Abstract
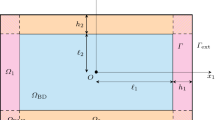
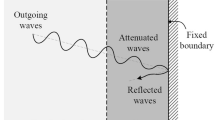
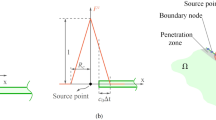
We discuss a new formulation for transient scalar wave simulations in heterogeneous semi-infinite domains. To deal with the semi-infinite extent of the physical domains, we introduce truncation boundaries and adopt perfectly matched layers (PMLs) as the boundary wave absorbers. Within this framework, we develop a new mixed displacement-stress (or stress memory) finite element formulation based on unsplit-field PMLs. We use, as typically done, complex-coordinate stretching transformations in the frequency domain, and recover the governing partial differential equations in the time-domain through the inverse Fourier transform. Upon spatial discretization, the resulting equations lead to a mixed semi-discrete form, where both displacements and stresses (or stress histories/memories) are treated as independent unknowns. We propose approximant pairs, which, numerically, are shown to be stable. The resulting mixed finite element scheme is relatively simple and straightforward to implement, when compared against split-field PML techniques. It also bypasses the need for complicated time integration schemes that arise when recent displacement-based formulations are used. We report numerical results for 1D and 2D scalar wave propagation in semi-infinite domains truncated by PMLs. We also conduct parametric studies and report on the effect the various PML parameter choices have on the simulation error.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mindlin, R.D., Bleich, H.H.: Response of an elastic cylindrical shell to a transverse, step shock wave. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 20, 189–195 (1953)
Schmidt, F.: A new approach to coupled interior-exterior Helmholtz-type problems: theory and applications. Habilitation Thesis, Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum Berlin, Fachbereich Mathematik und Informatik, FU Berlin (2001)
Schmidt, F., Hohage, T., Klose, R., Schadle, A., Zschiedrich, L.: Pole condition: a numerical method for Helmholtz-type scattering problem with inhomogeneous exterior domain. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 218, 61–69 (2008)
Zschiedrich, L., Klose, R., Schadle, A., Schmidt, F.: A new finite element realization of the perfectly matched layer method for Helmholtz scattering problems on polygonal domains in two dimensions. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 188, 12–32 (2006)
Givoli, D., Keller, J.B.: A finite element method for large domains. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 76, 41–66 (1989)
Givoli, D., Keller, J.B.: Non-reflecting boundary conditions for elastic waves. Wave Motion 12(3), 261–279 (1990)
Engquist, B., Majda, A.: Absorbing boundary conditions for the numerical simulation of waves. Math. Comput. 31(139), 629–651 (1977)
Bayliss, A., Turkel, E.: Radiation boundary conditions for wave-like equations. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 33, 707–725 (1980)
Higdon, R.L.: Absorbing boundary conditions for elastic waves. Geophysics 56(2), 231–241 (1991)
Givoli, D., Neta, B.: High-order non-reflecting boundary scheme for time-dependent waves. J. Comput. Phys. 186(1), 24–46 (2003)
Kallivokas, L.F., Lee, S.: Local absorbing boundaries of elliptical shape for scalar waves. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193, 4979–5015 (2004)
Bérenger, J.-P.: A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 114(2), 185–200 (1994)
Chew, W.C., Weedon, W.H.: A 3D perfectly matched medium from modified Maxwell’s equations with stretched coordinates. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 7(13), 599–604 (1994)
Hu, F.Q.: On absorbing boundary conditions for linearized Euler equations by a perfectly matched layer. J. Comput. Phys. 129, 201–219 (1996)
Hesthaven, J.S.: On the analysis and construction of perfectly matched layers for the linearized Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 142, 129–147 (1998)
Harari, I., Slavutin, M., Turkel, E.: Analytical and numerical studies of a finite element PML for the helmholtz equation. J. Comput. Acoust. 8(1), 121–137 (2000)
Harari, I., Albocher, U.: Studies of FE/PML for exterior problems of time-harmonic elastic waves. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195, 3854–3879 (2006)
Turkel, E., Yefet, A.: Absorbing PML boundary layers for wave-like equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 27, 533–557 (1998)
Israeli, M., Orszag, S.: Approximation of radiation boundary conditions. J. Comput. Phys. 41, 115–135 (1981)
Qi, Q., Geers, T.L.: Evaluation of the perfectly matched layer for computational acoustics. J. Comput. Phys. 139(1), 166–183 (1998)
Zeng, Y.Q., He, J.Q., Liu, Q.H.: The application of the perfectly matched layer in numerical modeling of wave propagation in poroelastic media. Geophysics 66(4), 1258–1266 (2001)
Chew, W.C., Liu, Q.H.: Perfectly matched layers for elastodynamics: a new absorbing boundary condition. J. Comput. Acoust. 4(4), 341–359 (1996)
Hastings, F.D., Schneider, J.B., Broschat, S.L.: Application of the perfectly matched layer (PML) absorbing boundary condition to elastic wave propagation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 100(5), 3061–3069 (1996)
Liu, Q.H.: Perfectly matched layers for elastic waves in cylindrical and spherical coordinates. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 105(4), 2075–2084 (1999)
Collino, F., Monk, P.: The perfectly matched layer in curvilinear coordinates. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19(6), 2061–2090 (1998)
Collino, F., Tsogka, C.: Application of the perfectly matched absorbing layer model to the linear elastodynamic problem in anisotropic heterogeneous media. Geophysics 66(1), 294–307 (2001)
Zheng, Y., Huang, X.: Anisotropic perfectly matched layers for elastic waves in cartesian and curvilinear coordinates. Earth Research Laboratory Report, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge (2002)
