Abstract
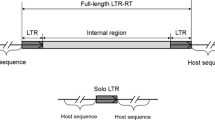
Birds have relatively few repetitive sequences compared to other groups of vertebrates; however, the members of order Piciformes (woodpeckers) have more of these sequences, composed mainly of transposable elements (TE). The TE most often found in birds is a retrotransposon chicken repeat 1 (CR1). Piciformes lineages were subjected to an expansion of the CR1 elements, carrying a larger fraction of transposable elements. This study compared patterns of chromosome distribution among five bird species, through chromosome mapping of the CR1 sequence and reconstructed their phylogenetic tree. We analyzed several members of Piciformes (Colaptes campestris, Colaptes melanochloros, Melanerpes candidus, and Veniliornis spilogaster), as well as Galliformes (Gallus gallus). Gallus gallus is the species with which most genomic and hence cytogenetic studies have been performed. The results showed that CR1 sequences are a monophyletic group and do not depend on their hosts. All species analyzed showed a hybridization signal by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). In all species, the chromosomal distribution of CR1 was not restricted to heterochromatin regions in the macrochromosomes, principally pair 1 and the Z sex chromosome. Accumulation in the Z sex chromosomes can serve as a refuge for transposable elements. These results highlight the importance of transposable elements in host genomes and karyotype evolution.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCA:
-
Colaptes campestris
- CME:
-
Colaptes melanochloros
- CR1:
-
Chicken repeat 1
- FISH:
-
Fluorescent in situ hybridization
- GGA:
-
Gallus gallus
- LINE:
-
Long interspersed nucleotide elements
- MCA:
-
Melanerpes candidus
- ORF:
-
Open reading frames
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PPU:
-
Picoides pubescens
- RT:
-
Reverse transcriptase
- TEs:
-
Transposable elements
- VSP:
-
Veniliornis spilogaster
References
Bachtrog D (2005) Sex chromosome evolution : molecular aspects of Y-chromosome degeneration in Drosophila. Genome Res 15:1393–1401. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.3543605
Bailly-Bechet M, Haudry A, Lerat E (2014) “One code to find them all”: a perl tool to conveniently parse RepeatMasker output files. Mob DNA 5:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1759-8753-5-13
Burch JB, Davis DL, Haas NB (1993) Chicken repeat 1 elements contain a pol-like open reading frame and belong to the non-long terminal repeat class of retrotransposons. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90(17):8199–8203
Charlesworth B, Sniegowski P, Stephan W (1994) The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 371:215–220
Charlesworth D, Charlesworth B, Marais G (2005) Steps in the evolution of heteromorphic sex chromosomes. Heredity (Edinb) 95:118–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6800697
Coullin P, Bed’Hom B, Candelier JJ, Vettese D, Maucolin S, Moulin S, Galkina SA, Bernheim A, Volobouev V (2005) Cytogenetic repartition of chicken CR1 sequences evidenced by PRINS in Galliformes and some other birds. Chromosom Res 13(7):665–673
de Oliveira TD, Kretschmer R, Bertocchi NA, Degrandi TM, de Oliveira EHC, Cioffi MB, Garnero AV, Gunski RJ (2017) Genomic organization of repetitive DNA in woodpeckers (Aves, Piciformes): implications for karyotype and ZW sex chromosome differentiation. PLoS One 12:e0169987. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169987
Garnero ADV, Gunski RJ (2000) Comparative analysis of the karyotypes of Nothura maculosa and Rynchotus rufescens (Aves, Tinamidae). A case of chromosomal polymorphism. Nucl 43:64–70
Gibbs RA, Weinstock GM, Metzker ML et al (2004) Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature 428:493–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02426
Green RE, Braun EL, Armstrong J, Earl D, Nguyen N, Hickey G, Vandewege MW, St. John JA, Capella-Gutierrez S, Castoe TA, Kern C, Fujita MK, Opazo JC, Jurka J, Kojima KK, Caballero J, Hubley RM, Smit AF, Platt RN, Lavoie CA, Ramakodi MP, Finger JW, Suh A, Isberg SR, Miles L, Chong AY, Jaratlerdsiri W, Gongora J, Moran C, Iriarte A, McCormack J, Burgess SC, Edwards SV, Lyons E, Williams C, Breen M, Howard JT, Gresham CR, Peterson DG, Schmitz J, Pollock DD, Haussler D, Triplett EW, Zhang G, Irie N, Jarvis ED, Brochu CA, Schmidt CJ, McCarthy FM, Faircloth BC, Hoffmann FG, Glenn TC, Gabaldon T, Paten B, Ray DA (2014) Three crocodilian genomes reveal ancestral patterns of evolution among archosaurs. Science 346(80):1254449. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254449
