa S, Ashida K, Asaka M, Asaki S, Nakamura T, Kobayashi K, Kajiyama G, Ogawa N, Yao T, Muto Y, Nakazawa S, Takemoto T: Peptic ulcer recurrence during maintenance therapy with H2-receptor antagonist following first-line therapy with proton pump inhibitor. J Gastroenterol 35(11):824–831, 2000
Corleto VD, Annibale B, Gibril F, Angeletti S, Serrano J, Venzon DJ, Delle Fave G, Jensen RT: Does the widespread use of proton pump inhibitors mask, complicate and/or delay the diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 15(10):1555–1561, 2001
Roy PK, Venzon DJ, Shojamanesh H, Abou-Saif A, Peghini P, Doppman JL, Gibril F, Jensen RT: Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Clinical presentation in 261 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 79(6):379–411, 2000
Nobels FR, Kwekkeboom DJ, Coopmans W, Schoenmakers CH, Lindemans J, De Herder WW, Krenning EP, Bouillon R, Lamberts SW: Chromogranin A as serum marker for neuroendocrine neoplasia: comparison with neuron-specific enolase and the alpha-subunit of glycoprotein hormones. J Clin Endocrinol and Metab 82(8):2622–2628, 1997
Panzuto F, Severi C, Cannizzaro R, Falconi M, Angeletti S, Pasquali A, Corleto VD, Annibale B, Buonadonna A, Pederzoli P, Delle Fave G: Utility of combined use of plasma levels of chromogranin A and pancreatic polypeptide in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal and pancreatic endocrine tumors. J Endocrinol Invest 27(1):6–11, 2004
Wada M, Komoto I, Doi R, Imamura M: Intravenous calcium injection test is a novel complementary procedure in differential diagnosis for gastrinoma. World J Surg 26(10):1291–1296, 2002 (epub 9/4/02)
Metz DC, Soffer E, Forsmark CE, Cryer B, Chey W, Bochenek W, Pisegna JR: Maintenance oral pantoprazole therapy is effective for patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and idiopathic hypersecretion. Am J Gastroenterol 98(2):301–307, 2003
Lew EA, Pisegna JR, Starr JA, Soffer EF, Forsmark C, Modlin IM, Walsh JH, Beg M, Bochenek W, Metz DC: Intravenous pantoprazole rapidly controls gastric acid hypersecretion in patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Gastroenterology 118(4):696–704, 2000
Gibril F, Reynolds JC, Doppman JL, Chen CC, Venzon DJ, Termanini B, Weber HC, Stewart CA, Jensen RT: Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy: its sensitivity compared with that of other imaging methods in detecting primary and metastatic gastrinomas. A prospective study. Ann Intern Med 125(1):26–34, 1996
Gibril F, Reynolds JC, Doppman JL, et al.: Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy: its sensitivity compared with that of other imaging methods in detecting primary and metastatic gastrinomas: a prospective study. Ann Intern Med 125:26–34, 1996
Kisker O, Bartsch D, Weinel RJ, Joseph K, Welcke UH, Zaraca F, Rothmund M: The value of somatostatin-receptor scintigraphy in newly diagnosed endocrine gastroenteropancreatic tumors. J Am Coll Surg 184(5):487–492, 1997
Norton JA, Jensen RT: Resolved and unresolved controversies in the surgical management of patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Ann Surg 240(5):757–773, 2004
Hung PD, Schubert ML, Mihas AA: Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.Curr Treat Opt Gastroenterol 6(2):163–170, 2003
Norton JA, Fraker DL, Alexander HR, Venzon DJ, Doppman JL, Serrano J, Goebel SU, Peghini PL, Roy PK, Gibril F, Jensen RT: Surgery to cure the Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. N Engl J Med 341(9):635–644, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guzzo, J.L., Duncan, M., Bass, B.L. et al. Severe and Refractory Peptic Ulcer Disease: The Diagnostic Dilemma. Dig Dis Sci 50, 1999–2008 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2999-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-2999-5