Abarbanel, S., Gottlieb, D.: A mathematical analysis of the PML method. J. Comput. Phys. 134, 357–363 (1997)
Becache, E., Fauqueux, S., Joly, P.: Stability of perfectly matched layers, group velocities and anisotropic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 188, 399–433 (2003)
Becache, E., Petropoulos, P.G., Gedney, S.D.: On the long-time behavior of unsplit perfectly matched layers. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 52(5), 1335–1342 (2004)
Komatitsch, D., Tromp, J.: A perfectly matched layer absorbing boundary condition for the second-order seismic wave equation. Geophys. J. Int. 154, 146–153 (2003)
Basu, U., Chopra, A.K.: Perfectly matched layers for transient elastodynamics of unbounded domains. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 59, 1039–1074 (2004)
Basu, U., Chopra, A.K.: Perfectly matched layers for time-harmonic elastodynamics of unbounded domains: theory and finite-element implementation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 192, 1337–1375 (2003)
Oden, J.T., Reddy, J.N.: On mixed finite element approximations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 13(3), 393–404 (1976)
Sheu, M.-G.: On theories and applications of mixed finite element methods for linear boundary-value problems. Comput. Math. Appl. 4(4), 333–347 (1978)
Brezzi, F., Bathe, K.J.: A discourse on the stability conditions for mixed finite element formulations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 82, 27–57 (1990)
Carey, G.F., Oden, J.T.: Finite Elements—A Second Course, vol. II. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1983)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed And Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (1991)
Arnold, D. N.: Mixed finite element methods for elliptic problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 82, 281–300 (1990)
Brezzi, F.: A survey of mixed finite element method. In: Dwoyer, D., Hussaini, M., Voigt, R. (eds.) Finite Elements Theory and Application, pp. 34–49. Springer, New York (1988)
Raviart, P.A., Thomas, J.M.: A mixed finite element method for second order elliptic problems. In: Galligani, I., Magenes, E. (eds.) Mathematical Aspects of the Finite Element Method. Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 606, pp. 292–315. Springer, New York (1977)
Johnson, C., Mercier, B.: Some equilibrium finite element methods for two-dimensional elasticity problems. Numer. Math. 30, 103–116 (1978)
Brezzi, F., Douglas, J., Marini, L.D.: Two families of mixed finite element methods for second order elliptic problems. Numer. Math. 47, 217–235 (1985)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: A stable finite element for the Stokes equations. Calcolo 21, 337–344 (1984)
Arnold, D.N., Brezzi, F., Douglas, J.: PEERS: a new mixed finite element for plane elasticity. Jpn. J. Appl. Math. 1, 347–367 (1984)
Nédélec, J.C.: Mixed finite elements in R 3. Numer. Math. 35, 315–341 (1980)
Arnold, D.N., Douglas, J., Gupta, C.P.: A family of higher order mixed finite element methods for plane elasticity. Numer. Math. 45, 1–22 (1984)
Marini, L.D.: An inexpensive method for the evaluation of the solution of the lowest order raviart-thomas mixed method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 22(3), 493–496 (1985)
Nédélec, J.C.: A new family of mixed finite elements in R 3. Numer. Math. 50, 57–81 (1986)
Arnold, D.N., Falk, R.S.: A new mixed formulation for elasticity. Numer. Math. 53, 13–30 (1988)
Stenberg, R.: A family of mixed finite elements for the elasticity problem. Numer. Math. 53, 513–538 (1988)
Frasca, L.P., Hughes, T.J.R., Loula, A.F.D., Miranda, I.: A new family of stable elements for nearly incompressible elasticity based on a mixed Petrov-Galerkin finite element formulation. Numer. Math. 53, 123–141 (1988)
Morley, M.E.: A family of mixed finite elements for linear elasticity. Numer. Math. 55, 633–666 (1989)
Brezzi, F., Marini, D.: A survey on mixed finite element approximations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 30(5), 3547–3551 (1994)
Bécache, E., Joly, P., Tsogka, C.: An analysis of new mixed finite elements for the approximation of wave propagation problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 37(4), 1053–1084 (2000)
Arnold, D.N., Winther, R.: Mixed finite elements for elasticity. Numer. Math. 92, 401–419 (2002)
Bécache, E., Joly, P., Tsogka, C.: A new family of mixed finite elements for the linear elastodynamic problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 39(6), 2109–2132 (2002)
Arnold, D.N., Winther, R.: Mixed finite elements for elasticity in the stress-displacement formulation. In: Chen, Z., Glowinski, R., Li, K. (eds.) Current Trends in Scientific Computing, Contemporary Mathematics, vol. 329, pp. 33–42 (2003)
Arnold, D.N., Awanou, G.: Rectangular mixed finite elements for elasticity. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 15(9), 1417–1429 (2005)
Chen, Z.: Finite Element Methods and Their Applications, 1st edn. Springer, New York (2005)
Arnold, D.N., Falk, R.S., Winther, R.: Mixed finite element methods for linear elasticity with weakly imposed symmetry. Math. Comput. 76(260), 1699–1723 (2005)
Festa, G., Vilotte, J.-P.: The Newmark scheme as velocity-stress time-staggering: an efficient PML implementation for spectral element simulations of elastodynamics. Geophys. J. Int. 161, 789–812 (2005)
Cohen, G., Fauqueux, S.: Mixed spectral finite elements for the linear elasticity system in unbounded domains. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 26(3), 864–884 (2005)
Chen, J., Chen, Z.: An adaptive perfectly matched layer technique for 3-D time-harmonic electromagnetic scattering problems. Math. Comput. 77(262), 673–698 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, J.W., Kallivokas, L.F. Mixed unsplit-field perfectly matched layers for transient simulations of scalar waves in heterogeneous domains. Comput Geosci 14, 623–648 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-009-9176-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-009-9176-4