Haas NB, Grabowski JM, Sivitz AB, Burch JBE (1997) Chicken repeat 1 (CR1) elements, which define an ancient family of vertebrate non-LTR retrotransposons, contain two closely spaced open reading frames. Gene 197(1-2):305–309
Haas NB, Grabowski JM, North J, Moran JV, Kazazian H, Burch JBE (2001) Subfamilies of CR1 non-LTR retrotransposons have different 5′UTR sequences but are otherwise conserved. Gene 265(1-2):175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00344-4
Hughes AL, Hughes MK (1995) Small genomes for better flyers. Nature 377:391
Jarvis ED, Mirarab S, Aberer AJ et al (2014) Whole-genome analyses resolve early branches in the tree of life of modern birds. Science 346(80):1126–1138. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251385
Jurka J, Kapitonov VV, Pavlicek A, Klonowski P, Kohany O, Walichiewicz J (2005) Repbase update, a database of eukaryotic repetitive elements. Cytogenet Genome Res 110:462–467. https://doi.org/10.1159/000084979
Kajikawa M, Ohshima K, Okada N (1997) Determination of the entire sequence of turtle CR1: the first open reading frame of the turtle CR1 element encodes a protein with a novel zinc finger motif. Mol Biol Evol 14(12):1206–1217
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2003) The esterase and PHD domains in CR1-like non-LTR retrotransposons. Mol Biol Evol 20(1):38–46
Kapusta A, Suh A (2017) Evolution of bird genomes-a transposon’s-eye view. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1389:164–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13295
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol 30:772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
Klein SJ, O’Neill RJ (2018) Transposable elements: genome innovation, chromosome diversity, and centromere conflict. Chromosom Res 26:5–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-017-9569-5
Kordiš D, Lovšin N, Gubenšek F, Shedlock A (2006) Phylogenomic analysis of the L1 retrotransposons in deuterostomia. Syst Biol 55(6):886–901
Kretschmer R, Ferguson-Smith M, de Oliveira E (2018) Karyotype evolution in birds: from conventional staining to chromosome painting. Genes (Basel) 9:181. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9040181
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Manthey JD, Moyle RG, Boissinot S (2018) Multiple and independent phases of transposable element amplification in the genomes of Piciformes (woodpeckers and allies). Genome Biol Evol 10:1445–1456. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evy105
Matsubara K, Meally DO, Azad B, et al (2016) Amplification of microsatellite repeat motifs is associated with the evolutionary differentiation and heterochromatinization of sex chromosomes in Sauropsida. 111–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-015-0531-z
Okonechnikov K, Golosova O, Fursov M et al (2012) Unipro UGENE: a unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 28:1166–1167. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts091
Sasaki M, Ikeuchi T, Makino S (1968) A feather pulp culture technique for avian chromosomes, with notes on the chromosomes of the peafowl and the ostrich. Experientia 24:1292–1293. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02146680
Shibusawa M, Nishibori M, Nishida-Umehara C, Tsudzuki M, Masabanda J, Griffin DK, Matsuda Y (2004) Karyotypic evolution in the Galliformes: an examination of the process of karyotypic evolution by comparison of the molecular cytogenetic findings with the molecular phylogeny. Cytogenet Genome Res 106:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1159/000078570
Steinemann M, Steinemann S (1992) Degenerating Y chromosome of Drosophila miranda: a trap for retrotransposons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:7591–7595
Stock AD, Arrighi FE, Stefos K (1974) Chromosome homology in birds: banding patterns of the chromosomes of the domestic chicken. Ring-necked dove, and domestic pigeon. Cytogenet Cell Genet 13:410–418
Stumph WE, Kristo P, Tsai M-J, O’Malley BW (1981) A chicken middle-repetitive DNA sequence which shares homology with mammalian ubiquitous repeats. Nucleic Acids Res 9(20):5383–5398
Suh A (2015) The specific requirements for CR1 retrotransposition explain the scarcity of retrogenes in birds. J Mol Evol 81(1-2):18–20
Suh A, Paus M, Kiefmann M, Churakov G, Franke FA, Brosius J, Kriegs JO, Schmitz J (2011) Mesozoic retroposons reveal parrots as the closest living relatives of passerine birds. Nat Commun 2:443. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1448
Suh A, Churakov G, Ramakodi MP, Platt RN II, Jurka J, Kojima KK, Caballero J, Smit AF, Vliet KA, Hoffmann FG, Brosius J, Green RE, Braun EL, Ray DA, Schmitz J (2014) Multiple lineages of ancient CR1 retroposons shaped the early genome evolution of amniotes. Genome Biol Evol 7:205–217. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evu256
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(72)90558-7
Supiwong W, Liehr T, Cioffi MB, Chaveerach A, Kosyakova N, Pinthong K, Tanee T, Tanomtong A (2013) Karyotype and cytogenetic mapping of 9 classes of repetitive DNAs in the genome of the naked catfish Mystus bocourti (Siluriformes, Bagridae). Mol Cytogenet 6:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8166-6-51
Wicker T, Robertson JS, Schulze SR, et al (2005) The repetitive landscape of the chicken genome. 126–136. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.2438005
Wong LH, Choo KHA (2004) Evolutionary dynamics of transposable elements at the centromere. Trends Genet 20:611–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2004.09.011
Zhang G, Li C, Li Q, Li B, Larkin DM, Lee C, Storz JF, Antunes A, Greenwold MJ, Meredith RW, Odeen A, Cui J, Zhou Q, Xu L, Pan H, Wang Z, Jin L, Zhang P, Hu H, Yang W, Hu J, Xiao J, Yang Z, Liu Y, Xie Q, Yu H, Lian J, Wen P, Zhang F, Li H, Zeng Y, Xiong Z, Liu S, Zhou L, Huang Z, An N, Wang J, Zheng Q, Xiong Y, Wang G, Wang B, Wang J, Fan Y, da Fonseca RR, Alfaro-Nunez A, Schubert M, Orlando L, Mourier T, Howard JT, Ganapathy G, Pfenning A, Whitney O, Rivas MV, Hara E, Smith J, Farre M, Narayan J, Slavov G, Romanov MN, Borges R, Machado JP, Khan I, Springer MS, Gatesy J, Hoffmann FG, Opazo JC, Hastad O, Sawyer RH, Kim H, Kim KW, Kim HJ, Cho S, Li N, Huang Y, Bruford MW, Zhan X, Dixon A, Bertelsen MF, Derryberry E, Warren W, Wilson RK, Li S, Ray DA, Green RE, O'Brien SJ, Griffin D, Johnson WE, Haussler D, Ryder OA, Willerslev E, Graves GR, Alstrom P, Fjeldsa J, Mindell DP, Edwards SV, Braun EL, Rahbek C, Burt DW, Houde P, Zhang Y, Yang H, Wang J, Avian Genome Consortium, Jarvis ED, Gilbert MTP, Wang J, Ye C, Liang S, Yan Z, Zepeda ML, Campos PF, Velazquez AMV, Samaniego JA, Avila-Arcos M, Martin MD, Barnett R, Ribeiro AM, Mello CV, Lovell PV, Almeida D, Maldonado E, Pereira J, Sunagar K, Philip S, Dominguez-Bello MG, Bunce M, Lambert D, Brumfield RT, Sheldon FH, Holmes EC, Gardner PP, Steeves TE, Stadler PF, Burge SW, Lyons E, Smith J, McCarthy F, Pitel F, Rhoads D, Froman DP (2014) Comparative genomics reveals insights into avian genome evolution and adaptation. Science 346(80):1311–1320. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251385
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Rafael Kretschmer for his inspiring comments on the manuscript and to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments to improve the manuscript.
Funding
CAPES (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior), and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) provided financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NAB and TDO conceived, designed research most of the experiments and contributed to the interpretation of results. NAB and TDO wrote the manuscript. NAB and RLBC did the in silico experiments. AVG and FPT supervised the project. NAB, TDO, RJG, AVG, CM and FPT performed research. NAB and TDO contributed equal. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experiments followed protocols approved by the Ethics Committee on the Use of Animals (CEUA – Universidade Federal do Pampa, 026/2012).
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Rachel O’Neill
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(XLS 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertocchi, N.A., de Oliveira, T.D., del Valle Garnero, A. et al. Distribution of CR1-like transposable element in woodpeckers (Aves Piciformes): Z sex chromosomes can act as a refuge for transposable elements. Chromosome Res 26, 333–343 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-018-9592-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-018-9592-1